Is your mobile app secure?
It shouldn’t come as a surprise that mobile apps are targeted by hackers, given the rapid adoption and increased usage globally. By some estimates, one out of every 36 mobile devices has high-risk apps installed.1
An even more sobering mobile app security statistic for businesses to hear: 71% of fraud transactions came from mobile apps and mobile browsers in the second quarter of 2018 compared to 29% on the web, up 16% year over year.
Although the number of mobile app attacks will all but certainly increase, integrating mobile app security into your strategy is essential to protecting your users and the trust you’ve established.
Learn more about the threats facing mobile app security today or jump to our infographic below for tips on how to protect your product.
Mobile App Security Threats: 5 Examples

Cybercriminals are not lacking in creativity, they’re hacking in it (sorry, that will be the first and last pun).
From accessing the microphone, camera, and location of a user’s device, to building convincing app clones — there are many strategies hackers employ to gain access to, and exploit, personal information of unsuspecting mobile app users.
Below are some common mobile app security threats you should be aware of. It’s important to note this list is by no means exhaustive, but simply a drop in the bucket.
1. Lack of Multifactor Authentication
Most of us are guilty of using the same insecure password across multiple accounts. Now think about how many users you have. Even if a user’s password was compromised through a breach at a different company, hackers often test passwords on other apps, which can lead to an attack on your company.
Multifactor authentication, often using two of the three possible factors of authentication, does not rely solely on the user’s password before certifying the user’s identity. This additional layer of authentication can be the answer to a personal question, an SMS confirmation code to input, or biometric authentication (fingerprint, retina, etc.).
2. Failure to Encrypt Properly
Encryption is the process of transposing data into an indecipherable code that is ideally only viewable after it has been translated back using the secret key. In other words, encryption changes the sequence of a combination lock, but be careful, hackers are gifted at picking locks.
According to Symantec, 13.4% of consumer devices and 10.5% of enterprise devices do not have encryption enabled. This means that if hackers gain access to those devices, personal data will be available in plain text.
Unfortunately, the software companies that do use encryption are not immune to an honest mistake. Developers are human and make mistakes that hackers can exploit. When it comes to encryption, it’s important to assess how easy it could be to crack your app’s code.
This common security vulnerability can have severe consequences including intellectual property theft, code theft, privacy violations, and reputational damage, just to name a few.
3. Reverse Engineering
The nature of programming exposes many apps to the very real threat of reverse engineering.
The healthy amount of metadata provided in code meant for debugging also helps an attacker understand how an app functions.
Reverse engineering can be used to reveal how the app functions on the back-end, expose encryption algorithms, modify the source code, and more. Your own code can be used against you and pave the way for hackers.
4. Malicious Code Injection Exposure
User-generated content, like forms and comments, can often be overlooked for their potential threat to mobile app security.
Let’s use the login form as an example. When a user inputs their username and password, the application communicates with server-side data to authenticate. Apps that do not limit what characters a user can successfully input run the risk of hackers injecting code to access the server.
If a malicious user inputs a line of JavaScript into a login form that does not guard against characters like the equal sign or colon (common in JavaScript), they can easily access private information.2
5. Data Storage
Insecure data storage can happen in many places within your app: SQL databases, cookie stores, binary data stores, and more. These can be caused by vulnerabilities in the OS, frameworks, compiler, or new and jailbroken devices.
If a hacker gains access to a device or database, they can modify the legitimate app to funnel information to their machines.
Even sophisticated encryption protections are rendered useless when a device is jailbroken or rooted, which allows hackers to bypass operating system restrictions and circumvent encryption.3
Many times, insecure data storage is caused by a lack of processes to handle cache of data, images, and key presses.
Mobile App Security Exploit Examples: Painful Real-life Lessons
The climate around mobile app security is heating up.
Mobile app vulnerabilities are exploited every day, resulting in expensive data breaches and loss of public trust.
In this section, we will try to learn from the failures of other companies and highlight how real the threats outlined above can be.
Timehop Fails To Trust Two-Factor Authentication
Starting in December of 2017, TimeHop was the victim of an attack that was not uncovered until July 4, 2018. Because TimeHop failed to use multifactor authentication, an employee’s credentials were used to log in to their cloud computing environment from an IP address in the Netherlands.4
The unauthorized user began conducting reconnaissance research into available information and continued to check back in over the ensuing seven month period. Finally, on June 22, 2018, the hacker discovered personally identifiable information on a database.
Internal alerts on July 4 signaled a dramatic spike in database read requests and users reported black screens as their apps crashed.
This mobile security threat resulted in the privacy breach of 21 million users. This might not have occurred if a multifactor authentication process had been in place to deny the hacker’s login credentials.
Fortnite Fakes From Reverse Engineering
When Fortnite launched their beta in August 2018, the invitation-only environment brought a surge in fraudulent links to download fake app clones with malicious intent.
These fake Fortnite apps were reverse engineered to look very convincing. They included the same loading screens, images, and music as the real app.
This genre of malware, known as FakeApp, was used to generate ad revenue, redirect to other apps, send SMS messages, and even download hidden apps.
The second half of 2018 saw a rapid increase in FakeApp detections of this sort, peaking in December with nearly 65,000 FakeApp detections.5
Mobile App Security Best Practices: How to Safeguard Your Mobile
Unfortunately, mobile app security is a problem that we continue to face.
The tools used to develop the top tier mobile apps, by their very nature, are the same tools used to exploit their vulnerabilities.
Despite the constant struggle to keep hackers at bay, there are some common threads of security best practices that protect some of the largest mobile companies around the globe.
1. Use Server-Side Authentication
Ideally, multifactor authentication requests are granted on the server side and only available once authorization is successful. If your app requires data to be stored on the client side and available on the device, ensure the encrypted data can only be accessed once the credentials are successfully validated.
If you use persistent authentication – or a “remember me” functionality – be mindful not to store password data on the device and create different authentication tokens for different devices.
2. Use Cryptographic Algorithms and Key Management Best Practices
One strategy to fend off encryption-related breaches is to avoid storing sensitive information on a mobile device. This includes hard-coded keys and passwords that could be made available in plain text or used by an attacker to gain access to the server.
iOS has protection in place to, in theory, stop reverse engineering through code encryption. It’s worth noting however that this is not a perfect solution and you should always assume attackers can decrypt information on the client side.
The most powerful encryption algorithm in the world will not prevent an attack if poor key management strategies are implemented. If your app is not protected against binary attacks, for example, keys could be intercepted when authentication responses are traveling from the server.
Never use algorithms that have been deprecated, or disapproved by the security community, and, unless you are an expert in security, do not try to create your own encryption protocols.6
3. Validate That All User Inputs Meet Sanity Check Standards
Hackers are opportunistic when testing your input validation. They scour your site for any potential for the acceptance of malformed data.
Input validation is a strategy to ensure only data that is expected can be passed through an input field. When uploading an image, for example, the file should have an extension that matches standard image file extensions and should be reasonably sized.
If your image input validation does not have parameters prohibiting unreasonable pixel counts or file sizes, a hacker could upload a malicious file claiming to be an image.
All input fields including form fields, audio, video, and command line inputs, among others, are susceptible to this vulnerability. This exploit was responsible for the first jailbroken iPhone.7
4. Build Threat Models To Defend Data
Threat modeling is a method used to deeply understand the problem that is being solved, where issues may exist, and strategies to defend against them.
A well-informed threat model insists the team understand how different operating systems, platforms, frameworks, and external APIs transfer and store their data. Building on top of frameworks and connecting with third-party APIs can expose you to their inefficiencies as well.8
5. Obfuscate To Prevent Reverse Engineering
You may be asking how can you possibly prevent reverse engineering?
In many cases, developers have the necessary skills and tools to build convincing replicas of a mobile app’s UI without gaining access to the source code. Proprietary business logic, on the other hand, requires much more thought and effort.
Commercial-grade obfuscation tools are available to make the business logic less readable and difficult to understand.
Developers use indentation to make their code more readable to humans, although the computer does not care about proper formatting. This is why minification, which removes all spaces, maintains functionality but makes it more difficult for hackers to understand the code.
Mobile App Security Testing and More
We’ve covered some of the most common mobile app security threats and best practices to defend against them, but this is by no means a complete list.
We didn’t even cover penetration testing, similar to ethical hacking, in which you attempt to find a vulnerability to exploit as a hacker would. While it’s best to start thinking about security from the beginning, it will likely be a concern throughout the life of your company.
Building a secure mobile app requires collaboration between developers, security experts, marketers, and C-level executives. Security protocols for individual password strength and the proper use of analytics tracking pixels, for example, are strategies that require buy-in from the whole team.
Another consideration for your mobile app security efforts is compliance. With the unraveling of GDPR and others to follow, it’s important to have a firm understanding of how your mobile app security is handled.
For more information about mobile app regulation and intelligent mobile marketing, check out our white papers, webinars, and case studies. 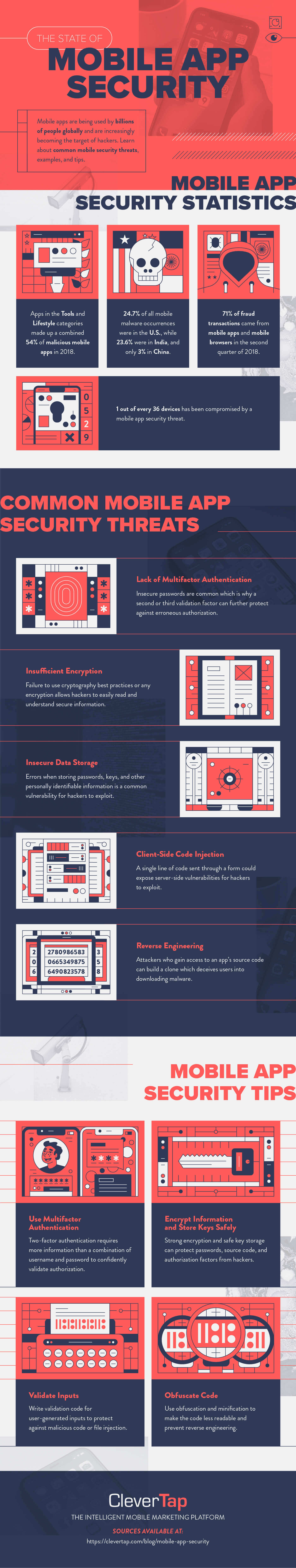

See how today’s top brands use CleverTap to drive long-term growth and retention
Subharun Mukherjee 
Heads Cross-Functional Marketing.Expert in SaaS Product Marketing, CX & GTM strategies.
Free Customer Engagement Guides
Join our newsletter for actionable tips and proven strategies to grow your business and engage your customers.