Next Best Action (NBA) is about treating customers like individuals, not entries in a segment. It uses real-time customer data and machine learning to decide what action, message, or offer will be most helpful for a person right now. The goal is to build engagement and long-term value by aligning business goals with what the customer actually needs in the moment.
Traditional batch campaigns work on assumptions. They rely on static segments, fixed rules, and preset schedules, which often lead to awkward experiences, like pushing an upgrade to someone who already signed up.
NBA changes that by making decisions one customer at a time. It looks at each user’s current behavior and intent and chooses the best response, whether that’s a nudge, a recommendation, or simply staying quiet. Unlike product recommendation alone, next best action can also determine timing, channel, messaging, and even when the best choice is to take no action at all.
By adjusting as customers move through different customer lifecycle stages, the NBA strategy reduces message fatigue, improves retention, and drives stronger lifetime value. Platforms like CleverTap make this approach practical by embedding real-time decisioning and predictive insights directly into everyday marketing workflows, without requiring deep data science expertise.
What Is Next Best Action and Why Is It Effective
The next best action is a decision-making strategy. It analyzes a user’s current state by evaluating their past behavior, time zone, location, device used, and predicted needs, and then recommends the single most effective action for that individual at that moment.
In practice, NBA is most effective when it relies on consented first-party behavioral and preference signals, combined with clear frequency and relevance guardrails.

For example, the next best action analytics system might note that a customer just bought a yoga mat and immediately propose complementary gear, such as resistance bands. This makes it a timely, cross-sell recommendation based on real data. As a result, the marketing is far more relevant and engaging than sending generic blasts.
Key reasons why next best action marketing is an effective strategy include the following:
- True hyper- personalization: NBA aligns each message with individual intent. AI selects unique content or offers per user, rather than one-size-fits-all campaigns, leading to higher response rates, conversions, and ROI.
- Timeliness and context: NBA reacts to real-time signals like recent actions or lifecycle stages, delivering messages when users are most receptive.
- Right action, right moment across the lifecycle: Next Best Action evaluates real-time context and intent to guide every stage, from acquisition to nurture, retention, and cross-sell/upsell, ensuring each customer receives the most relevant, timely, and value-driven action at every interaction.
- Higher loyalty and LTV: By extending beyond sales offers to meaningful interactions, next best action marketing builds stronger relationships and increases customer lifetime value and retention rate.
- Efficiency and scalability: AI-driven decisioning automates action selection, optimizing resources and reducing effort in manual segmentation.
- Reduced fatigue: Need-based actions minimize irrelevant outreach, keeping engagement high and avoiding message overload.
How Next Best Action Works End to End
The next best action pipeline has been described below.
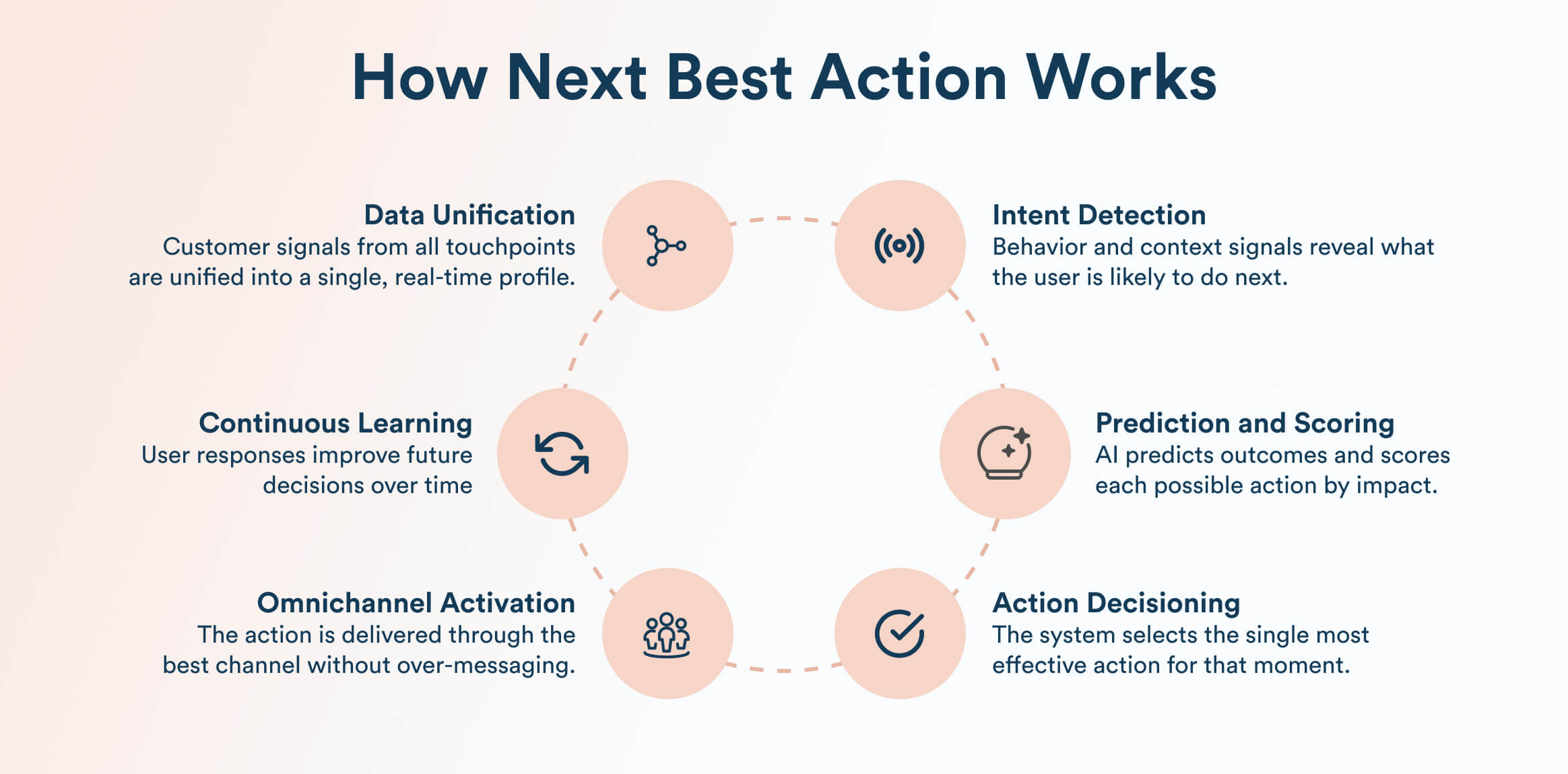
1. Data Collection and Unification
Next best action begins with collecting signals from every customer touchpoint. This includes actions like app clicks, page views, purchases, searches, form fills, and responses to past messages. Profile details such as preferences, location, device, and account status are added to this stream.
All of this data is then consolidated into a single, unified customer profile, creating a complete and up-to-date view of each user. This unified view ensures decisions are based on the full customer context, not isolated interactions.
2. Identifying Customer Intent and Context
Once data is unified, the system looks for signals that indicate intent. It considers the following
- Recency, or how recently the user engaged
- Frequency, or how often they interact
- Browsing behavior
- Transaction patterns
- Lifecycle stage
For example, repeated product views may signal purchase intent, while a long period of inactivity may indicate churn risk. By combining these signals, NBA understands what the customer is likely trying to do right now and what they might need next.
3. Prediction and Scoring Layer
In this stage, the system estimates how likely a user is to take certain actions. It predicts outcomes such as the likelihood to purchase, click a message, upgrade, disengage, or churn.
Each potential action, like sending an offer, a reminder, or educational content, is given a score based on expected impact. These scores help prioritize actions, ensuring decisions are driven by probability and relevance rather than assumptions or static rules.
4. Decisioning Engine: Selecting the Next Best Action
The decisioning engine evaluates all possible actions for a user at that moment. It combines predictive scores with business rules such as eligibility, frequency limits, compliance, or brand guidelines.
The engine may compare actions like sending a push notification now, triggering an email later, recommending a product, or taking no action at all. Using rules, machine learning, or a hybrid of both, it selects the single action most likely to achieve the desired outcome, whether that’s engagement, conversion, retention, or long-term value, while respecting user experience.
5. Activation Across Channels
After the best action is chosen, it is delivered through the most appropriate channel. This could be a push notification, in-app message, email, SMS, or an automated step in a larger journey.
NBA systems ensure channel coordination, so users don’t receive conflicting or repetitive messages. Each action fits seamlessly into the broader lifecycle flow, maintaining consistency across touchpoints and timing interactions when users are most receptive.
6. Continuous Optimization and Feedback Loop
Every customer response, in the form of clicks, conversions, ignores, or opt-outs, is fed back into the system. This real-world feedback helps refine predictions and decision logic over time.
As outcomes accumulate, the NBA engine learns which actions work best for different users and contexts, continuously improving accuracy. The result is a self-improving system that becomes smarter and more effective with every interaction.
Data Requirements for Effective Next Best Action
Next best action marketing thrives on rich, comprehensive customer data. This data must be fresh and unified in real time. NBA engines typically ingest streams of first-party data via analytics SDKs or event APIs and combine them into 360° customer profiles.
The types of data needed for reliable recommendations include:
- Behavioral events: Detailed activity streams, such as page views, clicks, searches, and feature use, capture what a user is doing on your site or app. This includes tracking every product a shopper views or every feature a user clicks.
- Transactional history: Past purchases, subscription changes, invoices, returns. These signal spending habits and value. For example, a big purchase or recurring spend pattern is invaluable context.
- Contextual signals: Device type, time of day, geolocation, referral source, weather, anything about when and where the user interacts. A late-night app open might yield a different offer than midday opens.
- User attributes and profiles: Demographics, loyalty tier, segment membership, or inferred preferences. For instance, knowing someone is a premium subscriber or a loyalty member changes what the next action will be.
Frameworks and Models Behind NBA
Next Best Action can be powered by several decisioning methods. Mentioned below are common NBA modeling approaches:
1. Rule-Based Models
Rule-based models use deterministic “if-then” rules or decision trees.
For example: If a user hasn’t logged in for 7 days and has items in the cart, then send a discount email.”
Such triggers are easy to implement and understand, and they ensure basic business policies are enforced. However, rule-based NBA cannot automatically adapt to new patterns or learn from outcomes; they are straightforward and miss out on the nuance.

Rule-based models are useful for initial pilots or compliance constraints, but on their own, they lack the personalization depth of ML approaches.
2. Propensity and Predictive Models
Propensity and predictive models use machine learning to predict outcomes like purchase, click, engagement, or churn likelihood.
These Models analyze historical data, such as demographics, behavior, and engagement, to estimate how likely a user is to take a specific action. NBA engines then compare these probabilities to choose an action.
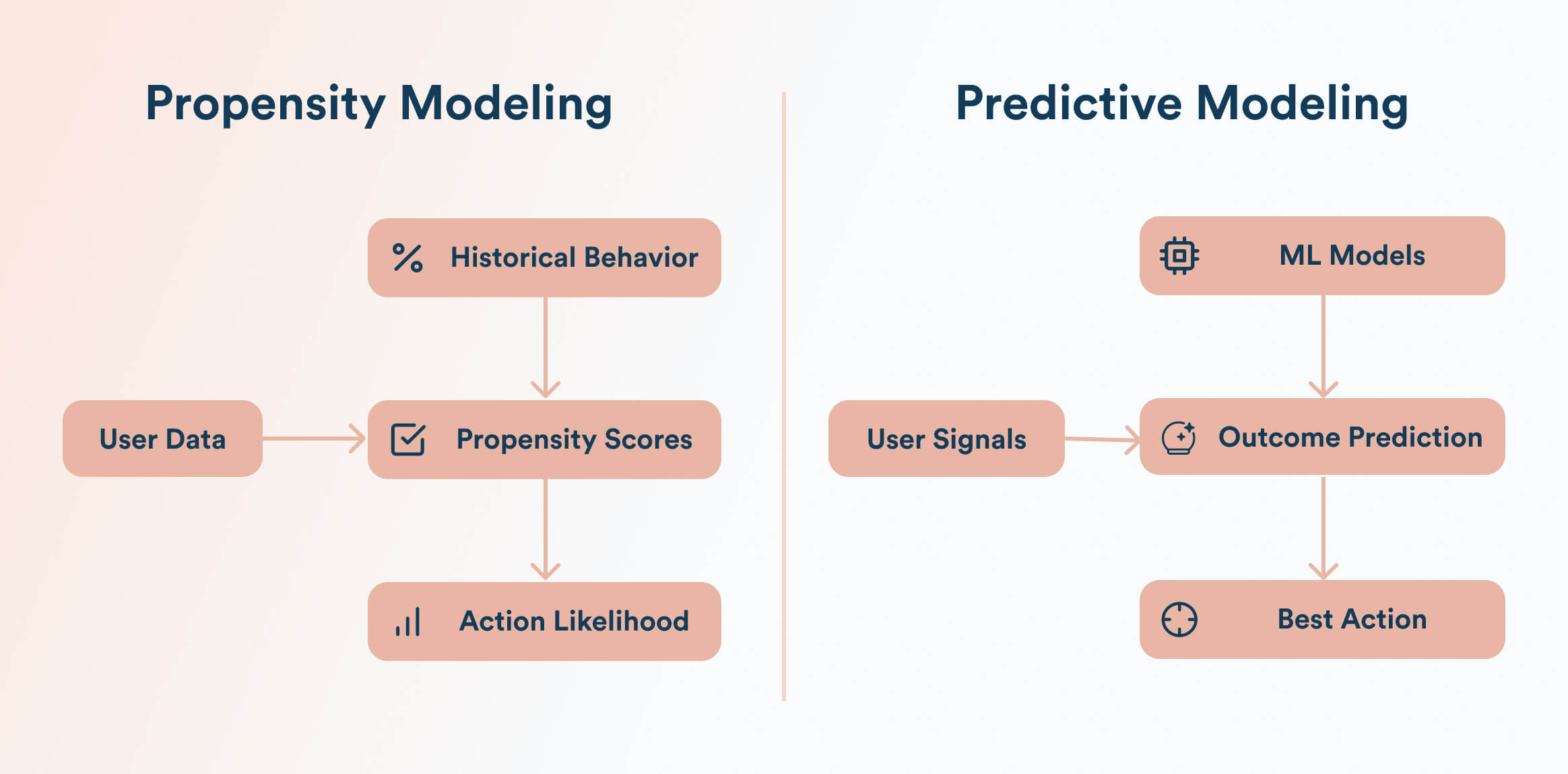
While effective for defined outcomes and small product sets, these models focus on past behavior and optimize individual actions, not overall strategy.
3. Recommendation Systems
Recommendation systems use recommender algorithms to power NBA, especially in media and retail with large catalogs.
Collaborative filtering predicts preferences based on similar users’ behavior, while content-based filtering recommends items with similar attributes to past choices.

- Example of collaborative filtering: If User A and B bought similar items, an NBA could cross-sell an item B liked to A.
- Example of content-based filtering: Recommending another thriller movie because the user liked similar plot or genre attributes.
These models score item relevance effectively but rely heavily on historical data and adapt slowly to new or unseen offerings without frequent retraining.
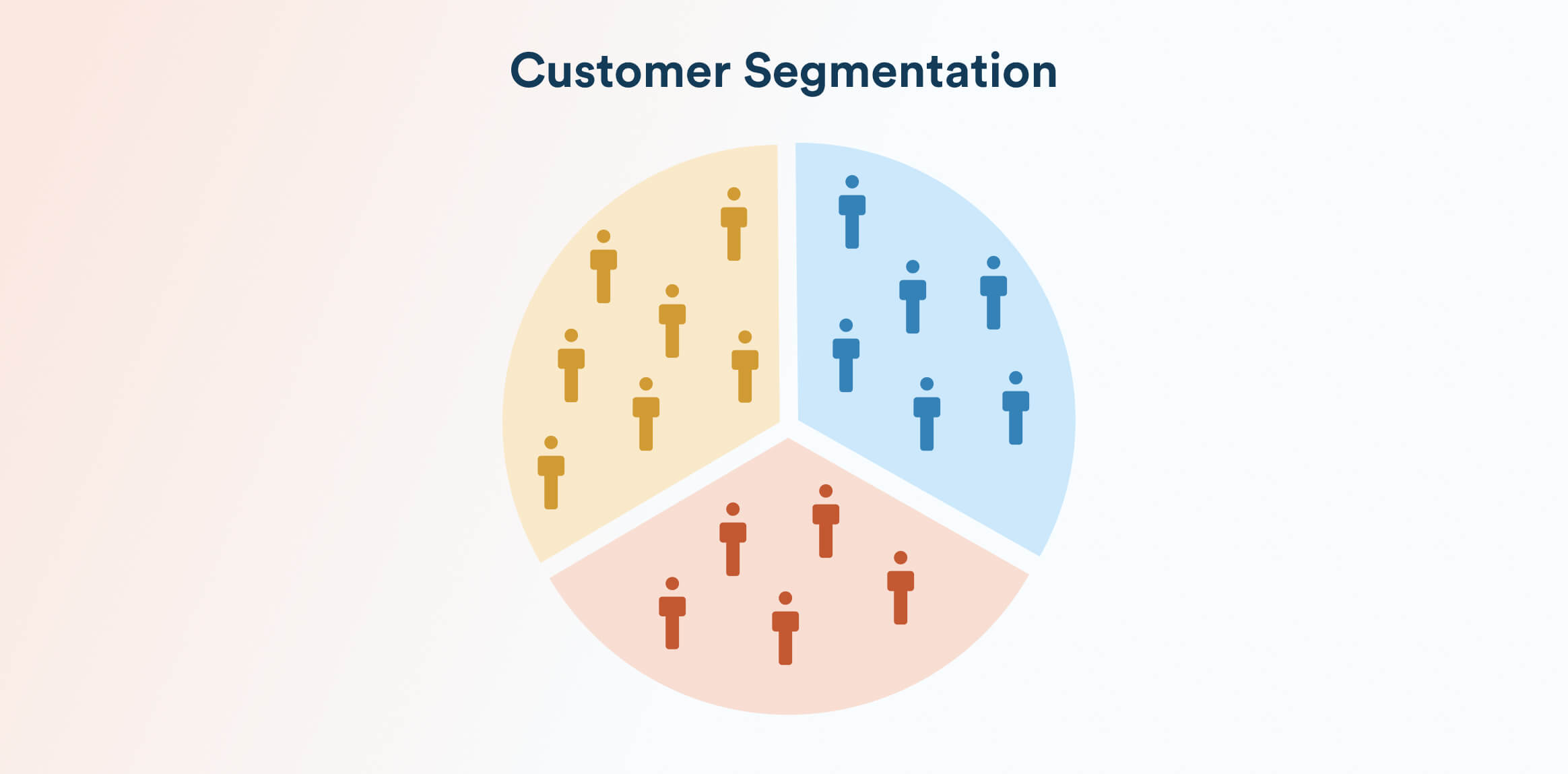
4. Segmentation and Clustering Models
Instead of modeling behavior at an individual level, this model groups customers into segments with shared characteristics using rules or clustering techniques like k-means or a recency, frequency, monetary (RFM) analysis.
NBA then applies group-level actions to each segment. For example, frequent high spenders may receive premium cross-sell recommendations, while inactive users get re-engagement incentives.
This method improves personalization over blanket campaigns, though it sacrifices some individual-level precision.
5. Reinforcement Learning (RL) Approaches
RL treats NBA as a continuous learning problem where the system improves decisions over time based on outcomes. Instead of relying only on past data, an RL agent tries different actions in real customer contexts and observes the results.
Each interaction generates feedback. Positive outcomes like a purchase, renewal, or engagement are treated as rewards, while poor outcomes reduce the likelihood of repeating that action. Over time, the model learns which actions maximize long-term value, such as lifetime value or retention, not just immediate conversions.

Example:
A streaming platform may test recommending premium content to different users. If such an offering increases long-term subscriptions for a segment, RL reinforces that choice.
Unlike static models, RL can keep experimenting, adapt to changing behavior, and uncover high-performing actions that weren’t historically promoted. But it requires a lot of data and careful reward modeling, which means defining what a “good outcome” really is.
The table explores how these frameworks differ in complexity and usage:
| Approach | How it works | Pros/Cons |
| Rule-Based | Static if-then triggers (e.g., “if X then do Y”) | Simple, transparent, but not adaptive or personalized |
| Predictive Models | ML models score conversion or churn propensity for specific outcomes | Data-driven, improves targeting for known outcomes, but doesn’t explore new options |
| Recommenders | Collaborative or content-based filters suggest items that users would like | Good for large catalogs, leverages peer patterns; may lag in novel situations |
| Segmentation | Group customers (e.g., RFM, clusters) and tailor offers per group | Balances scale and personalization; limited by segment granularity |
| Reinforcement Learning (RL) | The agent tries actions, learns over time to maximize long-term value | Dynamically adapts and explores new strategies; complex and data-hungry to implement |
Many NBA solutions use a hybrid approach. They use rules to filter or guardrail actions, predictive models to score them, and even RL or experimentation layers to fine-tune strategies. Marketers should understand these models conceptually so they can trust and guide the NBA engine.
Real World Next Best Action Marketing Examples and Use Cases
Next best action marketing is already widely used by consumer-first brands across industries. What separates leaders is how intelligently actions are chosen based on intent, timing, and predicted value.
Below are concrete next best action marketing examples from real brands, mapped clearly to triggers and outcomes.
1. Fintech
Fintech brands use NBA to move beyond reactive alerts into intent-driven financial nudges, such as rewards, card upgrade opportunities, and fraud alerts based on behavioral intent.
Example: American Express uses real-time, first-party transactional data to tailor offers to individual cardholders based on how and where they spend, rather than relying on generic promotions.
Its Amex Offers program generates personalized, card-linked deals that reflect each user’s unique transaction patterns, helping deliver the right offer at the right time and driving engagement and spending.
In one year, internal data from American Express showed 341 million U.S. offer enrollments and $9.8 billion in merchant spend, with over half of redeemers being Gen Z or millennial cardmembers, demonstrating the effectiveness of contextual, intent-based marketing.

2. E-commerce
E-commerce is one of the most mature environments for next best action marketing because of its rich, real-time behavioral data.
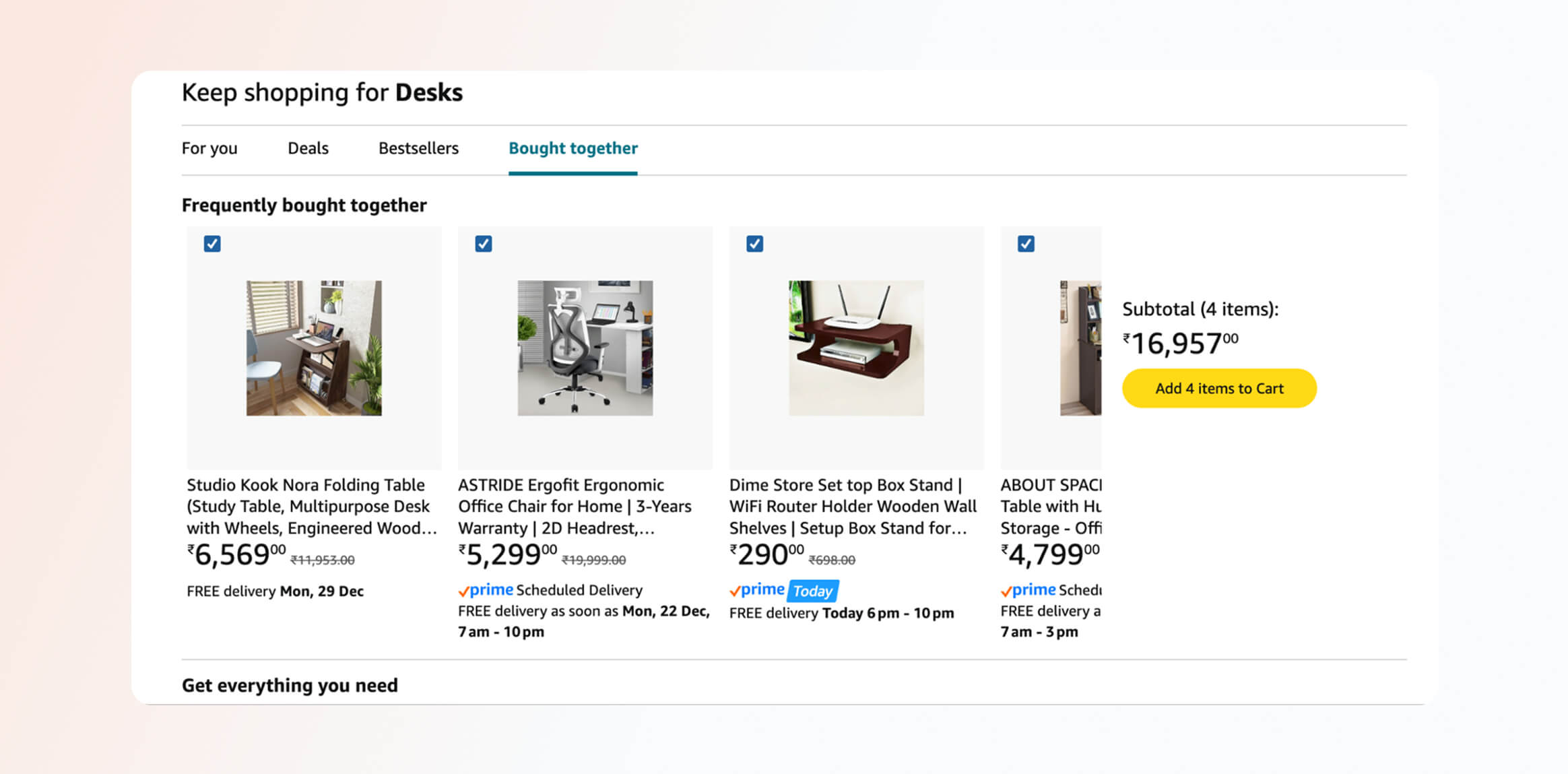
Example: Amazon is a canonical NBA example, using signals like product views, searches, and past purchases to power features such as Frequently Bought Together and Customers Who Viewed This Also Bought. These are real-time NBAs driven by collaborative filtering and purchase propensity models.
Amazon also applies NBA logic to category affinity triggers and cart recovery, dynamically surfacing relevant products, bundles, or reminders based on each shopper’s intent rather than generic promotions.
3. Media and Entertainment
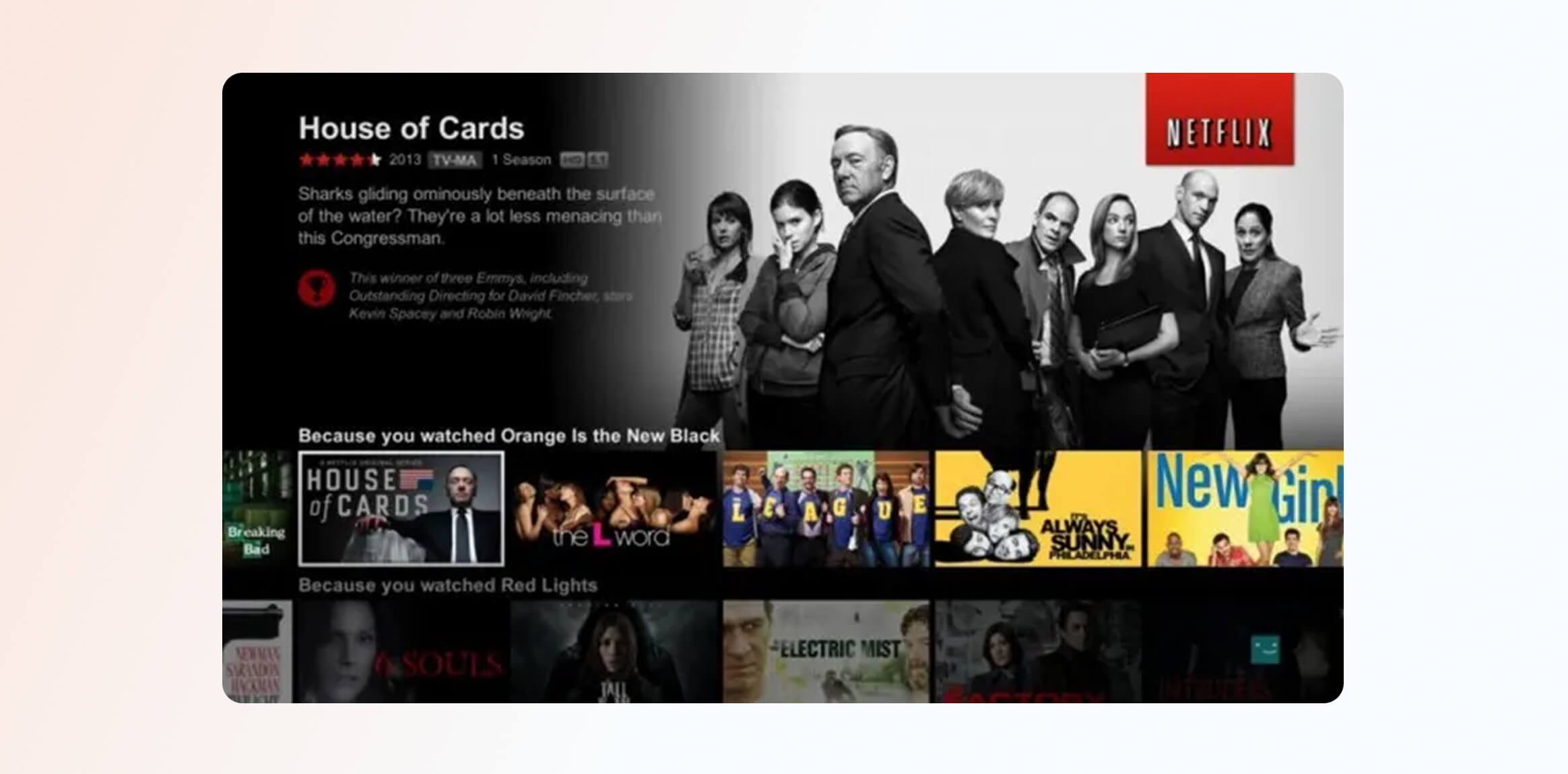
Media platforms rely heavily on next best action marketing to prevent churn and maximize engagement time. They use NBA models for content continuation suggestions, genre affinity recommendations, and watchlist nudges.
Example: Netflix continuously recalculates the next best content recommendation based on viewing history, completion rates, and time of day. After a series ends, it may recommend a similar title, spin-off, or shorter show for late-night viewers. By optimizing for intent over popularity, Netflix boosts watch time, reduces decision fatigue, and lowers churn.
4. Travel
Travel brands use next best action predictive models to capture high-intent but incomplete journeys. They perform search intent tracking to deliver flight price alerts and re-engagement prompts for unfinished journeys.
Example: Booking.com uses next best action to re-engage high-intent travelers who haven’t booked yet. By analyzing searches, filters, repeat hotel views, travel dates, and price sensitivity, it personalizes the next step. For repeat views, NBA can trigger a timely re-engagement prompt, such as a price drop alert, a reminder to complete booking, or availability messaging that reflects the user’s search intent.

5. Food Delivery
Food delivery platforms excel at predicting when and what users will order. Such platforms use next best action marketing for cuisine preference-based recommendations, timely meal time reminders, and reorder predictions.
Example: Swiggy applies next best action marketing by combining past orders, browsing behavior, location, and time-of-day signals to predict hunger moments and cuisine preferences. It may suggest quick meals during work hours or comfort foods on weekends, while also factoring in weather, delivery speed, and restaurant availability to increase conversion and repeat orders.
Next Best Action vs Traditional Campaign Marketing
Traditional campaign marketing follows a batch-based, one-to-many approach, while next best action marketing enables real-time, one-to-one engagement. The contrast becomes clear across four key dimensions:
| Dimension | Traditional Campaign Marketing | Next Best Action (NBA) |
| Personalization depth | Uses broad segments based on demographics or past behavior; everyone in a segment receives the same message | Treats each customer individually, using real-time context, behavior, and predictive insights |
| Timing | Scheduled around fixed calendars (newsletters, festivals, promotions) | Event-driven and continuous, responding instantly to user actions |
| Real-time adaptation | Static once launched, changes require manual intervention | Dynamically adapts in near real time based on live signals |
| Automation & efficiency | Pushes messages even to low-intent users, causing message fatigue | Suppresses irrelevant outreach and can choose “no action” when appropriate |
Why NBA Is More Effective as Compared to Traditional Campaign Marketing?
- Context-aware engagement: NBA reacts to what the customer is doing right now, not what was planned weeks ago.
- Reduced wastage: Instead of blasting offers, NBA targets only users who need a nudge, improving ROI.
- Cross-channel orchestration: NBA automatically selects the most effective channel, be it email, push, in-app, or sales follow-up, based on user response.
- Continuous learning: Unlike static campaigns, NBA models learn from every interaction and improve over time.
Implementation Challenges and How to Avoid Them
While next best action marketing delivers powerful personalization, its success depends on how well it is implemented. Below are common challenges and practical ways to address them:
- Poor data quality and integration: NBA relies on accurate, unified, and real-time data. Fragmented systems or stale records lead to weak recommendations. Invest in a strong data foundation or CDP that consolidates customer data across touchpoints. Clean existing data, resolve duplicate identities, and ensure reliable real-time pipelines before deploying NBA.
- Model opacity: Advanced ML models can feel like black boxes, making it hard for marketers to trust or explain decisions. Use hybrid decisioning by combining AI models with clear business rules and guardrails. Provide dashboards that show why an action was chosen and start with interpretable models for critical journeys.
- Rule explosion: Over-reliance on manual rules can create complex, unmanageable systems. Restrict hard-coded rules to essentials like compliance and frequency caps, and let AI handle personalization. Regularly review and simplify rules as models improve.
- Slow decisioning and scalability: NBA requires low-latency responses to remain relevant. Design for speed using stream processing, in-memory data stores, and performance testing under peak loads.
- Siloed channels: Disconnected tools prevent consistent cross-channel experiences. Use integrated platforms or strong APIs that connect analytics with engagement channels.
Next Best Action in Lifecycle Marketing
Next best action marketing delivers the greatest impact when applied across the entire customer lifecycle, ensuring every interaction is guided by predicted intent rather than static journeys or generic campaigns.
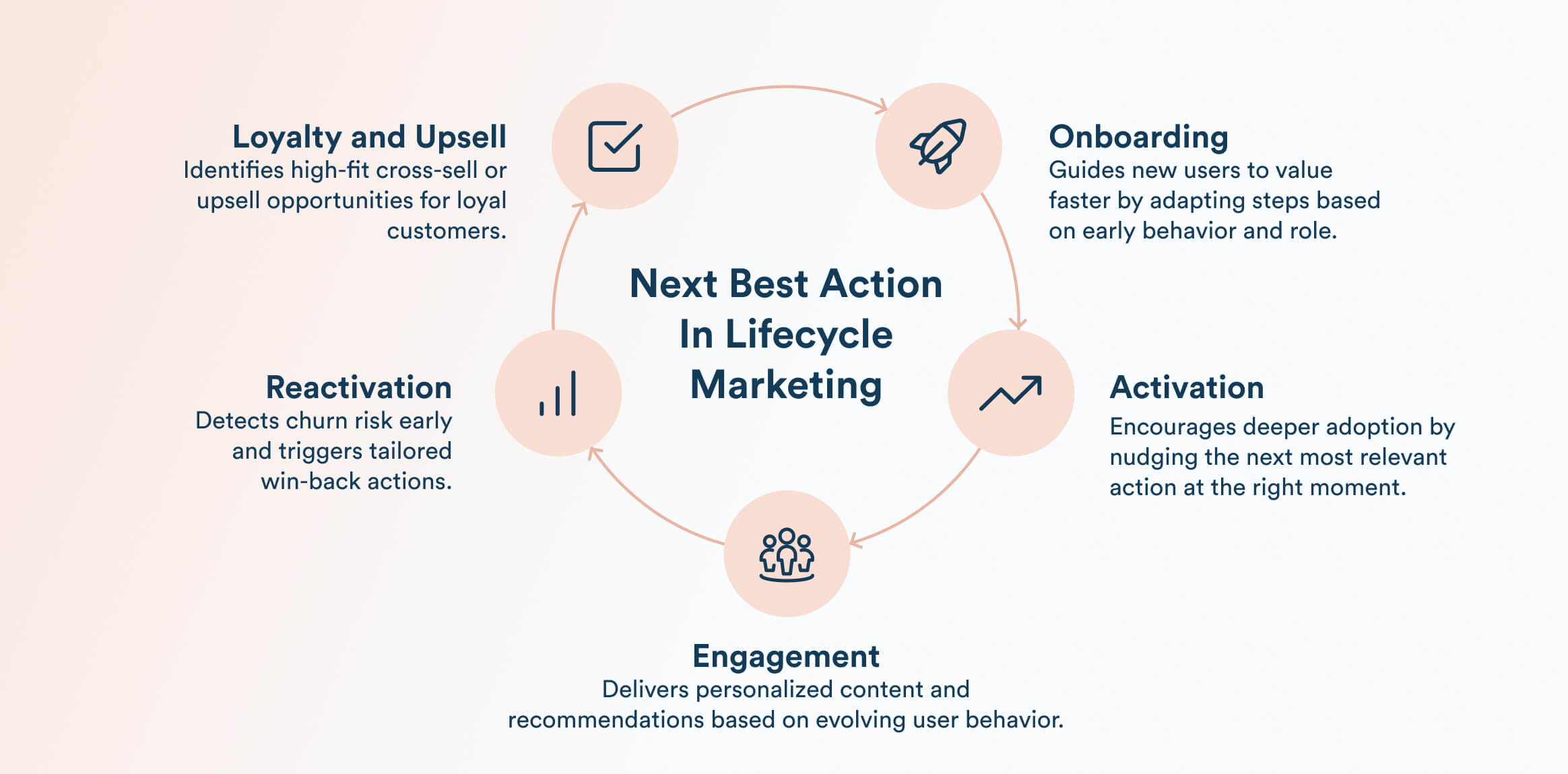
- Onboarding: During sign-up and early usage, NBA helps users reach value faster by guiding them step by step. If a new SaaS user completes basic setup but stalls before exploring key features, NBA may trigger an in-app walk-through or a contextual email tailored to their role. This adaptive guidance removes friction and increases the likelihood of early success.
- Activation: As users begin engaging, NBA encourages deeper adoption. After completing an initial tutorial, the system may recommend the next best task to sustain momentum. If activation signals are incomplete, such as a fintech user who hasn’t finished profile verification, NBA can deliver a timely nudge that removes blockers and drives progression.
- Engagement: During the growth phase, NBA adapts to evolving preferences. Media platforms recommend content based on recent behavior, while e-commerce brands trigger usage-based reminders or product suggestions. Because actions are triggered at moments of high intent, engagement feels relevant rather than disruptive.
- Reactivation: When engagement drops, NBA models detect early churn signals and initiate tailored win-back actions. A food subscription brand may offer a personalized recipe bundle or a limited-time incentive after repeated inactivity to encourage re-engagement.
- Loyalty and upsell: For loyal customers, next best action identifies high-fit upsell or cross-sell opportunities. A bank may suggest exclusive travel perks to premium users, ensuring rewards feel earned and relevant.
CleverTap for Intelligent Next Best Action Delivery
CleverTap helps brands operationalize next best action marketing by combining real-time customer data, predictive intelligence, and omnichannel execution in a single platform. Instead of relying on static segments or one-size-fits-all journeys, marketers can continuously decide what each customer needs next based on live behavior, lifecycle context, and expected outcomes.
Real-time customer context that powers NBA decisions
Next best action depends on knowing what the customer is doing right now. CleverTap captures behavioral events across mobile and web and builds continuously updated user profiles, ensuring that every action is triggered from current intent rather than outdated assumptions.
Predictive intelligence to prioritize the right intervention
CleverTap includes built-in prediction capabilities that help teams identify users likely to churn, convert, disengage, or upgrade. These predictive scores make it easier to determine which customers need attention next and what type of message or offer is most likely to drive impact.
CleverTap’s Clever.AI layer enhances this decisioning by surfacing insights faster, such as highlighting where engagement drops across the lifecycle or identifying high-risk segments before revenue opportunities are lost.
Journey orchestration that adapts in real time
With CleverTap Journeys, marketers can automate next best actions across onboarding, retention, and loyalty flows. Journeys respond instantly to customer behavior and branch dynamically based on outcomes, making NBA execution continuous rather than campaign-based.
For example, instead of sending the same follow-up to every user, journeys can adjust based on whether a customer engaged, ignored, or converted, ensuring the next step stays relevant.
Omnichannel delivery with timing and channel optimization
CleverTap activates next best actions across push, in-app messaging, email, SMS, and WhatsApp while coordinating outreach across channels. NBA strategies become stronger when the platform can determine not only what action to take, but also when and where it should be delivered.
Clever.AI supports this through optimization agents such as send-time and channel optimization, helping ensure messages land at the moment and touchpoint most likely to perform.
Personalization that scales beyond static segmentation
NBA requires personalization at the individual level, not broad cohort messaging. CleverTap supports dynamic behavioral segmentation, RFM modeling, and recommendation capabilities that update automatically as user intent changes. This enables marketers to keep actions aligned with real lifecycle movement rather than fixed campaign rules.
Continuous improvement through measurement and learning
CleverTap provides journey analytics, experimentation, and performance reporting so marketers can measure which actions drive retention, engagement, or long-term value. Over time, NBA strategies improve because decisions are tied directly to outcomes, not guesswork.
Make every customer interaction the right next step with CleverTap.
Turn Every Customer Moment Into the Right Action
Next best action works best when it is embedded directly into lifecycle marketing execution. CleverTap makes NBA practical by unifying real-time profiles, predictive intelligence, adaptive journeys, and cross-channel activation in one platform, with Clever.AI enhancing decision-making where automation and insight acceleration add the most value.
Ready to move beyond static campaigns? See how CleverTap helps brands deliver the next right action at scale.
Kiran Pius 
Leads Product Launches, Adoption, & Evangelism.Expert in cross-channel marketing strategies & platforms.
Free Customer Engagement Guides
Join our newsletter for actionable tips and proven strategies to grow your business and engage your customers.