AI agents, sometimes called intelligent agents, are autonomous software systems that perceive customer data, plan actions, and execute tasks with minimal human intervention. Analysts project the AI agents market will reach $7.6 billion by 2025 and $47 billion by 2030. In fact, ~85% of enterprises plan to deploy AI agents by 2025. Nearly 88% of marketers now use AI tools daily.
This shift toward agentic AI is driven by marketers’ desire for end-to-end automation. Instead of separate tools for each step, intelligent agents handle complete workflows. For example, an agent can draft an email, select the target audience, and schedule delivery automatically. This means campaigns can launch faster and adapt in real time without manual handoffs.
In this blog, we’ll briefly touch upon what AI agents are, and then discuss 40+ AI agent examples and use cases across different industries and job functions.
What Is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a software program that can perceive data, reason, and act to achieve a goal. Simple AI systems follow fixed rules, for example, an autoresponder that sends a preset reply when it sees a keyword.

In contrast, agentic AI uses machine learning and large language models to understand context and plan multi-step strategies. They autonomously adapt their actions and learn from outcomes, requiring minimal human oversight. This makes them suitable for complex tasks, such as optimizing marketing campaigns end-to-end.
Brief Overview of AI Agent Architecture & Technology
AI agents typically follow a sensing → reasoning → acting cycle. They gather inputs (user behaviors, CRM events, analytics), analyze them, and then execute actions via APIs or integrated tools.
Modern agents combine LLMs with external tools: for example, an agent might use a language model to draft an email and then call a marketing API to send it. They also incorporate memory via vector databases: past interactions are stored and retrieved as needed (a technique known as retrieval-augmented generation). Open-source frameworks offer pre-built memory modules and API integrations to simplify the development of these multi-step AI agents.
Learn how CleverAI Agents are rewriting the customer engagement playbook.
40+ Real-World AI Agent Examples & Use Cases
Let’s explore real-world AI agent examples across industries and see how this evolving technology can be tailored to meet specific business needs.
Marketing & Customer Engagement AI Agent Examples
Below are some AI agent examples for marketing and customer engagement roles:
1. CleverTap’s Agentic AI Engine: CleverAI™ by CleverTap is an agentic AI decisioning engine that drives personalized, data-led customer engagement. It uses autonomous intelligent agents to plan, predict, create, and execute individualized campaigns across channels. The decisioning engine continuously analyzes user behavior and context to select the best action or offer for each customer in real time.
Built on the CleverAI Dataverse and TesseractDB, it ensures scalability, transparency, and human-in-the-loop control within brand guardrails.
Clever AI for marketers includes:
- Strategy Agents to help define the optimal multi-step journey to achieve a goal.
- Decision Agents to match each user with the right message or offer
- Creative Agents to generate personalized content for a prospect or customer.
- Action Agents to orchestrate the delivery across channels in real time.
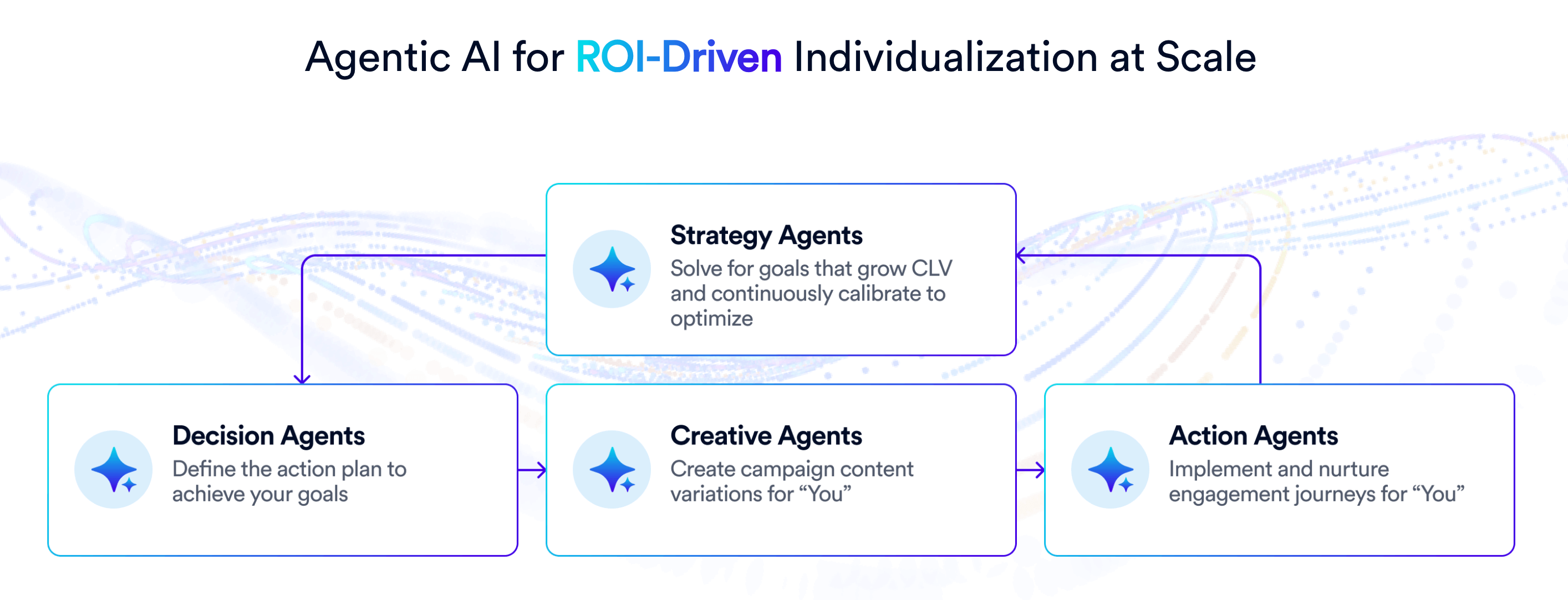
An Example of a Cross-Sell Workflow With Clever AI
Suppose a user just purchased a pair of running shoes through your app.
A strategy agent defines the goal of increasing the user’s average order value by promoting complementary products. It triggers a decision agent once the purchase event occurs. The decision agent analyzes the user’s behavior—past purchases, browsing history, and preferences—to predict which product the user is most likely to buy next (e.g., running socks or a fitness tracker).
The creative agent then crafts a personalized message like, “Complete your running kit, Alex! Grab these moisture-wicking socks at 15% off.” The action agent delivers it via the user’s preferred channel—perhaps a push notification within an hour of purchase.
If Alex engages, the system reinforces this approach; if not, it learns and may later attempt an email reminder with a different offer. The workflow runs autonomously, continuously optimizing for higher conversion and customer lifetime value.
Discover how CleverAI™, our agentic AI decisioning engine, empowers marketers to automate, personalize, and optimize customer journeys in real time.
2. Conversational Lead Qualification Agents: Conversational AI agents on websites or chat platforms autonomously qualify inbound leads. These autonomous SDR agents engage visitors 24/7, ask qualifying questions, and schedule demos with sales reps.
Integrated with CRM systems, they log lead details automatically and ensure instant responses, eliminating missed opportunities and accelerating the buyer journey.
3. Campaign Optimization Agents: Campaign optimization agents continuously monitor marketing campaigns and autonomously adjust tactics to boost performance. They perceive live data (click-throughs, conversions, engagement), reason about what’s working, and act by reallocating budgets or rewriting underperforming creatives.
For example, if an ad struggles in one region, the agent shifts spend to a higher-performing audience and deploys a new variation instantly.
4. Lifecycle Journey Orchestration Agents: These examples of AI agents autonomously design and manage entire customer journeys. They perceive actions like sign-ups, purchases, or inactivity, reason about lifecycle stages, and act by sending the right message through the most effective channel.
If a customer becomes dormant, the agent triggers re-engagement flows; if they convert, it shifts focus to retention. Unlike traditional workflows, these agentic AI examples evolve in real time based on each user’s behavior.

5. Dynamic Pricing & Promotion Agents: Dynamic pricing agents perceive inventory, competitor pricing, and demand signals to reason about profitability and adjust offers automatically.
If inventory levels rise, the agent deploys limited-time discounts; if demand spikes, it reduces promotions to protect margins. These agentic use cases work across e-commerce and marketing systems to continuously balance revenue and demand.
Learn what it means to implement AI in e-commerce marketing and it’s use cases in e-commerce.
6. Content Experimentation Agents: Content experimentation agents autonomously run A/B or multivariate tests across channels. They interpret performance data, deploy winning versions, and even generate new creative variants if results dip.
For instance, if an email’s open rate drops, the agent crafts new subject lines, tests them on small segments, and scales the winner across the campaign, closing the loop from perception to reasoning to action.
7. Influencer & Partnership Outreach Agents: Influencer and partnership outreach agents autonomously identify and engage creators aligned with brand goals. They analyze social metrics, evaluate audience relevance, and draft personalized outreach messages. Once a creator responds, these agentic AI examples can negotiate terms or schedule meetings, automating the top of the partnership funnel.
8. Predictive Journey Orchestration Agents: These agents plan entire customer journeys proactively. They define campaign objectives, design multi-step paths, and trigger the right touchpoint at the perfect time—email, push, or ad—based on predicted engagement likelihood.
By mapping journeys end-to-end, they ensure every interaction is contextual, timely, and goal-driven, optimizing engagement without human input.
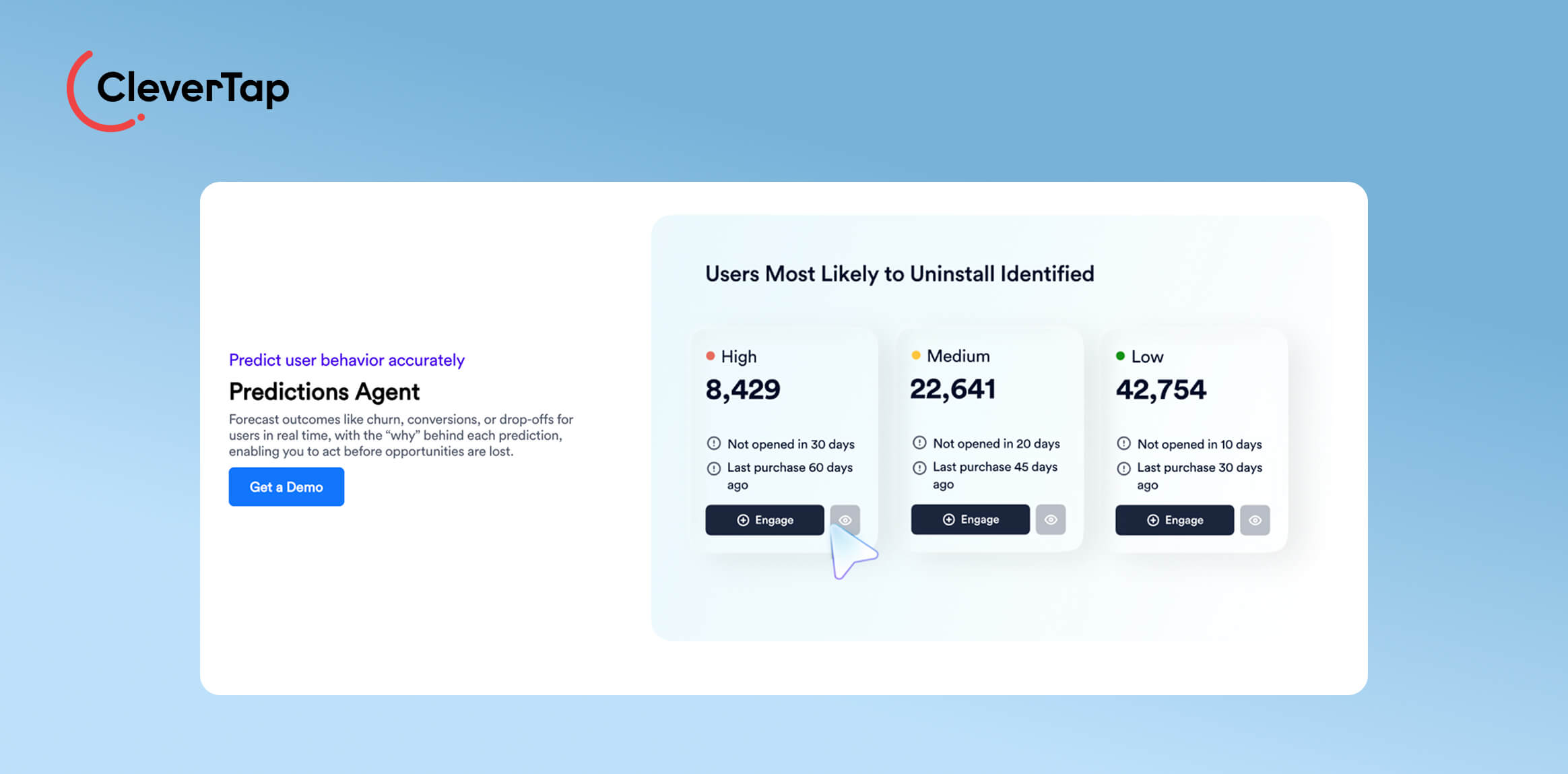
9. Retention Forecasting Agents: Retention forecasting agents analyze customer behavior and transaction history to predict churn. When they detect at-risk users, they automatically trigger retention workflows, such as loyalty offers or personalized reminders, to improve customer lifetime value. These agents continuously learn from outcomes to refine churn prediction accuracy.
10. Real-Time Audience Enrichment Agents: These agents continuously enrich and evolve audience segments based on real-time behavior. When users engage, convert, or shift preferences, the agent instantly reclassifies them (e.g., from “prospect” to “loyal customer”) and activates new campaigns.
This dynamic segmentation keeps personalization up to date, replacing static lists with living, adaptive customer profiles.
11. A/B Test Automation Agents: A/B testing agents eliminate manual experimentation by autonomously creating, testing, and scaling campaign variations. They analyze engagement metrics and shift traffic toward high-performing options in real time.
For example, the agent tests multiple subject lines, detects the best performer, and automatically rolls it out across the audience, continuously improving results through self-optimization.
12. Cohort Evolution Agents: Cohort evolution agents continuously learn from campaign results to evolve customer segment strategies. They detect which cohorts respond best to certain messaging styles (e.g., discounts vs. loyalty rewards) and adjust future communications accordingly.
This creates a learning feedback loop where every campaign iteration refines the next, improving engagement and retention over time.
How can AI influence customer segmentation? Learn here.
13. Cross-Channel Orchestration Agents: Cross-channel orchestration agents ensure consistent, seamless communication across all marketing touchpoints: email, SMS, push, in-app, or WhatsApp.
If an email remains unopened, the agent might follow up with an in-app message or push notification. By autonomously managing channel sequencing, these agents deliver cohesive, personalized experiences that maximize engagement across the entire user journey.
Customer Support AI Agent Examples
Customer support teams also leverage agentic AI examples extensively. For instance, Gartner predicts that by 2029, agentic AI will autonomously resolve 80% of common support issues (slashing costs by ~30%), and agents will even take actions like canceling subscriptions on behalf of customers.
Below are several ways support uses AI agents:
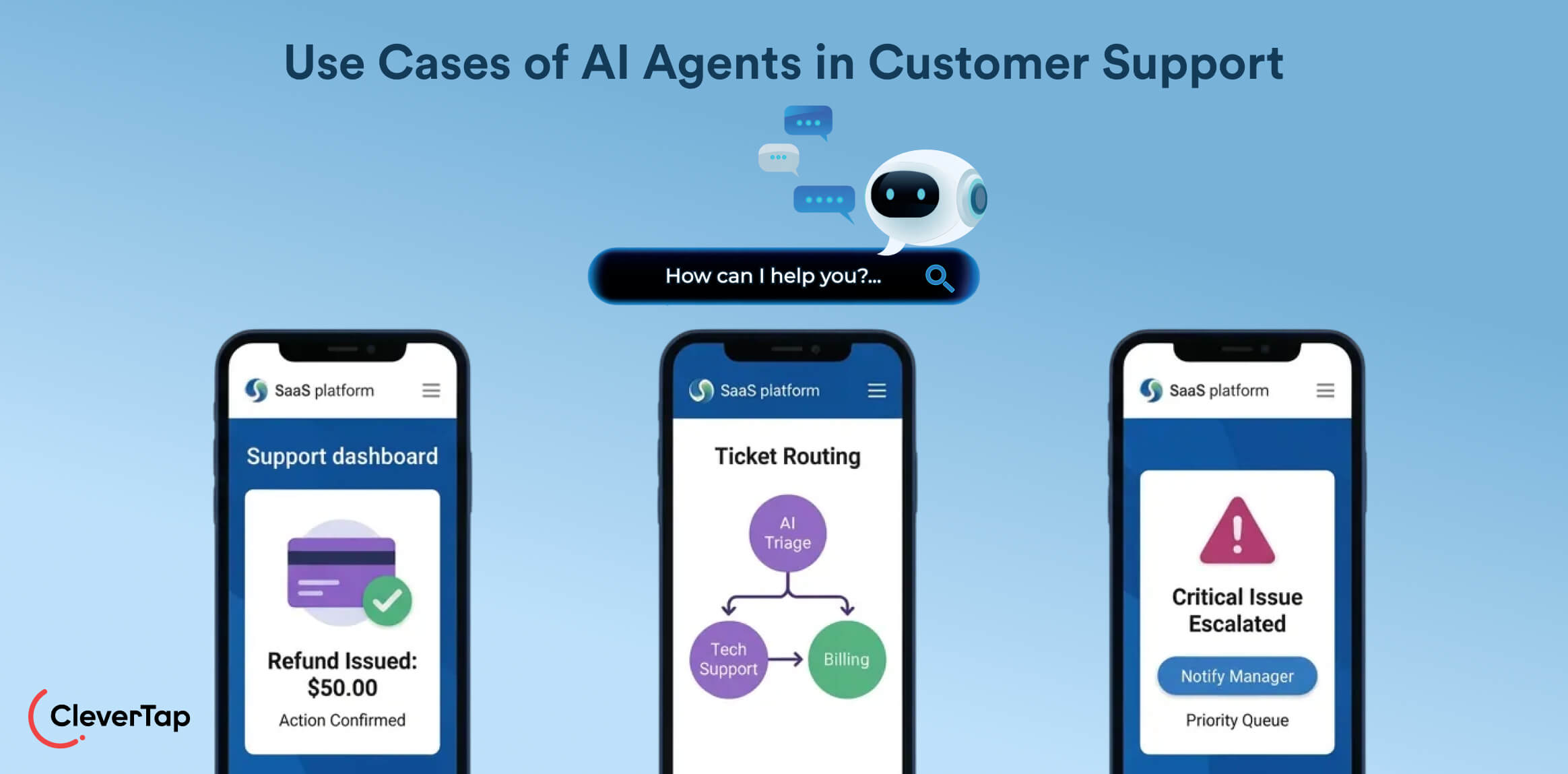
14. Advanced Support Assistants: Modern support bots can perform tasks, not just chat. They can handle password resets, order lookups, or refunds on the fly.
For example, AI support agents can “take actions on users’ behalf”, like processing a refund during a conversation. These assistants use NLP to understand a problem and then execute the required backend action, automating routine service steps 24/7.
15. Ticket Triaging and Routing: AI systems automatically classify and route incoming support tickets. The agent reads the ticket content (via NLP), tags it by topic (billing, tech, etc.), and sends it to the right team. This “auto-classifies, routes, and prioritizes” requests, drastically speeding up first response.
For instance, billing questions can be sent to finance, while login issues go to IT without manual sorting.
16. Escalation-Aware Bots: Agents can flag urgent issues automatically. By analyzing language and sentiment, the AI detects critical problems and escalates them to a human specialist.
For example, if a customer uses strong language or reports a major outage, the system immediately forwards the case to a Tier 2 team. This ensures critical issues (like compliance or safety incidents) get prompt human attention.
Sales & Revenue Operations AI Agent Examples
Below are some AI agent examples for sales and revenue operations roles:
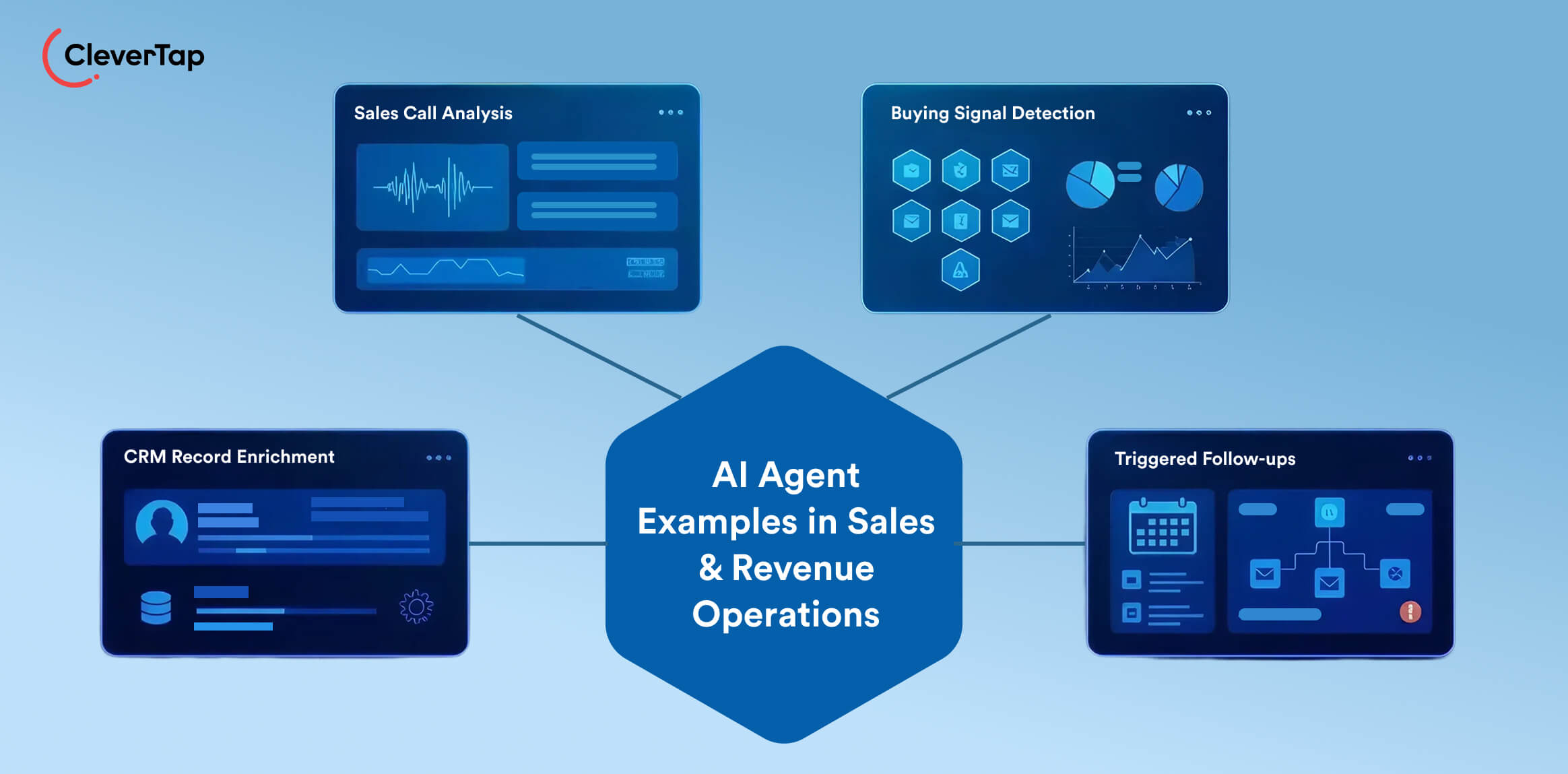
17. AI Sales Assistant: An AI sales assistant can autonomously record and analyze sales calls or chat transcripts to coach representatives and optimize deal outcomes. It processes conversation data to identify key insights, such as customer objections or buying signals, and then takes action by generating account briefs, drafting follow-up emails, or flagging potential deal risks.
Sales managers receive summaries like “Key contact expressed concern about pricing,” enabling timely adjustments to the pitch. By turning unstructured conversation data into clear, goal-oriented actions, such agents make sales processes more data-driven and proactive.
18. AI Research Agents: These types of AI agents gather intelligence on leads automatically. For instance, an agent might scan LinkedIn, Crunchbase, or news to compile a company profile. Agents can discover target companies and pull relevant data (funding, tech stack, hiring trends), and summarize it into profiles.
An AI sales researcher might automatically enrich CRM records with recent funding news or tech partnerships. The agent can even draft a personalized email based on that intel. This saves reps hours of manual research.
E-commerce & Personalization AI Agent Examples
E-commerce businesses rely heavily on AI agents for personalization and automation. Consider these AI agent examples:
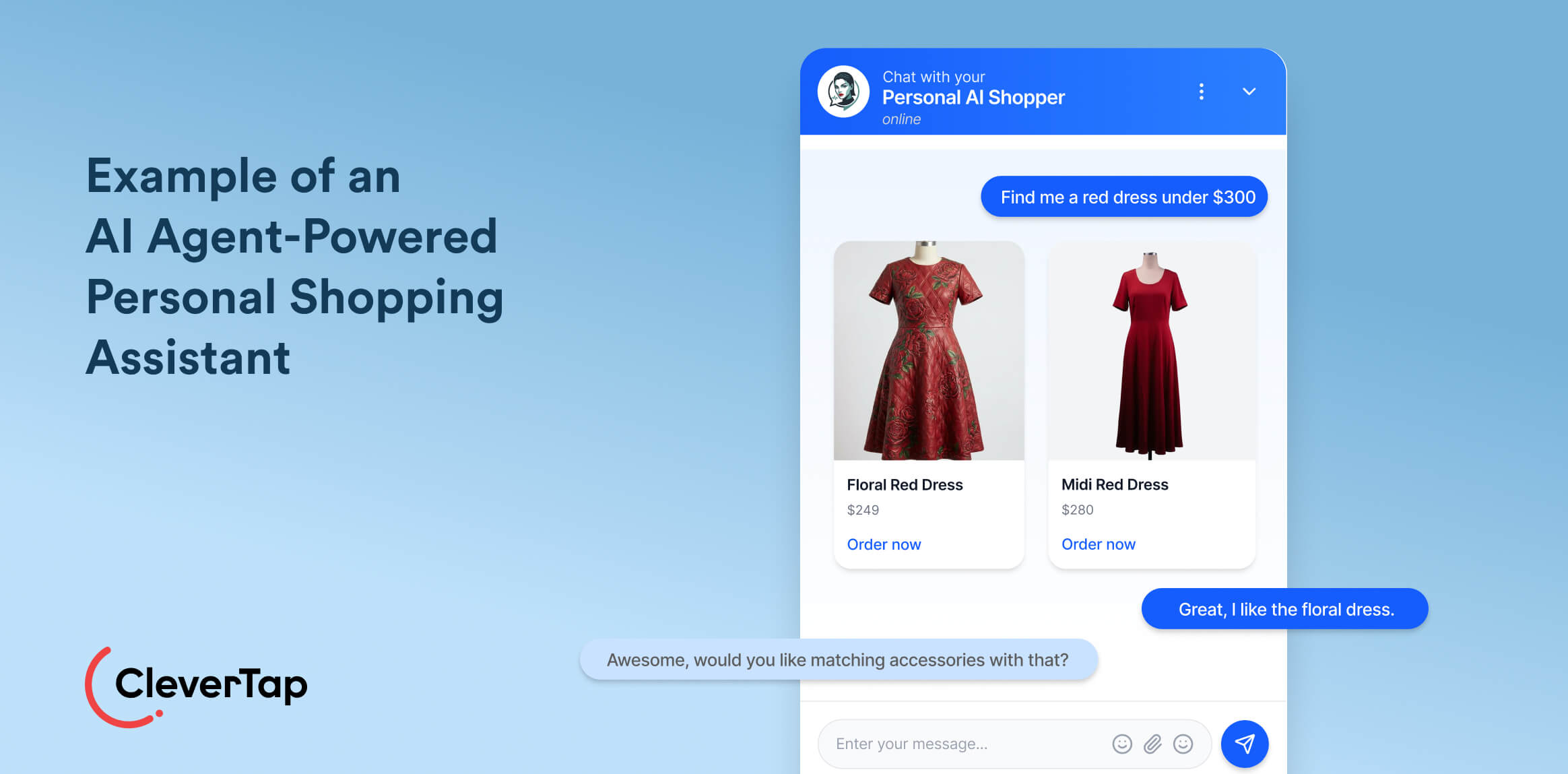
19. Conversational Shopping Assistants: AI agents on e-commerce sites act as personal concierges. A user might say, “Find me a red dress with a high neckline under $300,” and the assistant will parse that request and present matching products. This natural-language search saves shoppers time.
The agent uses NLP to extract attributes (color, style, price) and filters the inventory accordingly. It can also handle upsell suggestions (“Did you want matching accessories with that?”). This 24/7 chat guidance improves the shopping experience.
20. Cart Abandonment Recovery Agents: When a shopper leaves items in their cart, AI triggers follow-ups. These AI agent examples are able to detect the cart abandonment event and automatically send a personalized reminder or incentive (like a coupon) via email or push. It may even offer help (“Can I answer a question about product X?”) in a chat pop-up.
AI agents can “initiate personalized abandoned cart email flows” by acting before the shopper exits. For example, if a user lingers on checkout, the bot might prompt them on-screen, then follow up by email or SMS after a delay. These interventions recover lost sales with minimal manual work.
Finance or Fintech AI Agent Examples
Below are some AI agent examples for industries and roles such as digital banking, consumer lending, fintech, corporate banking, robo‐advisor platforms or private wealth management firms, and remittance firms:
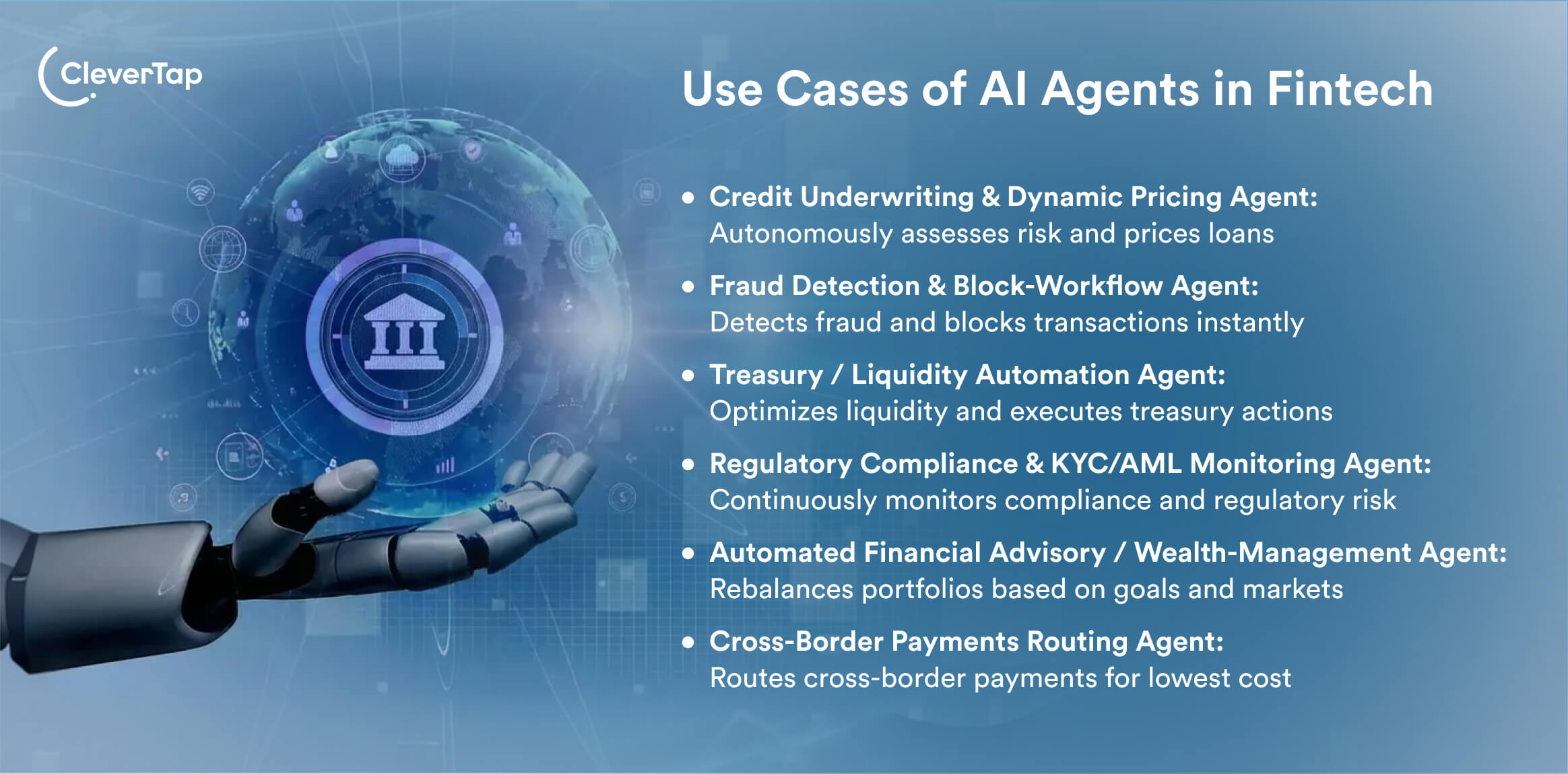
21. Credit Underwriting & Dynamic Pricing Agent: A fully autonomous agent:
- Monitors applicant data, including traditional and alternative data: transactions, spending behaviour, social signals in real-time
- Assesses risk
- Reasons about the appropriate terms (interest rate, amount, tenure)
- Initiates the contract (or declines) without human intervention
For example, an agent triggers an offer: “Based on your profile, you qualify for Rs. 2 lakh at 10.5% for 3 years” and routes the approval or human review if confidence is below the threshold. This covers perception (data ingestion), reasoning (risk model + business policy), and action (initiate offer or decline). These agentic AI use cases span from digital banks to consumer lending.
22. Fraud Detection & Block-Workflow Agent: An autonomous agent for banks, card issuers, and fintech businesses:
- Monitors transactions in real time
- Detects anomalous patterns (e.g., unusual location, volume, counterparty)
- Reasons: Is this fraud or a false positive?
- If there is high confidence, it executes the following actions: auto-blocks the transaction, notifies the user, initiates further authentication, or escalates to investigations
23. Treasury / Liquidity Automation Agent: In corporate or banking treasury, an agent monitors cash flows, internal/external accounts, foreign‐exchange rates, interest rates, and debt obligations. It reasons about when to transfer funds, hedge exposures, or rebalance liquidity across rails, then executes routing of payments or hedging steps according to policy.
24. Regulatory Compliance & KYC/AML Monitoring Agent: An agent across banking, fintech, or insurance continuously scans regulatory updates, checks transactions/customers for compliance (KYC, AML), reasons about risk, and acts: flags accounts, freezes operations, generates audit logs, triggers remediation workflows.
25. Automated Financial Advisory / Wealth-Management Agent: An intelligent agent for robo‐advisor platforms or private wealth management firms monitors user portfolio, market conditions, user goals/risk tolerance, reasons about adjustments (rebalance, switch funds, tax-loss harvesting), and executes trades or triggers human advisor actions.
26. Cross-Border Payments Routing Agent: An agent for fintech or remittance firms handles multi-rail payments, monitors exchange rates, fees, and anti-fraud checks, routes the payment through the optimal path (rail/bank/currency) to minimise cost/time, and executes the routing automatically.
Learn how AI works in banking and how you can implement it to enhance customer engagement.
Travel & Hospitality AI Agent Examples
Let’s take a look at AI agent examples across the travel and hospitality industries.
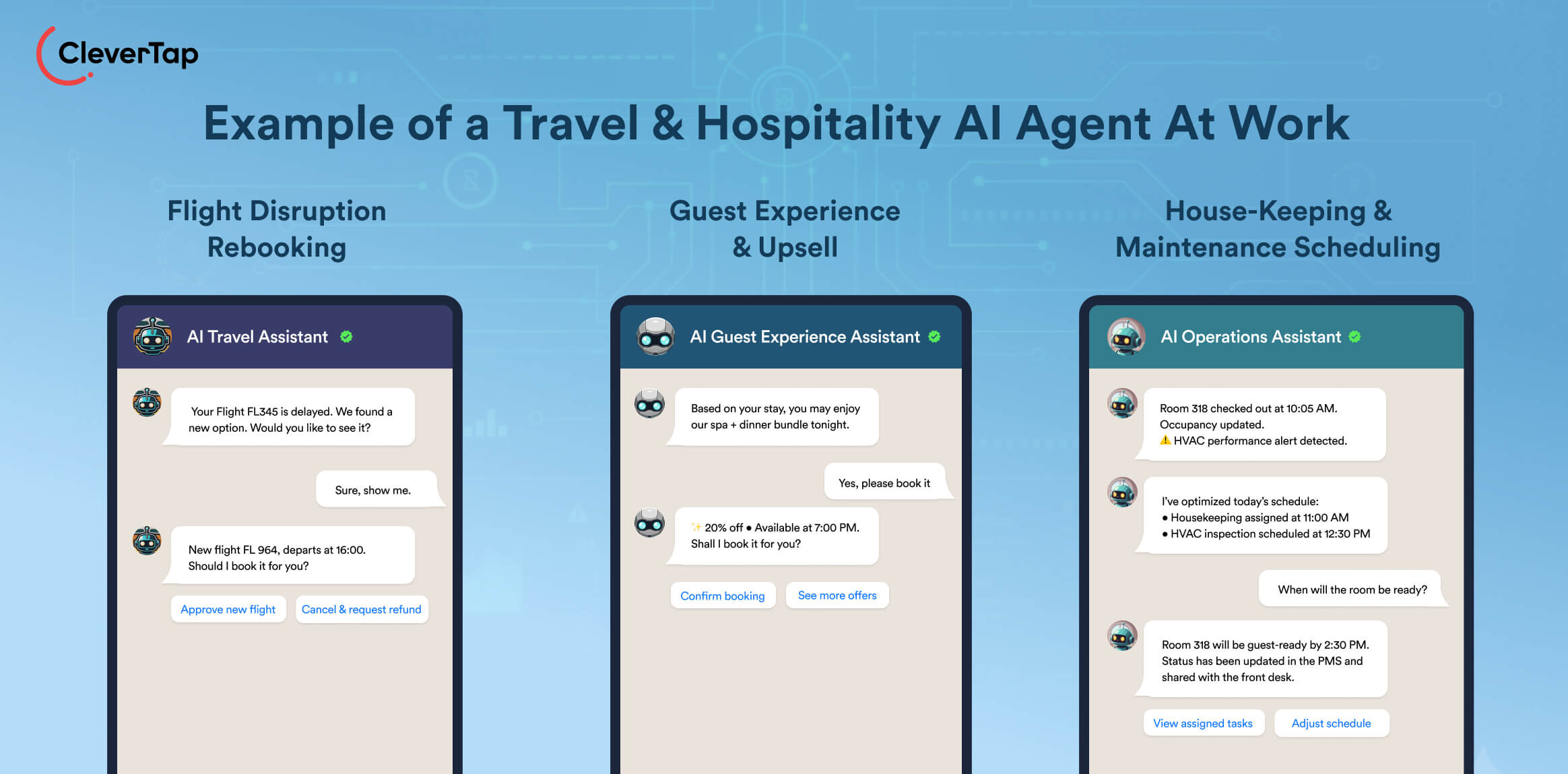
27. Travel Disruption & Rebooking Agent: For an airline or travel-booking platform, when a flight is delayed/cancelled, an agent perceives the disruption event, reasons about impact on connecting flights/hotels/ground transport for a particular traveler, then acts by re-booking the next best option, sending the itinerary update, triggering accommodation or transport changes, and notifying the traveller.
28. Multilingual Guest Concierge Agent: At a hotel or resort, a 24×7 agent converses (voice or chat) in multiple languages, handles guest requests (like “I’d like a late checkout”, “Book a spa”, “What are local dinner options?”), reasons about availability, billing, loyalty status, executes booking or scheduling, and escalates to a human only when needed.
29. Guest Experience & Upsell Agent: Within a hotel stay, an agent that monitors guest behaviour (room usage, spa visits, dining patterns), reasons about personalised offers (upgrade to premium room, spa bundle, local tour), and acts by sending the offer, booking it if the guest accepts, and adjusting billing.
30. House-Keeping & Maintenance Scheduling Agent: An agent connected to the hotel property management system and IoT sensors perceives check‐outs, occupancy rates, room maintenance alerts (smoke detector, HVAC), reasons about optimal scheduling of cleaning/maintenance, then acts by allocating staff, dispatching tasks, and updating room readiness status.
Healthcare AI Agent Examples
Healthcare is one of the most impactful sectors for agentic AI, where intelligent agents assist both patients and providers by perceiving medical data, reasoning with clinical logic, and acting to streamline care. Below are some AI agent examples:
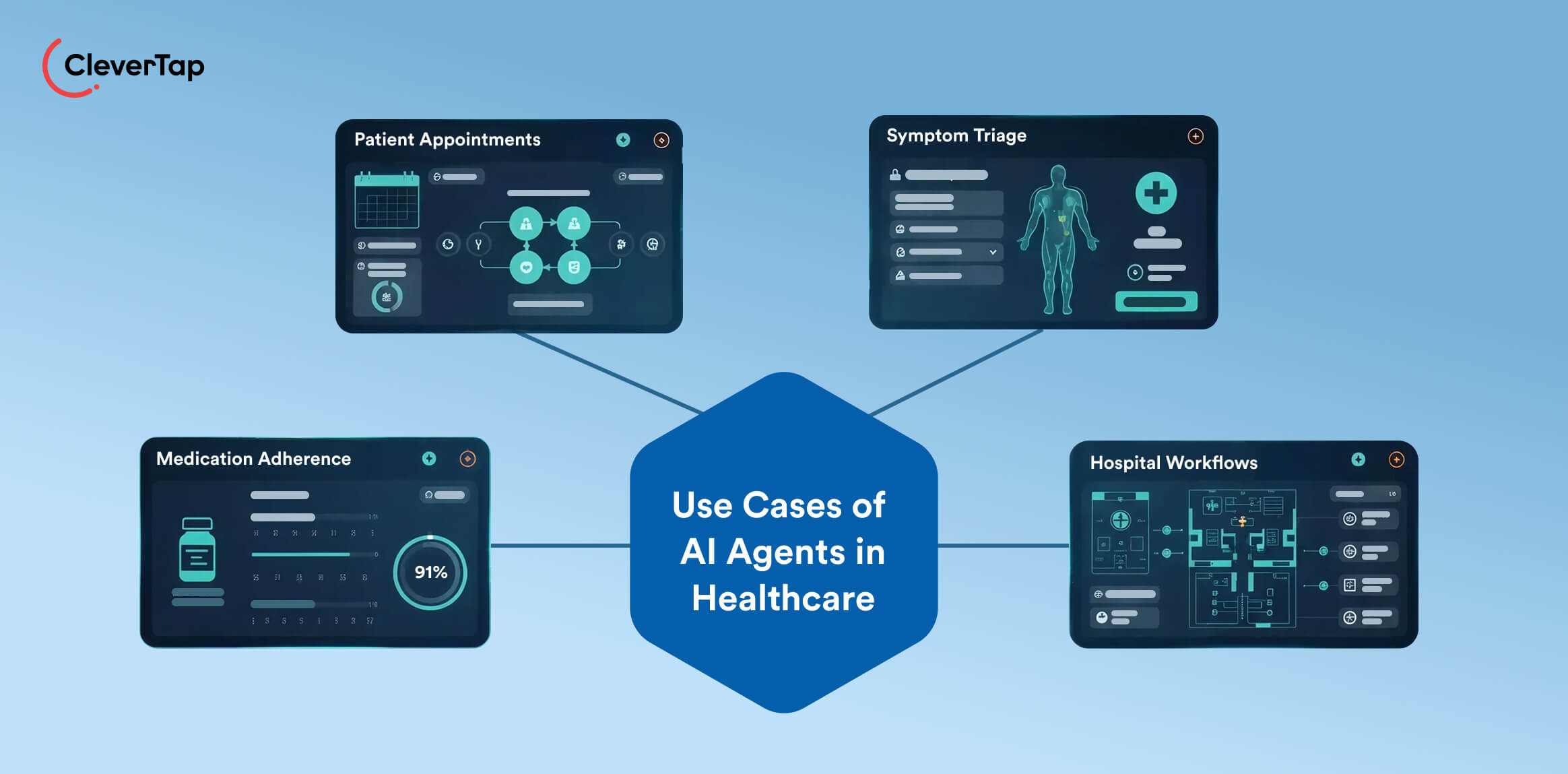
31. Appointment & Continuity of Care Agent: These agents autonomously manage patient scheduling and follow-up care. They monitor appointment calendars, detect missed or upcoming visits, and reason about the best available slots based on clinician availability and patient convenience.
When gaps appear—like a missed lab test or overdue check-up—the agent automatically reschedules, sends reminders, and updates both the patient and care team. This proactive orchestration ensures continuous, coordinated care and reduces no-shows.
32. Symptom-Triage & Escalation Agents: Symptom-triage agents engage patients through chat or voice to assess health conditions. They perceive patient inputs (e.g., “fever and body ache”), reason using medical knowledge bases and risk models, and act by providing guidance—whether self-care, teleconsultation, or emergency escalation.
If symptoms indicate high risk, the agent books an appointment with a clinician or alerts emergency staff, ensuring timely intervention and reducing clinical load.
33. Medication Adherence & Care-Navigation Agents: Medication adherence agents monitor a patient’s prescriptions, vitals, and pharmacy refill data. When they perceive missed doses or abnormal readings, they reason about potential health risks and act by sending reminders, arranging refills, or connecting the patient with a care nurse. They can escalate urgent cases automatically to a doctor.
By integrating across EHR, pharmacy, and patient apps, these agents maintain consistent, data-driven adherence support.
34. Clinical Workflow Automation Agents: Within hospitals, clinical workflow agents autonomously manage operational tasks. They perceive changes in patient data—such as new lab results or vitals—reason about the next best action (ordering diagnostics, scheduling consults, discharging patients), and act by triggering the appropriate workflow.
By continuously monitoring the care journey, these agents free healthcare staff from repetitive coordination tasks and improve overall efficiency.
HR & Internal Workflow Automation Agentic AI Use Cases
HR and enterprise operations are ideal for agentic AI adoption, as these AI agent examples can autonomously manage processes that rely on perception, reasoning, and action, spanning recruiting, onboarding, and workforce optimization.

35. Talent Sourcing & Screening Agents: Talent sourcing agents autonomously review incoming job applications, social profiles, and skills databases. They perceive candidate attributes, reason about role fit using competency and behavioral models, and act by shortlisting candidates, scheduling interviews, or sending assessments.
The agent logs its reasoning trail for transparency and routes ambiguous cases to recruiters for human review, speeding up hiring cycles while maintaining fairness and accuracy.
36. Onboarding & Compliance Agents: These agents manage the end-to-end onboarding experience for new hires. They track each employee’s progress, perceive pending tasks (like policy sign-offs or document submissions), reason about dependencies (e.g., access required before training), and act by triggering IT setup, sending reminders, or escalating incomplete actions.
This ensures that every new hire becomes productive faster while maintaining compliance with organizational policies.
37. Employee Services & Helpdesk Agents: Employee helpdesk agents provide real-time, self-service support for HR, payroll, and IT issues. They perceive employee queries (“I need to reset my password” or “How many leaves do I have left?”), reason about the correct response or workflow, and act by resolving the issue directly, resetting access, submitting requests, or escalating complex queries to a human specialist.
These agents operate 24/7, reducing internal support load and improving employee satisfaction.
38. Workforce Planning & Skill-Matching Agents: These agents continuously analyze workforce data—skills, performance, and project pipelines—to identify resource gaps or development opportunities.
They perceive skill shortages, reason about whether to retrain, reassign, or hire, and act by recommending learning modules, triggering training enrollments, or notifying HR teams to open requisitions. Over time, they help build a self-correcting, data-driven workforce planning loop that aligns talent with business needs.
Cross-Industry Productivity Tools
Finally, general AI frameworks enable cross-industry solutions. For instance:
39. AutoGPT (Autonomous AI Workflows): AutoGPT is an open-source agent framework where users set high-level goals and the AI breaks them into tasks. You give it a mission (like “launch a social campaign”), and it plans and executes subtasks autonomously. It can research, write content, and iterate on tasks until it meets the goal, without further prompts. This demonstrates how multi-task agents can function as virtual project managers.
40. LangChain Multi-Agent Systems: LangChain is a developer toolkit for chaining LLM calls with tools and memory. It lets you build agents that, for example, analyze documents or query databases. A LangChain agent could load a set of legal contracts, use its vector-memory (RAG) to find relevant clauses, and answer user questions.
In industry, LangChain’s agents have been used for tasks like automated policy enforcement and data quality checks. Its combination of LLMs, vector databases, and APIs illustrates advanced agent architecture.
41. SuperAGI (Agent Orchestration): SuperAGI is a platform for orchestrating many AI agents together. Companies use multi-agent orchestration to automate entire processes end-to-end. For example, IBM built an agent orchestration platform that automates data processing and customer service tasks, dramatically improving efficiency.
In a SuperAGI-style pipeline, one agent might scrape sales leads, another analyzes the data, and a third triggers marketing actions. Large enterprises are already seeing benefits: Gartner predicts such agentic automation will continue to replace manual tasks, improving productivity across domains.
Lessons from Real-World AI Agent Examples
Agentic AI is redefining the industry through autonomy and intelligence. Success starts with clear goals, clean data, and tight integration across your CRM, analytics, and automation stack.
Begin small—automate a single workflow, measure outcomes, and scale up. Human oversight remains crucial to ensure accuracy, ethics, and alignment with brand standards.
Early adopters are already realizing major gains in personalization and productivity. With AI agents as collaborators, marketers can adapt faster, engage smarter, and transform customer experiences in real time.
See what CleverTap’s AI agents can do for your business. Transform your engagement strategy with intelligent automation and predictive insights.
Subharun Mukherjee 
Heads Cross-Functional Marketing.Expert in SaaS Product Marketing, CX & GTM strategies.
Free Customer Engagement Guides
Join our newsletter for actionable tips and proven strategies to grow your business and engage your customers.