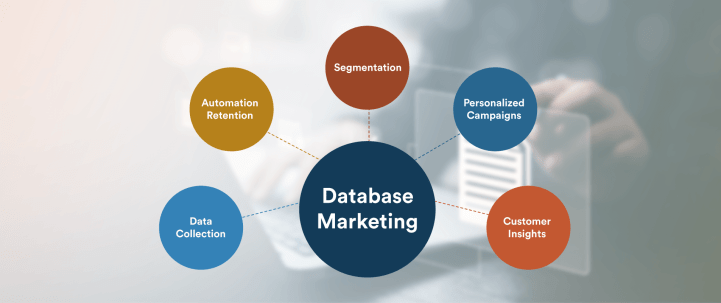
Database marketing leverages customer data to create targeted marketing campaigns that drive engagement and sales. This blog explores the fundamentals of database marketing and provides practical strategies to help you effectively utilize your customer data for better marketing results.
Real-time data. Actionable insights. 360-degree customer views. Personalized engagement strategies. Omnichannel campaigns. They may be buzzwords, but they’re also critical to effective marketing and business growth. And database marketing is the key to all of them.
So what is database marketing and why is it important?
What is Database Marketing?
Let’s start with a basic definition. Database marketing is a form of direct marketing that involves collecting customer data such as names, addresses, emails, phone numbers, transaction histories, and customer interactions. This data is then analyzed and used to create personalized experiences for each customer or to attract potential customers more effectively.

Traditional direct marketing focuses on broad, impersonal campaigns—think mass mailers or blanket email blasts to a general list of potential customers. Database marketing takes that strategy a step further by seeking to understand how customers want to be marketed to and then applying those insights to fulfill the customer’s need via the best channel.
But database marketing is more than just a method for gathering customer data—it’s a strategic tool for building deeper, more meaningful relationships with your audience, while also driving long-term business growth.
In today’s digital world, database marketing is important because it:
- Builds Strong Customer Relationships: Personalized messaging powered by rich customer data helps foster loyalty, keep your customers engaged, and create lasting connections with your brand.
- Drives Higher ROI: Data-driven marketing campaigns are more targeted and efficient. This leads to better conversion rates and a higher return on investment, often at a lower cost.
- Improves Customer Experience: You can craft a more satisfying, engaging experience, which keeps customers coming back for more by delivering relevant content based on customer preferences and behavior.
Benefits of Database Marketing
Database marketing offers a wide range of benefits that can enhance your overall marketing strategy. You can create more targeted campaigns, improve customer satisfaction, and drive long-term growth by leveraging customer data to its full potential. Here are some key benefits:
- Personalization: Craft highly personalized messages based on individual customer preferences and behaviors.
- Increased ROI: Reach the right audience with the right message and optimize your marketing spend.
- Better customer retention: Use data to identify at-risk customers and engage them with tailored offers before they churn.
- Improved decision-making: Data-backed insights enable you to make more informed decisions about campaign strategy and execution.
Now, let’s explore how various industries can apply database marketing for a transformative impact:
- Retail: Retailers can track customer purchases to send personalized offers. For example, a fashion brand might promote discounts on frequently bought items to boost repeat sales.
- Travel & Hospitality: Travel companies can use booking history to suggest tailored offers. For example, they can offer destination recommendations based on past trips to enhance the customer experience.
- E-commerce: E-commerce brands leverage purchase data to suggest complementary products. This can drive cross-sell and upsell opportunities.
- Finance: Financial institutions can analyze transaction data to personalize loan offers or financial advice, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers can use patient history to send appointment reminders or health tips. This can foster proactive care and better patient engagement.
Every industry can harness the power of database marketing to improve customer engagement and drive business growth.
Is Database Marketing Right for Your Business?
Database marketing can provide invaluable insights into your customers’ needs and preferences for various kinds of businesses including retail, finance, healthcare, or any other sector. The key question is: Are you prepared to leverage the data at your disposal?
If personalized experiences, better targeting, and stronger customer relationships are priorities for your business, then database marketing should be a cornerstone of your strategy. Just ensure you have the right tools and infrastructure in place to manage, analyze, and act on customer data effectively.
How Does Database Marketing Work? Steps To Get Started
Starting with database marketing doesn’t have to be daunting. You can build a data-driven marketing strategy that drives engagement and results by following these steps. Here’s how it works:
- Defining Your Audience: Understanding your target audience is the first step. Who are your customers, and what do they care about? Defining key segments within your customer base will help you tailor your marketing efforts.
- Collecting Customer Data: Gathering customer details—such as names, emails, preferences, and purchase histories—sets the foundation for database marketing. This information can be collected from websites, social media, or customer service interactions. Ensure ethical data practices by obtaining consent and adhering to privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
- Organizing and Centralizing Data: Store data in a centralized system, such as a CRM, for easy access and analysis. Keeping your database organized, accurate, and up-to-date enables you to build reliable campaigns based on consistent insights. Integrate marketing automation tools to streamline processes and manage customer data efficiently.
- Analyzing the Data: Using analytics tools to uncover patterns, behaviors, and customer segments is key to database marketing. This process helps you identify high-value customers and understand common preferences, allowing you to craft actionable marketing strategies.
- Segmenting Your Audience: Grouping customers with similar characteristics or behaviors into segments allows you to create more relevant and targeted messages. Effective segmentation ensures your marketing efforts resonate with each group, driving better engagement.
- Personalizing Communications: Crafting personalized messages based on customer data, such as tailored emails, ads, or recommendations, increases the likelihood of engagement. Marketing automation tools enable you to deliver these messages efficiently and at scale, improving conversion rates.
- Creating Targeted Campaigns: Designing campaigns that cater to specific customer segments ensures that the content, offers, and promotions are relevant. Monitoring and refining targeting criteria continuously keeps campaigns impactful and results-driven.
- Optimizing Marketing Spend: Allocating resources to the customer segments most likely to respond helps you optimize your marketing budget. Tracking campaign performance and reallocating spending to high-performing areas maximizes return on investment.
- Maintaining Data Quality: Regularly updating and cleaning your database ensures accuracy and reliability. Removing duplicates, correcting errors, and validating entries enhance the effectiveness of your campaigns, fostering stronger customer relationships through timely and relevant outreach.
- Improving Customer Service: Using customer data to provide personalized support improves overall satisfaction. Understanding individual preferences and histories enables you to address inquiries effectively, resolve issues faster, and elevate the customer experience.
- Continuously Refining Your Approach: Adapting your database marketing strategy over time ensures it stays relevant. Regularly updating data, testing campaigns, and integrating new tools and trends keep your efforts aligned with customer needs and business goals.
By following these steps, you’ll be well on your way to building a successful database marketing strategy that speaks directly to your customers’ needs.
Effective Database Marketing Strategies
How should you get started creating your own database marketing strategy? Begin with the following steps.
Identify Your Target Audience: Build a detailed profile of your ideal customer. Consider factors like age, income level, job title, location, interests, and purchasing behavior. Use this customer profile to determine the types of information you need in your database.
Collaborate with Other Teams: Engage with marketing, sales, and support teams, as they have direct contact with customers and prospects. Determine what information each team needs to be more effective and ensure that it’s captured in your database.
Find the Right Software: Choose a tool that makes it easy to organize and access customer data. Your software should allow your team to view different types of customer information, categorize customer profiles by product or service, and segment your audience as needed.
Gather Customer Data: Collect information from both internal and external sources, such as:
- Acquisition Data: Where did new customers come from? Which marketing campaign or channel brought them in?
- Demographic Data: What is the customer’s age, gender, marital status, education level, and location?
- Technographic Data: What devices do they use to interact with your brand—desktop or mobile? Android or iOS?
- Psychographic Data: What are their values, interests, and motivations?
- Activity Data: How have they engaged with your website, social media, or mobile app?
- Transaction Data: How often do they purchase? What do they typically buy, and how much do they spend?
- Correspondence Data: Have they submitted support tickets, asked questions, or posted complaints on social media? Responded to surveys?
Keep Data Up-to-Date and Backed Up: Safeguard your database investment by protecting against power outages or technical failures. Use CRM software that updates profiles when customers provide new information. Consider tools that prevent data decay by tracking activity and keeping customer information fresh.
Respect Customer Privacy: While social media offers valuable insights into customers’ interests and behavior, ensure you use this data responsibly. Focus on delivering relevant messages to the right audience without overstepping privacy boundaries.
Once you’ve built your database, you can start with some basic user segmentation. For instance, create a campaign for specific groups, such as first-time buyers, new customers, or loyalty program members.
For more complex segmentation, analyze multiple data points to develop more refined user segments. A useful method is RFM Analysis (Recency, Frequency, Monetary value) which categorizes customers based on their engagement (how recently and frequently they interact) and spending habits. This helps you easily identify and engage your champion customers, new buyers, or dormant customers.
Database Marketing Examples To Inspire You
Here are some database marketing examples to show you how businesses like yours can use customer data to drive targeted campaigns and improve engagement:
Identify High-Value Customers and Potential Upsells
An OTT app wants to identify frequent binge-watchers who are ready for an upsell to a premium subscription plan. By analyzing their customer database, they pinpoint high-value, frequent watchers and launch a combined email and push notification campaign. They offer these users a free month of premium as an incentive to purchase a subscription. Using predictive analytics, the team forecasts how many recipients will convert, allowing them to allocate marketing resources efficiently and prove ROI.
Provide Personalized Customer Support
A customer service representative for an eCommerce app receives an incoming call. They quickly access the caller’s profile and see that they are a new customer who recently purchased a smart home device. With this information, the rep can deliver personalized support by helping the customer set up and troubleshoot the device, providing a faster and more relevant resolution tailored to the customer’s needs.
Know Which Products and Services to Pitch Customers
A travel app wants to introduce guided backpacking tours but needs to ensure there’s demand before investing resources. They analyze their customer database to examine purchase trends and demographic patterns. This analysis reveals whether customers would book these trips and which segments are most likely to be interested. With this data-driven approach, the travel app can focus its efforts on offering products their customers actually want.
Predict Who Will Buy and When
For a food delivery app, timing is everything. Engaging users at the right moment can mean the difference between beating the competition and losing a sale. Instead of sending promotions at every mealtime, they use predictive analytics to forecast which users are most likely to order. This allows the app to send targeted notifications and promo codes precisely when users are most likely to buy. Additionally, they can identify users at risk of churning and reach out with a compelling promo campaign to win them back.

Metrics That Matter for Growth: A Handbook for Mobile Marketers
Challenges of Database Marketing
While database marketing offers many advantages, it’s not without its challenges. Watch out for these common database marketing challenges to maximize it’s potential:

- Data Decay: Anytime a customer or prospect changes jobs or earns a promotion, moves to a new address, changes their name, gets a new email address, or makes any other life change, their profile becomes out of date. A well-managed database decays at an average of 2-3% each month, which means in just a year, a third of your data could be invalid.* To limit data decay, focus on information that is less likely to change: name and phone number, for example, rather than business email.
- Data Accuracy: Customers don’t always provide accurate information. Typos, handwriting legibility, or incomplete info can have a big impact on the quality of your database. You can limit inaccuracies by replacing input fields with standardized drop-down menus or checkboxes.
- Privacy Concerns: With growing attention on data privacy, especially with regulations such as GDPR, you have to handle customer information with care. Ensuring that your data practices comply with legal requirements not only protects your business from penalties but also builds customer trust. Prioritize data protection to maintain stronger, long-term relationships with your customers.
- Timely Action on Customer Data: Gathering customer data is just the first step. You have to act on it quickly is critical to making the most of customer engagement. This is where marketing automation tools like CleverTap become so important. It unifies user profiles with advanced segmentation and omnichannel marketing, allowing you to deliver timely and personalized experiences. Acting promptly on customer data helps you capitalize on their interest and interactions, ensuring better engagement and loyalty.
Addressing these challenges head-on can lead to more effective campaigns and improved customer relationships.
Database Marketing vs. CRM: What’s the Difference?
It’s easy to confuse database marketing with Customer Relationship Management (CRM), but they serve distinct purposes.
- Database marketing focuses on analyzing customer data to create more targeted, personalized marketing campaigns.
- CRM, on the other hand, is about managing and nurturing customer relationships over time, from acquisition to retention, and tracking all interactions with your brand.
While both are essential to a customer-centric approach, database marketing is more data-driven, whereas CRM is focused on relationship management.
Database Marketing vs. Direct Marketing
While both database and direct marketing aim to reach customers, the difference lies in how they do it:
- Direct marketing typically involves reaching out to a broad audience with a generic message to attract interest.
- Database marketing uses data to refine and target specific segments with more personalized, relevant messages that are more likely to resonate.
With database marketing, you increase the likelihood of your marketing efforts as you connect with the right audience at the right time.
The Next Phase of Database Marketing
We’ve now entered the era of relationship marketing. These days, brands focus not just on making a sale, but on building long-term relationships by consistently delivering value to customers. At the heart of this shift is database marketing, which serves as the foundation for creating meaningful customer interactions.
CleverTap’s machine learning capabilities are driving this evolution to the next level. These advanced tools can instantly analyze millions of customer data points. They can automatically generate detailed user segments, determine the best time and channel to engage each user, and even predict what users will do next.
Shivkumar M 
Head Product Launches, Adoption, & Evangelism.Expert in cross channel marketing strategies & platforms.
Free Customer Engagement Guides
Join our newsletter for actionable tips and proven strategies to grow your business and engage your customers.