Geodemographic segmentation is a marketing strategy that groups customers using location and demographic data. This type of segmentation helps marketing teams transform generic campaigns into targeted communications. These campaigns precisely match consumer preferences based on where they live and who they are.
By delivering personalized experiences to the right audiences, businesses significantly improve customer engagement, retention, and lifetime value while optimizing their marketing investments.
In this blog, we’ll discuss geodemographic segmentation and its importance in marketing. We will also look at a few examples of geodemographic segmentation and learn about some key strategies.
What is Geodemographic Segmentation?
Geodemographic segmentation is a marketing strategy that involves dividing the target audience into groups using geographic and demographic data. This method allows marketers to create rich profiles of consumer groups that not only focus on customer demographics, such as age, gender, and income, but also how location influences consumer behavior and preferences, enabling more targeted and effective marketing campaigns.
Key Components of Geodemographic Segmentation
- Geographic Data: Physical location (urban, suburban, rural), climate, population density, regional cultural influences.
- Demographic Data: Age, gender, income, education level, occupation, family structure.
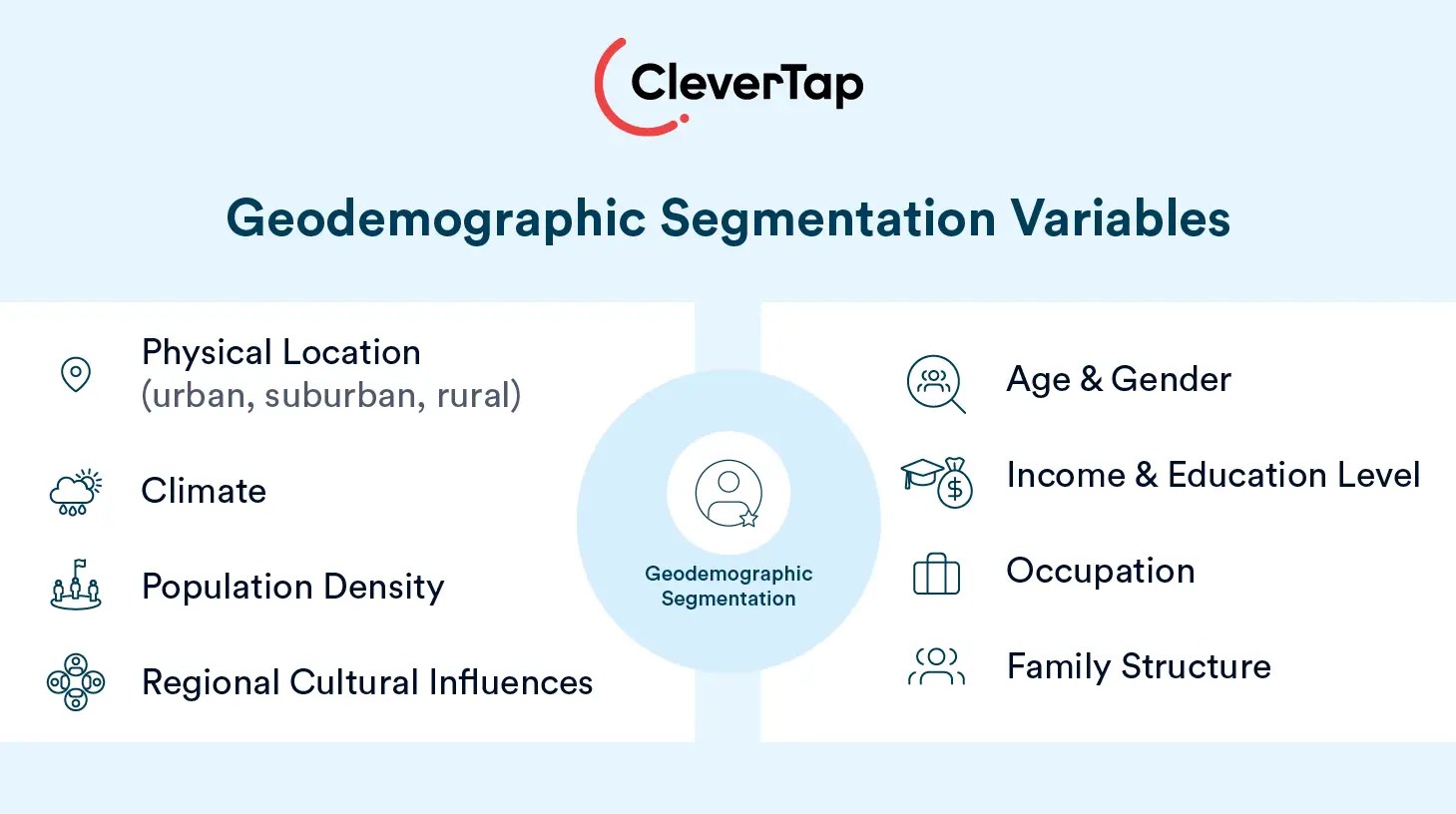
Merging these two data sets helps marketers create nuanced customer segments that reflect both where people live and their personal characteristics. This combination provides a more comprehensive view of consumer behavior than either geographic or demographic data alone.
How Geodemographic Segmentation Differs from Other Methods
While traditional customer segmentation methods often focus on single dimensions (e.g., age groups or income brackets), geodemographic segmentation offers a multidimensional approach. This allows for more precise targeting and a deeper understanding of consumer motivations and preferences.
Consider two families with young children, both earning similar household incomes. Traditional demographic segmentation might classify them together. However, geodemographic segmentation takes into account their neighborhoods—one family living in an urban apartment complex with access to public transport and entertainment, while the other resides in a suburban community with larger homes and a focus on outdoor activities.
Implementing Geodemographic Segmentation: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let’s understand how to implement geodemographic segmentation in your marketing strategy.
1. Define Your Business Objectives
Begin by establishing precise customer engagement and retention goals that align with your overall business strategy. Rather than vague aspirations like “improve customer retention,” set specific, measurable targets such as increasing customer lifetime value by 20% or reducing churn rate in high-value segments by 15% within a defined timeframe.
Determine which key performance indicators (KPIs) will accurately measure your progress. These might include repeat purchase rate, average order value, customer lifetime value, or retention rate by segment.
2. Identify Relevant Variables
Select geographic factors that genuinely influence your customers’ behavior. For retail businesses, this might include urban density, walkability scores, and proximity to competitors. Service businesses might focus on climate zones that affect seasonal demand patterns or neighborhood income levels.
Choose customer demographic variables with a proven impact on purchasing decisions in your industry. Look beyond basic age and income to consider household composition, education level, occupation, and life stage milestones that trigger specific needs your products address.
3. Collect and Clean Data
Gather data from reliable sources to create a comprehensive view. Census data provides demographic baselines, while your CRM contains valuable purchase history and engagement metrics. Conducting market research through surveys and questionnaires can provide valuable insights into customer needs and preferences.
Invest time in thorough data cleaning before analysis begins. Address missing values, identify and resolve inconsistencies, remove duplicates, and standardize formats across sources to prevent misleading segment definitions.
4. Perform Cluster Analysis
Apply appropriate statistical techniques (k-means clustering, hierarchical clustering, or latent class analysis) to group customers with similar characteristics and behaviors. The goal is to create segments that are internally homogeneous yet distinct from each other.
Validate your clusters using statistical measures to determine whether the segments reveal actionable differences in purchase patterns, communication preferences, or retention risk factors.
5. Create Detailed Segment Profiles
Develop rich, multidimensional segment descriptions that go beyond raw data to tell a coherent story about each customer group. Include both quantitative metrics and qualitative insights.
Assign intuitive, memorable names to each segment that capture their essence and facilitate internal communication. Names like “Urban Tech Enthusiasts” or “Suburban Value Families” create instant recognition among team members.
For example, a cluster might be described as “Urban Young Professionals” and characterized by attributes such as:
- Age: 25-35
- Gender: Female
- Location: City center
- Income: Above average
- Education: College degree or higher
6. Develop Targeted Marketing Strategies
Craft personalized marketing strategies for each segment, focusing on their specific pain points and motivators. Consider how product features, pricing strategies, communication styles, and incentives should vary across segments.
Select channels that align with each segment’s media consumption habits and preferences. Some segments may respond better to email marketing, while others engage more through mobile apps or direct mail.
7. Implement Campaigns
Execute your targeted campaigns with meticulous attention to timing, frequency, and content relevance. Ensure that the customer experience remains consistent across all touchpoints while still addressing segment-specific needs.
Implement proper tracking mechanisms to attribute responses and conversions to specific campaign elements and segments.
8. Monitor and Measure Results
Establish a regular cadence for reviewing key metrics by segment. Look for both immediate response indicators and longer-term retention metrics to gauge campaign effectiveness.
Compare performance against both pre-campaign baselines and control groups to isolate the impact of your geodemographic approach from external factors affecting the market.
9. Refine and Optimize
Use A/B testing to continuously refine messaging, offers, and channel strategies for each segment. Let data guide incremental improvements rather than making wholesale changes.
Revisit your segmentation model periodically to ensure it remains relevant as customer behaviors evolve and new data becomes available.
By following this structured approach, geodemographic segmentation can create highly targeted and effective campaigns that resonate with specific customer groups.
Real-World Geodemographic Segmentation Examples Across Industries
Several leading brands have successfully implemented geodemographic segmentation to tailor their products, services, and marketing to diverse customer bases. Below are four prominent examples showcasing how companies use geodemographic segmentation to improve customer engagement and business performance.
1. Walmart – Localized Inventory Strategy
Walmart employs a hyper-localized inventory strategy under its “Store of the Community” initiative, using geodemographic data to adjust store offerings based on the surrounding population. The company analyzes neighborhood demographics—such as family composition, ethnicity, and income levels—to stock products that best fit local demand.

Source: Walmart
For instance, Walmart stores in college towns stock extra dorm furnishings, quick meal options, and affordable student-friendly products during back-to-school seasons. In contrast, locations in family-dense suburbs emphasize baby products, bulk grocery items, and children’s clothing.
Stores in retirement communities carry expanded selections of health products, easy-to-prepare meals, and gardening supplies to cater to older consumers. By aligning inventory with local consumer needs, Walmart reduces waste, increases sales, and enhances customer satisfaction.
2. American Express – Targeted Credit Card Offers
American Express integrates geodemographic segmentation by tailoring credit card offers based on customers’ geographic locations and financial behaviors. The company segments its market by urban vs. suburban populations, income brackets, and spending patterns.

Source: American Express
For instance, in affluent urban areas with high concentrations of young professionals, the brand promotes premium travel rewards credit cards offering airport lounge access and travel perks. In suburban regions, where families prioritize household expenses, AmEx markets cash-back cards with rewards for grocery and gas purchases.
Additionally, in regions with a strong small business presence, AmEx targets entrepreneurs with specialized business credit cards designed to support their specific industry needs. This precise segmentation has led to higher customer acquisition rates and improved retention, as users receive offers that genuinely align with their spending habits.
3. Starbucks – Focus on Affluent Urban Markets
Starbucks strategically positions itself in high-income, urban areas by leveraging geodemographic insights. The coffee chain’s target audience consists primarily of young, college-educated professionals with disposable income who are willing to spend on premium coffee experiences.

Source: Unsplash
Starbucks stores are concentrated in affluent urban and suburban locations, where foot traffic is high, and customers are more likely to embrace specialty coffee culture. The brand aligns its marketing and product offerings—such as mobile ordering, drive-through locations, and premium espresso drinks—to fit the fast-paced lifestyle of city dwellers.
By locating stores in wealthy, high-traffic areas and catering to a specific demographic, Starbucks has cultivated a loyal customer base and maintained its premium brand positioning.
4. Home Depot – Tailoring Assortments to Urban vs. Rural Needs
Home Depot utilizes geodemographic segmentation by adjusting its product selection to reflect urban and rural customers’ distinct needs.
For example, Home Depot stores in large cities stock space-efficient solutions like balcony gardening supplies, reflecting the limited space available to urban residents. In rural and suburban areas, Home Depot prioritizes large-scale landscaping materials, bulk home improvement supplies, and DIY kits, catering to homeowners with larger properties.
Source: Home Depot
By segmenting its markets this way, Home Depot ensures that each store is stocked with the most relevant products for its local customers, boosting sales and enhancing the shopping experience.
Impact of Geodemographic Segmentation on These Brands
The impact of geodemographic segmentation has allowed these brands to optimize inventory, enhance customer experience, and increase profitability. By aligning product offerings with local demographics and geographical factors, businesses can cater more effectively to consumer preferences, leading to higher sales conversion rates, customer retention, and operational efficiency.
Walmart’s community-based merchandising has reduced excess inventory, ensuring that each store meets the unique demands of its location. American Express has improved customer engagement and retention through targeted marketing strategies, while Starbucks has strengthened its brand loyalty by catering to urban professionals with high spending power. Home Depot has successfully adjusted product assortments to maximize sales in both urban and rural markets.
These real-world applications demonstrate how geodemographic segmentation is a powerful tool for businesses to stay competitive and maximize revenue by delivering localized, highly relevant offerings to their target markets.
Advanced Targeting Strategies for Digital Campaigns Using Geodemographic Segmentation
Geodemographic segmentation has evolved to incorporate online behavior and real-time location data, enabling even more precise and dynamic marketing strategies.
IP-Based Geodemographic Targeting
IP-based targeting allows marketers to deliver location-specific content and offers based on a user’s internet connection. This technique is particularly useful for:
- Displaying region-specific promotions on e-commerce websites: Using IP data to show targeted offers using location-based marketing techniques and demographics (e.g., luxury items for affluent areas, budget deals for others).
- Customizing landing pages to reflect local cultural preferences: Adapting content to regional traditions and demographic groups (e.g., adventure trips for young travelers, family vacations for suburban users).
- Adjusting product recommendations based on climate or local events: Suggests products based on weather and user profiles (e.g., running gear for active users in warm areas, indoor fitness equipment for older users in cold regions).
Social Media Advertising Applications
Social media platforms offer robust geodemographic targeting options, allowing marketers to:
- Create custom audiences based on location, demographics, and interests
- Use lookalike audiences to reach new potential customers with similar profiles to existing high-value customers
- Implement dynamic ad content that changes based on the viewer’s location and demographic attributes
Mobile Marketing and Geofencing
Mobile devices provide unprecedented opportunities for geodemographic marketing:
- Push notifications can be triggered when a customer enters a specific geographic area: Alerts trigger when users enter a specific location, personalized based on demographics (e.g., student discounts near campuses, VIP offers in luxury districts).
- App content can be customized based on the user’s current location and time of day: Apps adjust based on location, time, and user profile (e.g., coffee deals at nearby cafes in the morning for commuters, etc.)
- Location history can be used to build more detailed customer profiles for future targeting: Past visits refine customer profiles (e.g., frequent gym-goers receive fitness deals, travelers see hotel offers in past destinations).
How CleverTap Helps with Geodemographic Segmentation
CleverTap empowers businesses to conduct precise geographic and demographic segmentation by leveraging its advanced analytics and real-time customer engagement capabilities.
Geographic Segmentation:
- Location-based Targeting: Segment users by country, state, city, or neighborhood for precise marketing.
- Geofencing & Location Triggers: Send real-time push notifications when users enter or leave specific areas.
- Regional Personalization: Customize campaigns based on local events, weather, or cultural preferences.
- Real-time Updates: Automatically adjust segmentation as users move across locations.
Demographic Segmentation:
- Age & Gender-based Targeting: Personalize content and offers based on user demographics.
- Language Preferences: Deliver messages in the user’s preferred language for better engagement.
- Income & Purchase Behavior: Target high-value customers with premium offers while providing discounts to price-sensitive users.
- Device & Platform-Specific Campaigns: Optimize engagement strategies for mobile, desktop, or tablet users.
AI-Driven Personalization:
- Behavioral Insights: Combine demographic and geographic data with real-time actions for hyper-personalized engagement.
- Predictive Analytics: Use AI customer segmentation to identify high-converting user segments and tailor marketing accordingly.
- Automated Campaign Optimization: Continuously refine messaging for different audience segments based on performance.
By integrating these capabilities, CleverTap ensures businesses can deliver highly relevant, data-driven marketing campaigns that boost engagement, conversions, and customer retention.
Future Trends in Geodemographic Segmentation
Geodemographic segmentation is evolving as new technologies reshape how marketers understand and connect with customers.
- Big data and IoT integration will provide unprecedented visibility into population movements through smart city initiatives, generating continuous data streams that reveal not just where people live but how they interact with their environments.
- Connected devices in homes and public spaces will constantly generate contextual data, offering deeper insights into lifestyle patterns than traditional static demographic profiles ever could.
- Real-time segmentation powered by AI systems will process location and demographic signals instantaneously, allowing marketing messages to adapt to consumers’ immediate contexts—whether commuting, shopping, or at home.
- Dynamic targeting will make marketing interactions feel more relevant and helpful by perfectly aligning with customers’ current situations and needs rather than relying on outdated segment assumptions.
- Privacy concerns will grow in parallel with these capabilities, requiring marketers to navigate increasingly stringent regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and others and develop transparent data practices that earn consumer trust.
- Predictive algorithms will shift marketing from reactive to anticipatory approaches, forecasting how customer segments will evolve and addressing needs before they’re explicitly expressed.
These unified customer journeys will be simultaneously tailored to both demographic profiles and geographic contexts, creating more personalized and effective marketing engagements.
Maximizing Marketing ROI with Geodemographic Segmentation Insights
Combining geographic and demographic data helps create highly targeted campaigns that resonate with specific customer groups.
Key benefits of implementing geodemographic segmentation include:
- Improved targeting accuracy
- Enhanced customer understanding
- Optimized resource allocation
- More personalized marketing messages
To maximize the impact of geodemographic segmentation, marketers should:
- Invest in quality data collection and analysis tools
- Continuously update and refine segment profiles
- Test and iterate on targeting strategies
- Balance personalization with privacy concerns
- Stay informed about emerging trends and technologies in the field
As the marketing landscape continues to evolve, geodemographic segmentation will remain a crucial strategy for marketers looking to create more effective, efficient, and customer-centric campaigns. By mastering this approach, marketers can not only retain their valuable customers but also foster deeper, more meaningful relationships that drive long-term business success.
Learn more about CleverTap segments.
Kiran Pius 
Leads Product Launches, Adoption, & Evangelism.Expert in cross-channel marketing strategies & platforms.
Free Customer Engagement Guides
Join our newsletter for actionable tips and proven strategies to grow your business and engage your customers.