Cohort analysis helps marketers track customer behavior by grouping users with shared characteristics. This blog highlights its benefits, offers a straightforward guide to get started, and shares relatable examples to enhance retention and drive growth.
What is Cohort Analysis?
Cohort analysis is the process of analyzing user behavior by grouping individuals into related groups called cohorts, each made up of users who share a common characteristic or starting point, such as signing up on the same day or completing a specific action. Marketers track how these cohorts behave over time to uncover patterns in engagement, identify drop-off points, and make targeted improvements to increase retention and growth.
Monitoring these cohorts helps businesses pinpoint behavioral trends, assess the effectiveness of campaigns or onboarding flows, and optimize both marketing and product strategies. This makes cohort analysis especially useful for identifying what is working, what needs improvement, and when users tend to disengage.
For instance, an e-commerce platform might compare the purchasing behaviors of users acquired through different marketing channels, while a subscription service might identify time periods or actions that correlate with increased churn. However, for insights to be meaningful, cohorts must be clearly defined. If cohorts are too broad, too small, or based on non-representative user actions, the resulting analysis may be misleading or inconclusive.
Cohort analysis differs from RFM analysis (Recency, Frequency, Monetary value), which categorizes users by purchase behavior and customer value. While RFM is useful for segmentation based on transactional patterns, cohort analysis focuses on time-based behavioral changes. It is especially powerful when combined with behavioral segmentation or psychographic segmentation to gain a deeper understanding of user engagement.
A practical example would be sending an email campaign to 1,000 users and measuring how many of them make a purchase on Day 1, Day 2, Day 3, and so on. If a new cohort receives a similar campaign a few weeks later, comparing the two sets of results can reveal whether the timing, message, or context made a difference. Another example could involve an app tracking the percentage of new users who return each day for the first 10 days after installation, helping teams assess early retention trends.
To illustrate the concept, here’s an example of cohort analysis. With this cohort chart, let’s track a daily cohort of users who launched an app for the first time and revisited it over the next 10 days.
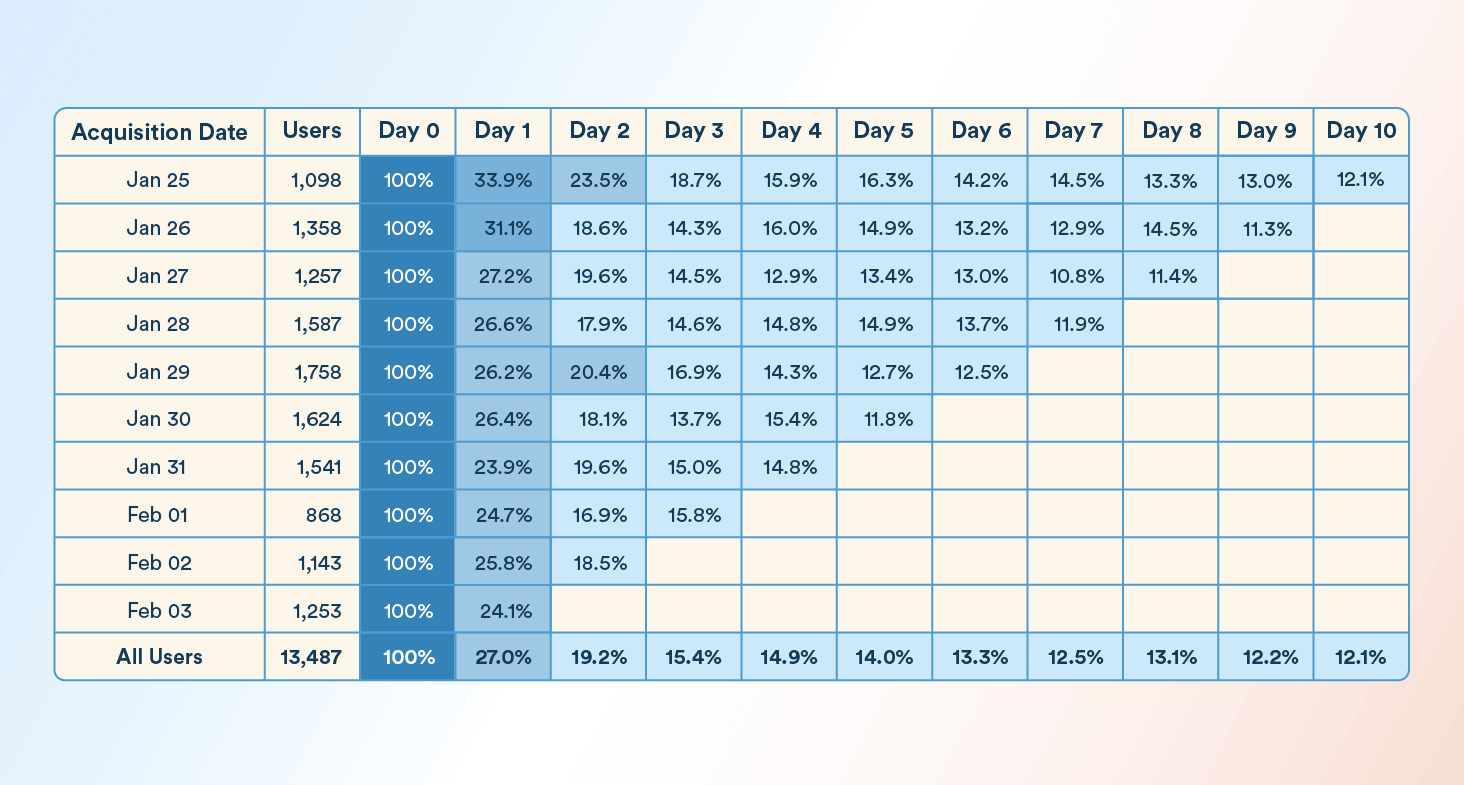
Focusing on the January 26 cohort as an example:
- Initial Launch: 1,358 users launched the app
- Day 1 Retention: 31.1 percent
- Day 4 Retention: 16.0 percent
- Day 7 Retention: 12.9 percent
- Day 10 Retention: 12.1 percent
From this data, we can see that by Day 7, only around one in eight users who launched the app on January 26 were still active. When looking at the broader “All Users” row, which represents a total of 13,487 users across all cohorts, Day 1 retention stands at 27.0 percent and gradually drops to 12.1 percent by Day 10.
This pattern highlights the importance of early user experience, as most users tend to disengage within the first few days unless they find immediate value in the product.
Key Concepts in Cohort Analysis
These core terms help you understand and apply cohort analysis more effectively:
- Cohorts: Groups of users who share a common trait or starting point, such as sign-up date or first transaction. Used to analyze how similar users behave over time.
Example: Track weekly acquisition cohorts to compare retention performance by marketing channel. - Retention Rate: Measures the percentage of users in a cohort who continue engaging with your app or product after a set period (e.g., Day 1, Day 7). Retention rate a key metric for evaluating user stickiness.
Example: Use Day 1 and Day 7 retention rates to assess how well your onboarding drives repeat engagement. - Churn Rate: The percentage of users who drop off or stop engaging over time. Churn rate helps identify friction points in the user journey.
Example: A retention drop after Day 3 may point to a poor post-onboarding experience. - Activation Rate: Tracks the percentage of users who reach a key milestone that signals value realization, like completing onboarding or making their first purchase.
Example: Boosting activation within the first two sessions can significantly improve long-term retention.
Key Metrics Derived from Cohort Analysis:
- Product Lifetime Metrics: These metrics compare all cohorts on the same day after acquisition (e.g., Day 1 across multiple cohorts). In a cohort table, this corresponds to analyzing values vertically down a single column. Product lifetime metrics reveal how well your onboarding, activation, or early product experiences perform at specific time milestones across different user groups.
- User Lifetime Metrics: These track how a specific cohort performs over time, from Day 1 to Day 7, for example. In a cohort table, this is analyzed horizontally across a single row. User lifetime metrics help you understand long-term engagement, how value builds over time, and how well a specific group retains compared to others.
- Conversion Rate by Cohort: Shows how different cohorts progress toward key goals like purchases, upgrades, or feature adoption. Conversion rate is useful for measuring campaign or product experiment effectiveness.
- Drop-Off Detection: Reveals when and where users disengage, helping teams improve lifecycle flows, reduce friction, or time nudges more effectively.
- LTV by Cohort: Tracks customer lifetime value across cohorts to reveal which acquisition sources or behaviors lead to higher-value users, aiding in budget allocation and pricing optimization.
You might like to read: 14 customer retention metrics & KPIs to measure retention (with formulas)
Types of Cohorts
Cohort analysis becomes far more powerful when you segment users based on how they enter or interact with your product. The right cohort structure allows you to pinpoint not just when churn or engagement shifts happen, but also why. Here are the key types of cohorts to consider:
Acquisition Cohorts: Identifying Key Drop-Off Points
Acquisition cohorts group users based on when they first entered your product or app, typically by day, week, or month of acquisition. These cohorts help track how retention and engagement evolve from the moment users first arrive, making them essential for identifying early churn and assessing onboarding effectiveness.
Acquisition cohorts track users from their first interaction, such as sign-up date or first app launch, and reveal how retention changes over time. They help pinpoint when customer engagement starts to decline, especially during the critical early stages.
To visualize how retention changes across acquisition cohorts, here’s a sample cohort chart showing 7-day retention by install date from Day 0 to Day 10:
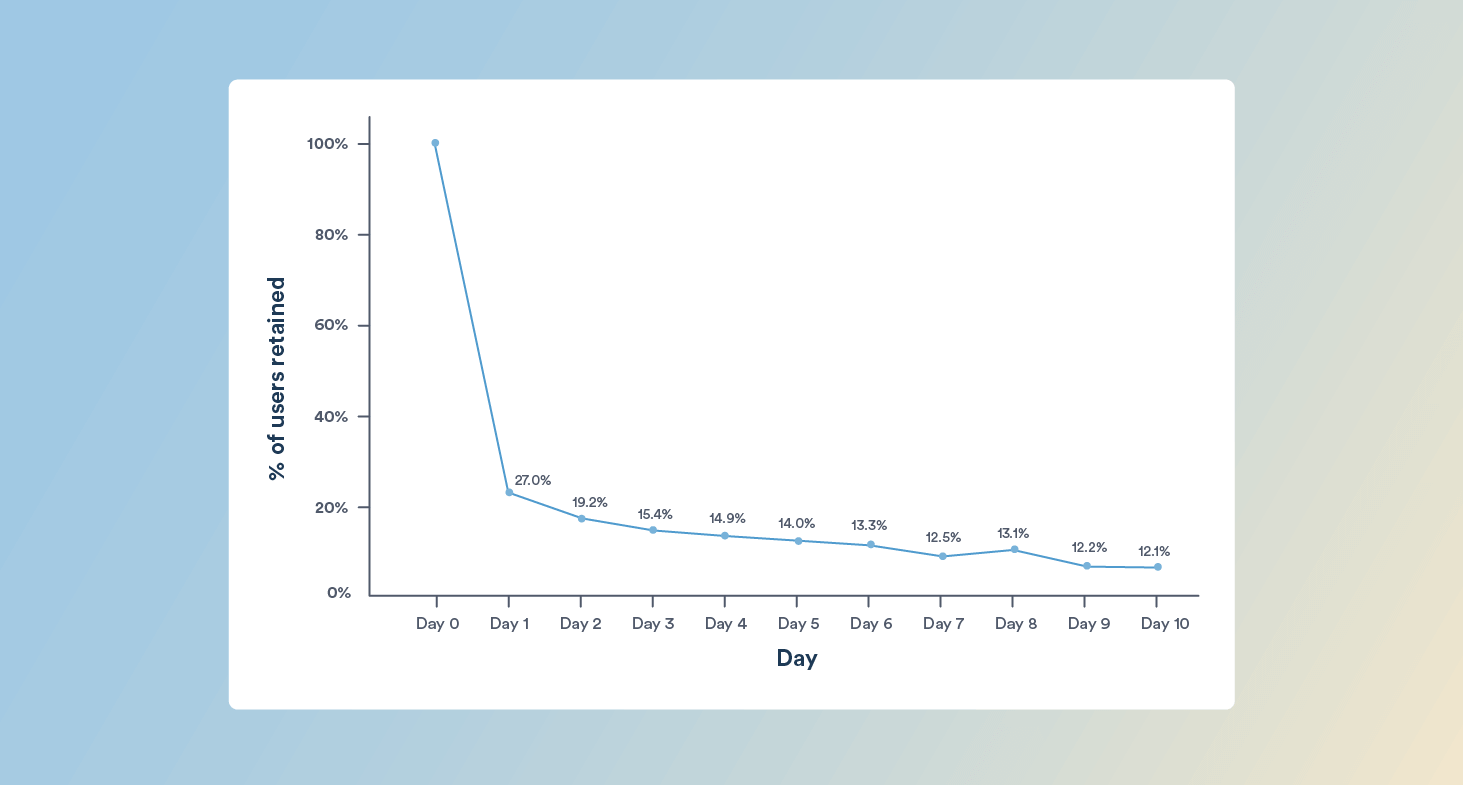
The graph shows a sharp drop-off after Day 0, with retention falling from 100 percent to 27 percent on Day 1. This means nearly three out of four users do not return after their first session. Retention continues to decline steadily over the next several days, landing at 12.1 percent by Day 10.
This pattern suggests that most users are not reaching the app’s core value within the first few interactions. For marketers and product teams, this insight is critical. To improve early retention, focus on strengthening your Day 0 and Day 1 experience. This may include streamlining onboarding, guiding users toward key actions, or delivering immediate value through personalization or contextual nudges.
Insight: Acquisition cohort analysis helps you pinpoint the earliest signs of churn. If most users drop off on Day 1, your onboarding or value communication may be falling short. Focus your optimizations on Day 0 and Day 1 to prevent churn before it begins.
Acquisition cohort analysis is ideal for identifying when churn occurs, but to understand why users drop off, you’ll need to explore behavioral cohorts.
Behavioral Cohorts: Understanding Why Users Leave
Behavioral cohorts group users based on the actions they take, or don’t take, within a specific time window. These cohorts allow you to identify how specific behaviors impact long-term engagement, making them powerful for uncovering what drives retention, monetization, or churn.
Behavioral cohorts are formed by grouping users based on specific in-app actions within a defined time period, such as making a transaction, launching the app, or abandoning a cart. These cohorts help uncover which behaviors drive long-term engagement and which ones signal early churn risk.
Let’s examine two real behavioral cohorts based on the charts below.
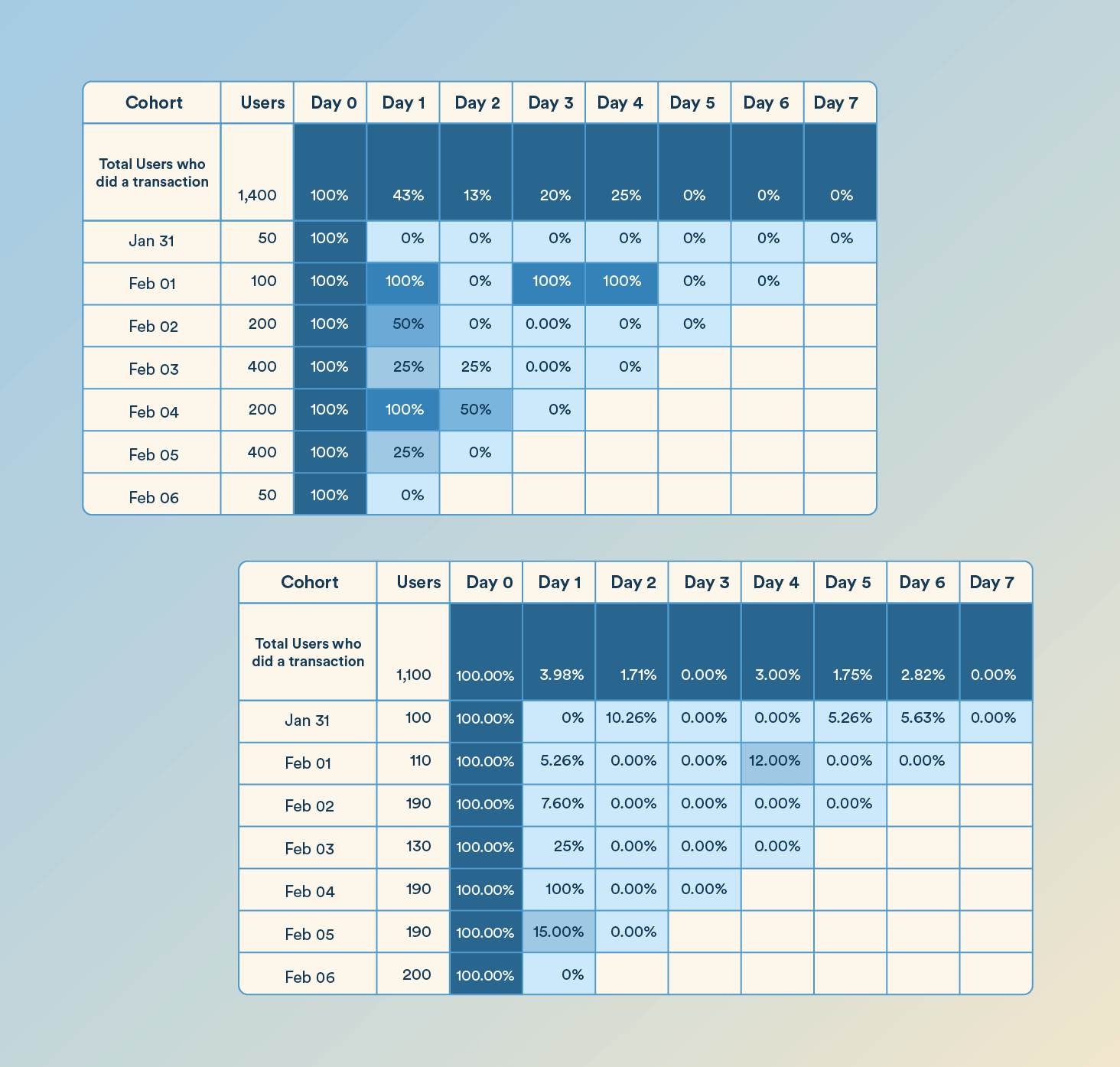
Users Who Completed a Transaction
In the first cohort, we’re tracking 1,400 users who completed a transaction. Day 1 retention stands at 43 percent, which is relatively high. This then drops to 13 percent by Day 2.
Interestingly, there’s a retention spike on Day 3 and Day 4—climbing to 20 percent and 25 percent, respectively. This pattern may indicate that well-timed re-engagement, such as a campaign notification, successfully brought users back. The spike on Day 4, in particular, points to an opportunity for follow-up strategies like personalized product recommendations, loyalty nudges, or limited-time offers to maintain momentum.
Insight: Users who transact early may not become instantly loyal. To maintain momentum, follow up within 3–4 days with relevant value or personalized content.
Users Who Abandoned a Cart
Now compare this with a behavioral cohort of 1,100 users who abandoned a cart. Retention drops sharply: only 3.98 percent re-engage on Day 1, and just 1.71 percent on Day 2. Engagement remains extremely low throughout the week, with Day 7 retention at zero percent.
This steep drop-off suggests that cart abandoners lose intent quickly and rarely return without proactive intervention. These users require immediate and targeted re-engagement, ideally within 24 to 48 hours, using strategies like urgency-based push notifications, time-limited discounts, or social proof reminders.
Insight: Cart abandoners represent lost intent that fades fast. Timely retargeting within the first 48 hours is critical to bring them back.
By comparing these behavioral cohorts, you can identify critical engagement windows and customize campaigns accordingly. Users who complete transactions may need nudges to return and buy again, while cart abandoners require fast, high-impact interventions to recover lost revenue.
Tip: Pair behavioral cohort analysis with campaign triggers. Use automated journeys to activate specific flows based on the user’s last meaningful action.
Time-Based Cohorts: Measuring the Impact of Timing and Context
Time-based cohorts group users by when they performed a specific action or were active during a particular period, such as a marketing campaign, holiday season, or product update window. These cohorts help you analyze how external context or timing affects user behavior.
These cohorts are especially useful when you’re trying to evaluate the influence of time-sensitive factors, such as a festive sale, seasonal content, or pricing changes, on user retention or engagement.
For example, a retail app might compare user retention across cohorts active during Black Friday, New Year’s, and a regular month to measure the long-term value of promotion-driven users.
By comparing time-based cohorts, you can determine:
- Whether your campaigns attract long-term users or short-term opportunists
- How different timing windows influence onboarding or purchase behaviors
- Whether product or pricing changes had a positive or negative retention impact
Insight: Time-based cohort analysis is essential for evaluating the lasting impact of external events and internal product changes.
Segment-Based Cohorts: Personalizing by User Type
Segment-based cohorts are formed by grouping users with shared attributes, such as location, device type, subscription tier, or customer persona. These cohorts help you understand how different user segments engage with your product over time and which groups require more personalized strategies.
Segment-based analysis is useful for identifying patterns tied to specific user types. For instance, power users on iOS may behave differently from low-engagement Android users, or freemium users may require different nudges than paying subscribers.
For example, a music streaming app might find that premium users on iOS show higher retention than free users on Android, prompting a targeted upgrade campaign or device-specific feature optimization.
Use segment-based cohorts to:
- Prioritize product improvements for specific user groups
- Design tailored onboarding flows or lifecycle journeys
- Identify which user segments are underperforming and why
Insight: Segment-based cohorts help you align engagement strategies with the needs, limitations, and expectations of different user types.
Size-Based Cohorts: Comparing Small vs. Large User Groups
Size-based cohorts group users according to the scale of the segment they belong to, such as early-access users in a beta test versus a full public launch audience. This helps you evaluate how user behavior changes as your product or campaign scales from controlled environments to wider audiences.
These cohorts are especially useful when testing how scalable your product experience, messaging, or onboarding truly is. What works well for a small, high-intent group may not translate to broader audiences without friction.
Example: A mobile app may find that beta users retained 40 percent by Day 7, but public launch users retained only 12 percent, indicating that what resonated with early adopters didn’t carry over at scale.
Use size-based cohorts to:
- Validate whether early results hold up under broader user volumes
- Identify product or UX breakdowns that occur when scaling
- Fine-tune feature rollout plans before going fully live
Insight: Size-based cohorts help expose scalability gaps that aren’t visible during small-scale tests or controlled rollouts.
Benefits of Cohort Analysis
Cohort analysis uncovers actionable insights into user behavior, helping you optimize marketing and product strategies. By identifying when and why cohorts churn, you can build targeted retention strategies. Analyzing high-engagement cohorts shows where to invest time and resources for a stronger customer experience and long-term growth.
Reduces Churn
By tracking when users from specific cohorts drop off, you can detect patterns in disengagement at a daily, weekly, or event-driven level. This allows teams to time interventions more precisely, whether through targeted campaigns or in-product nudges. Unlike aggregate churn metrics, cohort-level analysis highlights churn inflection points and decay rates, making it easier to take corrective action early.
Improves Retention
Analyzing the behavior of high-retention cohorts helps identify what keeps users engaged, such as completed actions, session depth, or usage frequency. These insights inform improvements in onboarding, activation, and lifecycle communication, enabling teams to reinforce successful behaviors and replicate them across future cohorts.
Optimizes Acquisition Quality
Cohort analysis goes beyond volume-based metrics by revealing which acquisition sources lead to longer-lasting, higher-value users. By examining post-acquisition retention and engagement patterns across channels, marketers can reallocate spend toward sources that deliver sustainable user growth and better return on investment.
Exposes Drop-Offs in the Customer Journey
Cohort tracking enables visibility into how users progress, or fail to progress, through lifecycle stages such as onboarding, activation, engagement, and monetization. By identifying which cohorts stall at specific stages, teams can focus on removing friction or improving guidance to accelerate time-to-value and reduce lifecycle leakage.
Measures Long-Term Impact of Changes
Unlike A/B tests that focus on immediate metrics, cohort analysis allows you to assess the long-term effects of product releases, onboarding redesigns, or campaign changes. Comparing performance across cohorts launched before and after an initiative provides clearer attribution and validates whether the change delivered lasting impact on retention or usage behavior.
How Cohort Analysis Works
Cohort analysis is a simple yet powerful way to understand how user behavior changes over time. It involves grouping users based on a shared starting point and tracking how those groups behave across specific time intervals.
Here’s a high-level view of how it works:
1. Group Users into Cohorts
Start by identifying a common trait to group users. For example, the day they signed up, installed the app, or completed a key action.
2. Track Their Behavior
Measure what these users do over the next few days or weeks. Common metrics include retention rate, engagement frequency, conversions, or churn.
3. Compare and Spot Patterns
Analyze how different cohorts perform. You might notice that users acquired on one day retain better than those from another, or that certain behaviors correlate with long-term engagement.
4. Use the Insights
Use these trends to refine onboarding, optimize campaigns, improve product experiences, or allocate resources more effectively.
How to Conduct a Cohort Analysis
A cohort analysis delivers meaningful insight only when it follows a focused, structured approach. Below is a step-by-step walkthrough of how to conduct one, starting from defining the objective to creating and interpreting a fully functional cohort chart or table. We’ll use a mobile app’s 7-day retention analysis as an example to illustrate the process.
1. Set a Clear Goal for the Analysis
Every cohort analysis should begin with a focused objective. The goal defines the type of cohort you’ll build (e.g., acquisition, behavioral), the time window for analysis, and the metrics you’ll measure.
For example, if you’re trying to understand early retention trends, your goal might be: “Measure how many new users return to the app over the first 7 days post-install.”
Without this specificity, you risk collecting data that doesn’t align with your business question or, worse, making decisions based on noise rather than signal.
2. Define the Cohorts Precisely
Once the goal is clear, define what qualifies users to be in the same cohort. This could be based on acquisition date, signup event, first transaction, or any other shared starting point relevant to your analysis.
In our example, we’ll use daily acquisition cohorts. Each cohort will contain all users who installed the app on a specific day in January—e.g., Jan 1 cohort, Jan 2 cohort, and so on.
Make sure that:
- The event used to define cohort entry is mutually exclusive and clear (e.g., first install date).
- Users are only assigned to one cohort, unless you’re explicitly doing multi-event or overlapping cohort studies.
3. Select the Right Metrics to Track Over Time
After defining the cohorts, determine what behavior you want to observe longitudinally. This could be retention (returning users), conversion (purchasing), activation (completing onboarding), or any other user action that signals value.
For this walkthrough, we’ll focus on retention, specifically, whether users in each cohort return to the app on subsequent days (Day 1 through Day 7). This allows you to observe engagement decay and assess how sticky or valuable the experience is during the first week.
This metric is often a reliable indicator of product-market fit, onboarding effectiveness, or acquisition quality in mobile app environments.
4. Structure the Cohort Table (Rows, Columns, and Values)
Now that you’ve defined cohorts and metrics, it’s time to build the actual cohort table—the analytical foundation of your insights.
How to Structure the Table:
- Rows: Each row represents a cohort. In our case, that’s one row per day in January (e.g., Jan 1 to Jan 31), each consisting of all users who installed the app on that day.
- Columns: Each column represents the number of days after acquisition. For example: Day 0 (install day), Day 1 (next day), up to Day 7.
- Cells: The cell at the intersection of row and column contains the retention rate, calculated as:
Day X Retention = (Users from cohort who returned on Day X ÷ Total users in that cohort) × 100
In a raw data sheet, you’ll typically start with a row showing:
Jan 1 | 1,200 users | 100% | 28% | 17% | 12% | …
Where:
- “1,200 users” is the cohort size
- “100%” is Day 0 (install day)
- Subsequent percentages show how many returned from Day 1 to Day 7 retention
This structure forms the basis for identifying drop-offs, evaluating patterns, and comparing performance across time-based user groups.
5. Populate the Table with Real Data
This is where your analytics tool or backend data comes in. Pull the raw event logs or aggregated metrics that match your cohort definition and behavior metric.
For each day:
- Count how many users entered the product (e.g., installed the app) to determine cohort size.
- Then, for each following day, count how many from that same cohort returned to the app.
Let’s say:
- On Jan 5, 1,000 users installed the app.
- On Day 1, 300 returned → 30% retention.
- On Day 2, 180 returned → 18% retention.
- By Day 7, 100 remained → 10% retention.
These percentages populate your cohort table horizontally from left to right for that cohort.
Ensure that your data is clean and consistent. Double-counting users, misaligned event timestamps, or cohort leakage (users assigned to the wrong day) can distort your entire analysis.
6. Visualize the Cohort Table
Once the table is populated, visualize it to make patterns easier to detect. The two most common formats are:
- Cohort Table with Conditional Formatting: Use color gradients to highlight high vs. low retention. For instance, darker cells for high retention, lighter for drop-offs. This helps you immediately spot cohorts that outperform or underperform.
- Retention Curves: Plot Day X retention (Y-axis) over time (X-axis) for each cohort. Overlay multiple cohorts on the same graph to compare patterns.
These visualizations not only make the data digestible but also help communicate insights to stakeholders who may not be deep in the analytics themselves.
To see these concepts in action, here’s a sample 7-day retention cohort chart for Jan 1–7:
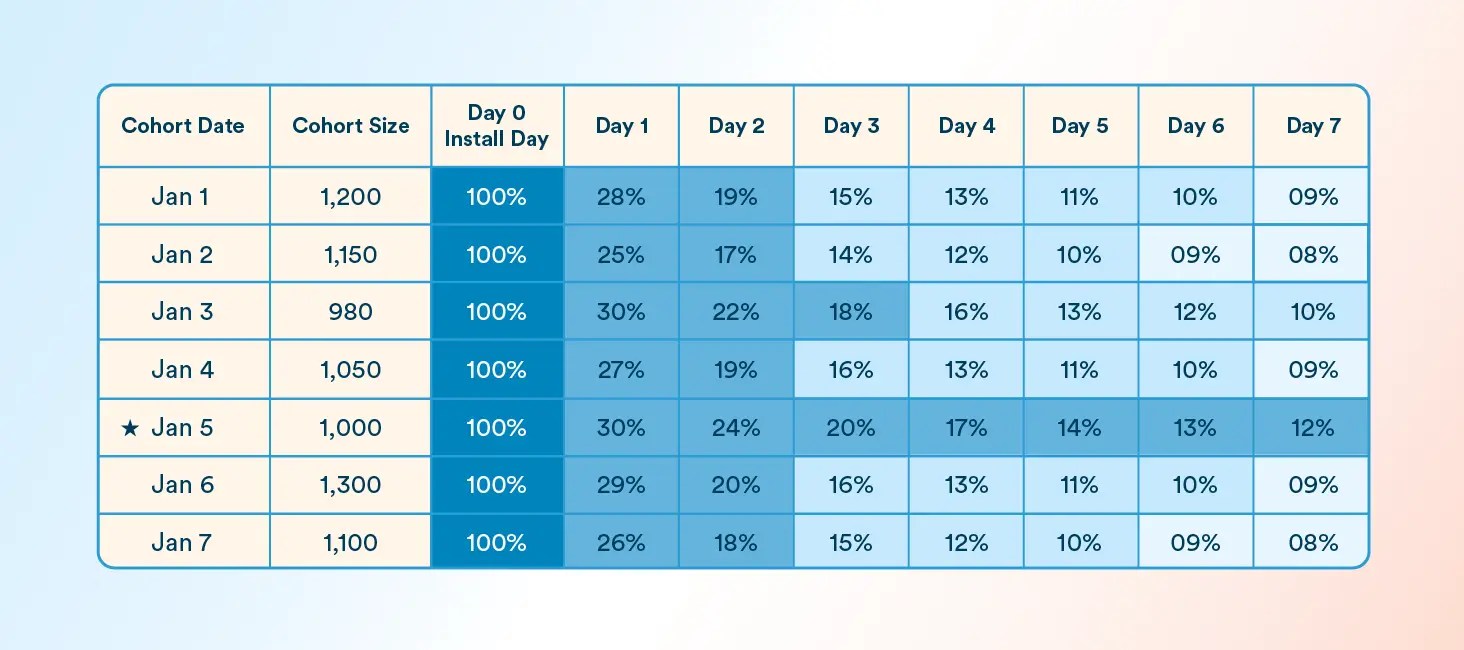
This cohort table displays 7-day retention performance by acquisition date. Each row represents a daily cohort, and each column shows what percentage of that group returned to the app on a given day. Color-coded shading (dark to light blue) highlights retention strength to help identify drop-offs, success patterns, and behavior shifts across segments.
Color Legend:
| Color Description | Retention Range |
| Dark Blue | 100% (Day 0 – install day) |
| Medium Blue | High retention (20% – 30%) |
| Light Blue | Moderate retention (13% – 19%) |
| Very Light Blue | Low retention (≤ 12%) |
Annotation:
Jan 5 ★ – Personalized onboarding feature launched
7. Interpret Patterns and Extract Insights
Now comes the most critical step: interpreting what the data tells you.
Look for:
- Drop-off inflection points: Where does retention plummet? Is there a consistent drop on Day 2 or Day 3?
- Outlier cohorts: Are there cohorts that perform significantly better or worse than the rest? What was different about that day (e.g., marketing source, product update)?
- Decay trends: Is the retention curve flattening at a specific point, or does it decline steadily?
Returning to our example, if the Jan 5 cohort shows 30% Day 1 retention compared to 25% average, and we know Jan 10 had a personalized onboarding feature launched, this cohort may prove that the feature had a positive impact.
Over time, cohort analysis evolves from a retrospective diagnostic into a proactive tool for identifying opportunities, validating experiments, and improving the customer experience at every touchpoint.
How to Select the Right Tool for Cohort Analysis
Choosing the right tool for cohort analysis is crucial for gaining actionable insights. Look for a platform that offers flexibility, intuitive data visualization, and advanced analytics. Here’s what to keep in mind when evaluating your options:
- Cohort Creation: The tool should allow you to define cohorts based on various criteria.
- Data Visualization: An effective tool provides clear visualizations, like retention curves.
- Usability: The tool should integrate easily with your systems and be user-friendly.
CleverTap is one such tool that offers these functionalities, helping you create and analyze cohorts, visualize data, and derive actionable insights.
How CleverTap Can Help with Cohort Analysis
When it comes to effective cohort analysis, selecting the right tool is crucial. CleverTap stands out as a comprehensive platform that provides all the necessary features to conduct insightful cohort analysis and enhance user engagement.
Here are the key capabilities that set CleverTap apart from other platforms:
- Cohort Creation and Segmentation
CleverTap enables you to easily create and manage cohorts based on various criteria, such as user behavior or specific actions. This flexibility allows you to segment users in ways that align with your business objectives, providing a clear view of how different groups interact with your app over time. - Advanced Data Visualization
CleverTap offers sophisticated visualization tools, including retention curves, cohort tables, and heatmaps. These visualizations help you quickly identify trends and patterns in user behavior, making it easier to pinpoint issues and opportunities for improvement. - Actionable Campaign Creation
With CleverTap, you can take action directly from the cohorts you create, instantly launching personalized campaigns without leaving the platform. This seamless integration saves time and allows you to immediately act on insights from your cohort analysis. - Integration and Automation
CleverTap integrates seamlessly with your existing CRM and marketing systems, streamlining data management and analysis. Its automation features support the creation of trigger-based campaigns and personalized user interactions, enhancing the overall efficiency of your marketing efforts. - User-Friendly Interface
The platform’s intuitive interface simplifies the process of setting up and executing cohort analyses. Its easy-to-use dashboards and reporting tools make it accessible to users of all experience levels, from beginners to advanced analysts. - Custom Reporting
CleverTap allows you to generate customized reports that focus on the metrics most relevant to your business. This feature enables you to tailor insights and share them with your team, facilitating data-driven decision-making.
Want deeper retention insights? See CleverTap’s cohort analysis in action.
Beyond Cohorts: Powerful Segmentation That Drives Growth
CleverTap offers far more than cohort analysis. Its advanced segmentation engine empowers marketers to create highly targeted audiences in real time, enabling hyper-personalized communication across the customer lifecycle.
Real-Time Segmentation
CleverTap supports dynamic segmentation with instant audience refresh, using live behavioral and profile data. Whether users are adding items to a cart, viewing content, or dropping off at checkout, you can instantly engage them based on that activity.
Unlimited Historical Lookback
Thanks to TesseractDB™, CleverTap provides segmentation with up to 10 years of historical data, a clear differentiator. You can build segments using long-term behaviors and trends without limitations on data depth or event volume.
Advanced Segmentation Features:
- Nested Logic and Boolean Operators: Easily build complex segments using combinations of events, properties, and user attributes.
Segment Nesting (up to 10 levels deep): Reuse segments within other segments to manage large campaigns with precision. - AND/OR Condition Grouping: Create advanced rules like (X AND Y) OR (Z AND A), which many platforms restrict.
Actionable RFM Modeling
CleverTap includes built-in RFM (Recency, Frequency, Monetary) segmentation, allowing you to automatically identify high-value customers, at-risk users, and loyalists. Each segment can be targeted with tailored campaigns launched directly from the RFM grid.
Intent-Based Segmentation
With Clever.AI, you can define business goals, like increasing purchases or preventing churn, and the system predicts the likelihood of each user achieving that goal. You can then segment users based on their predicted intent and intervene proactively.
With these features, CleverTap enables you to conduct in-depth cohort analysis, create powerful segments, and implement personalized strategies that enhance engagement and drive revenue.
Take a deeper dive into CleverTap’s segmentation capabilities
Case Study: How BukuKas Improved New User Activation by 60% Using CleverTap
BukuKas was launched in December 2019 by Krishnan M Menon. It is an SME digitization startup offering a digital ledger app for Indonesian small businesses. The company serves nearly 2 million monthly users by helping them manage cash, inventory, and analytics. BukuKas is expanding its services to include digital payments and social commerce. Here’s how CleverTap helped BukuKas hit outstanding goals:
Goals For BukuKas
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Reduction: Needed an integrated solution for product analytics, A/B testing, and CRM.
- Engagement Automation: Required automated and personalized engagement strategies.
- User Education: Needed to help users transition from physical ledgers to digital.
Solutions with CleverTap
- Funnels: Tracked user behavior from app launch to feature engagement.
- Product Experiences: Enabled A/B testing and rapid feature iteration.
- Cohort Analysis: Provided insights into user retention and engagement across different groups.
- RFM Analysis: Identified valuable and at-risk users for targeted retention efforts.
Results
- 60% Increase in Conversion Rates: Enhanced onboarding and engagement strategies.
- Streamlined Operations: Reduced complexity with an integrated platform.
- Improved Retention: Better understanding of user behavior through detailed analysis.
CleverTap’s cohort analysis offers powerful insights into user behavior, helping businesses track and compare engagement across different groups. This enables tailored strategies that improve user retention and drive growth.
Meet CleverTap at App Promotion Summit in Berlin on 27 November.
Shivkumar M 
Head Product Launches, Adoption, & Evangelism.Expert in cross channel marketing strategies & platforms.
Free Customer Engagement Guides
Join our newsletter for actionable tips and proven strategies to grow your business and engage your customers.