Learn how you can Unlock Limitless Customer Lifetime Value with CleverTap’s All-in-One Customer Engagement Platform.

Congratulations on developing your new mobile app! However, to maximize its impact, it’s crucial to consider accessibility in your design. With over 1 billion people worldwide having some form of disability, neglecting accessibility could significantly limit your app’s audience. Disabilities are diverse, making inclusive design essential. Here’s how to ensure your app reaches everyone.
Mobile app accessibility describes the importance of designing mobile applications for smartphones, tablets, and wearables to be user-friendly to the 1+ billion people worldwide who have a disability.
Mobile app accessibility from a legal standpoint is confusing and vague. No concrete standards have been put in place, though U.S. Federal courts and regulations have determined that mobile apps must be accessible in the following 4 cases: 3,4,5,6 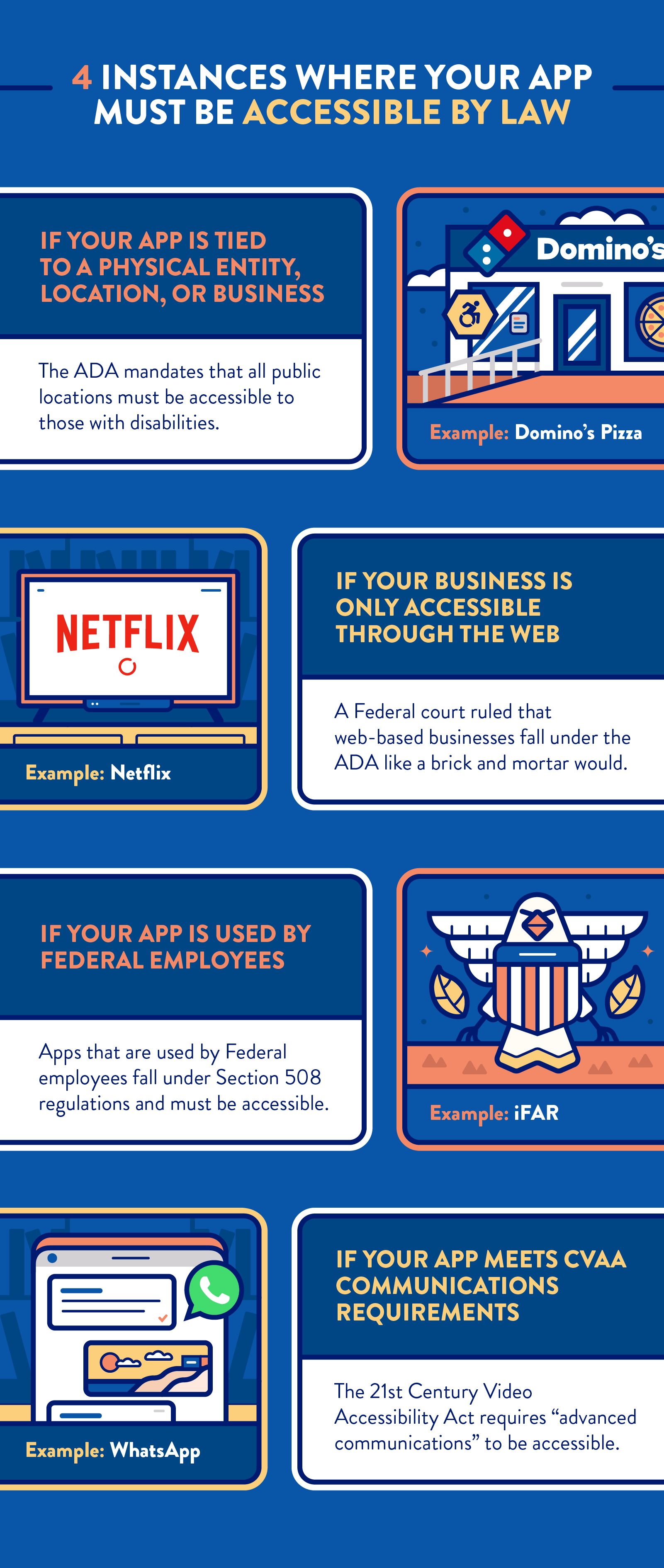
But even if your app isn’t legally required to be accessible according to any of these scenarios, it’s still in your best interest to always ensure that yours is.
Making your mobile app accessible significantly increases the size of your potential market. Plus, studies show that accessibility and good user experience are very closely related.7
To get a feel for the impact accessibility can have on your app’s success, consider the data below: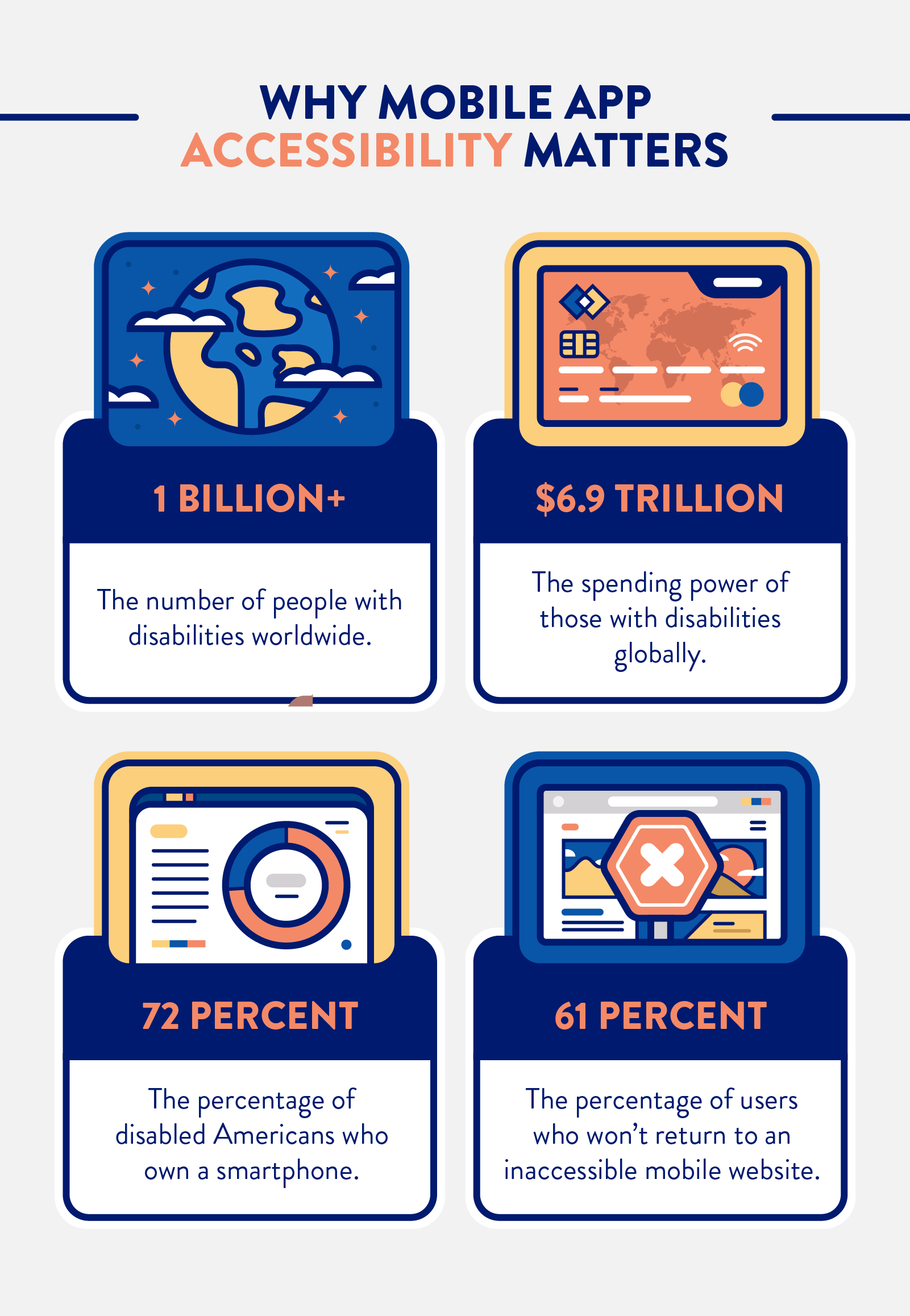
Even minor accessibility design features can have a major business impact — something as simple as adding captions to your videos can increase engagement by 532%.8
Here are other things to keep in mind to ensure your app is accessible.
Although disabilities are incredibly diverse, most fall into one of the following 4 categories. Designing with these in mind can accommodate a large percentage of people: 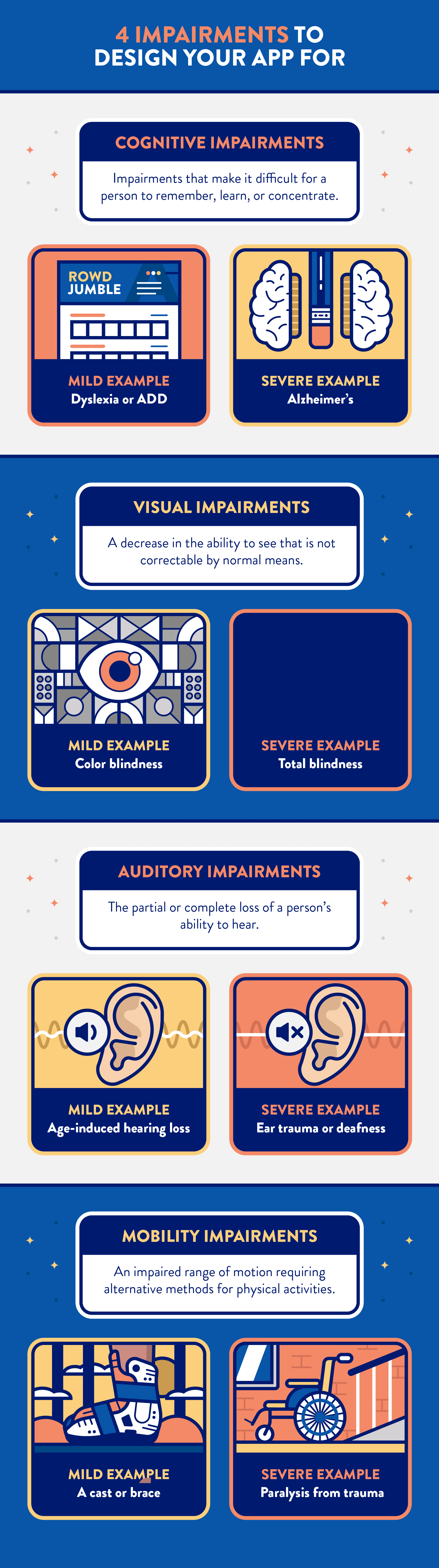
The good news is, many mobile devices are equipped with built-in accessibility tools that help those with the impairments above. So first and foremost, you’ll want to make sure that your app plays nicely with these.
If you’re unsure how to approach this, both Apple and Android have accessibility guidelines for developers.9,10
Additionally, although they are written for web pages, the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are an excellent resource for understanding how to best design your app to be accessible.
Here are some specific UX design tips from those guidelines:
Someone who is colorblind may not be able to tell the difference between plain text and a blue text hyperlink unless there is some other way to identify it.
Though they are the same color as the rest of the text, the underline clearly identifies which words are hyperlinks.
You’ll want to ensure that all of the content you produce is perceivable in more than just a single way like this, especially navigational elements.
Screen readers help those with visual impairments make sense of what is happening on their screen by reading your content aloud.
That’s why labeling inputs, buttons, and more are so important for accessibility — they make it easy for screen readers to turn important visual information into sound.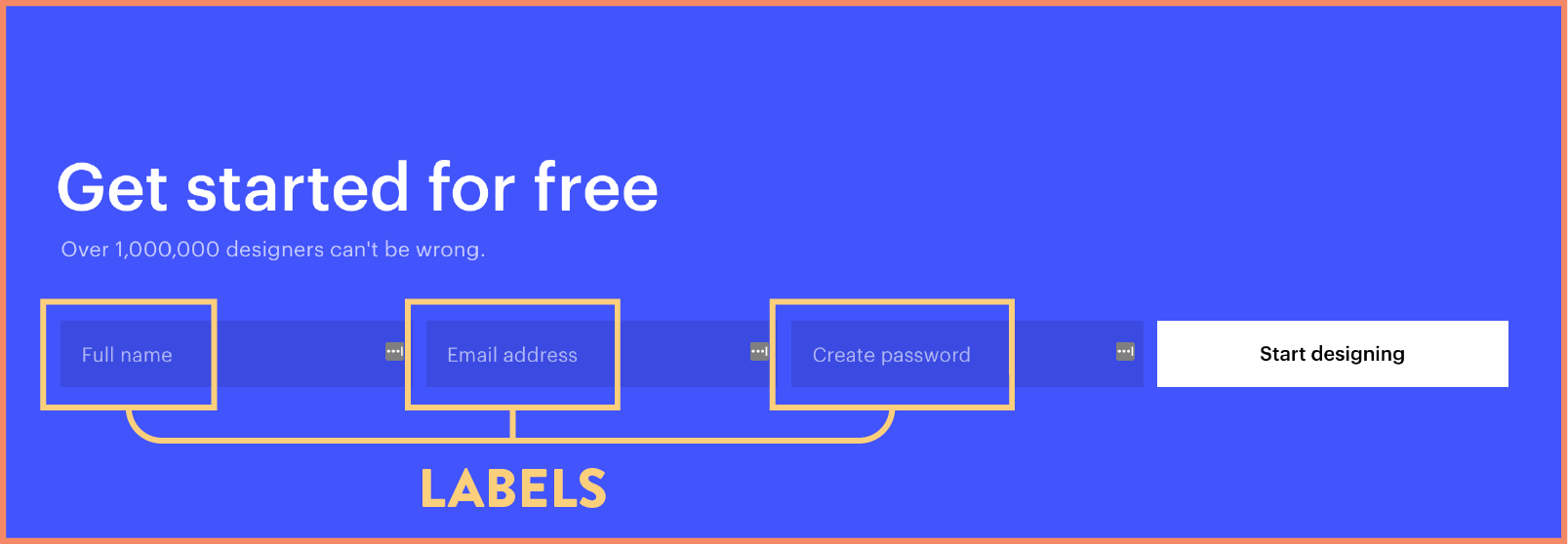
Labels can also be coded in such a way that they are hidden visually, but will be read aloud when your users are using a screen reader.11
Even if you don’t have a disability, navigating app screens that are constantly changing in layout or design can be difficult.
But for those with visual, cognitive, or even auditory disabilities, it provides an extra challenge since they have a harder time perceiving your content in the first place.
To ensure your app design is consistent, the WCAG 2.0 recommends the following:12
Color contrasts are important for making the content and elements within your app’s interface easily distinguishable and legible to those with visual impairments.
The WCAG 2.0 guidelines state that most images and text should have a color contrast minimum of 4.5:1 in order to be considered accessible, with the exception being those that are non-essential to the functionality of your app.13
Much like written content, audio-visual content should be optimized to be perceived in multiple ways as well. Especially given the rise of voice commands in mobile marketing.
Adding captions to all of your video content or including a transcription of audio content ensures that easy accessibility to those who may have a disability that otherwise would prevent them from interacting with a specific format.
Testing your app with real users is a key part of any app development process and accessibility design is no different.
Not sure how to conduct a usability test? We’ve created a guide to help. Whether to test for accessibility or to simply improve your user experience, learn more about conducting usability tests here.

Industry Benchmark Reports