Remember when Pokémon could only be played on a GameBoy or Nintendo DS, or even playing cards?
That all changed in 2016 with Pokémon Go. Suddenly, thanks to augmented reality (AR), you could find Pokémon in the real world and “catch ‘em all.”
Pokémon Go made augmented reality mainstream, and the technology has only grown since. In 2016, global revenue from consumer-facing augmented reality mobile apps was more than $725 million. By 2022, estimates suggest that number will skyrocket to $15.5 billion.1
It’s safe to say that with such a promising market outlook, augmented reality is catching the attention of mobile marketers across the globe.
Ready to learn more about augmented reality? Read on, or jump to our infographic to find out how augmented reality can be used to create a more powerful marketing campaign.
What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented reality is a technology that superimposes digital information like sound, video, and text onto your view of the real world.2
Think of Snapchat’s filters where, with the flick of a finger, you can take dog-eared selfies or swap faces with your BFF.
However, AR isn’t just for fun photos, it can be used brilliantly in mobile marketing to boost engagement and create realistic, virtual experiences with products.
Apps like IKEA Place allow shoppers to virtually see how a couch or lamp would look anywhere in their home so they can make sure it fits their space and aesthetic before they purchase.
Augmented Reality vs. Virtual Reality
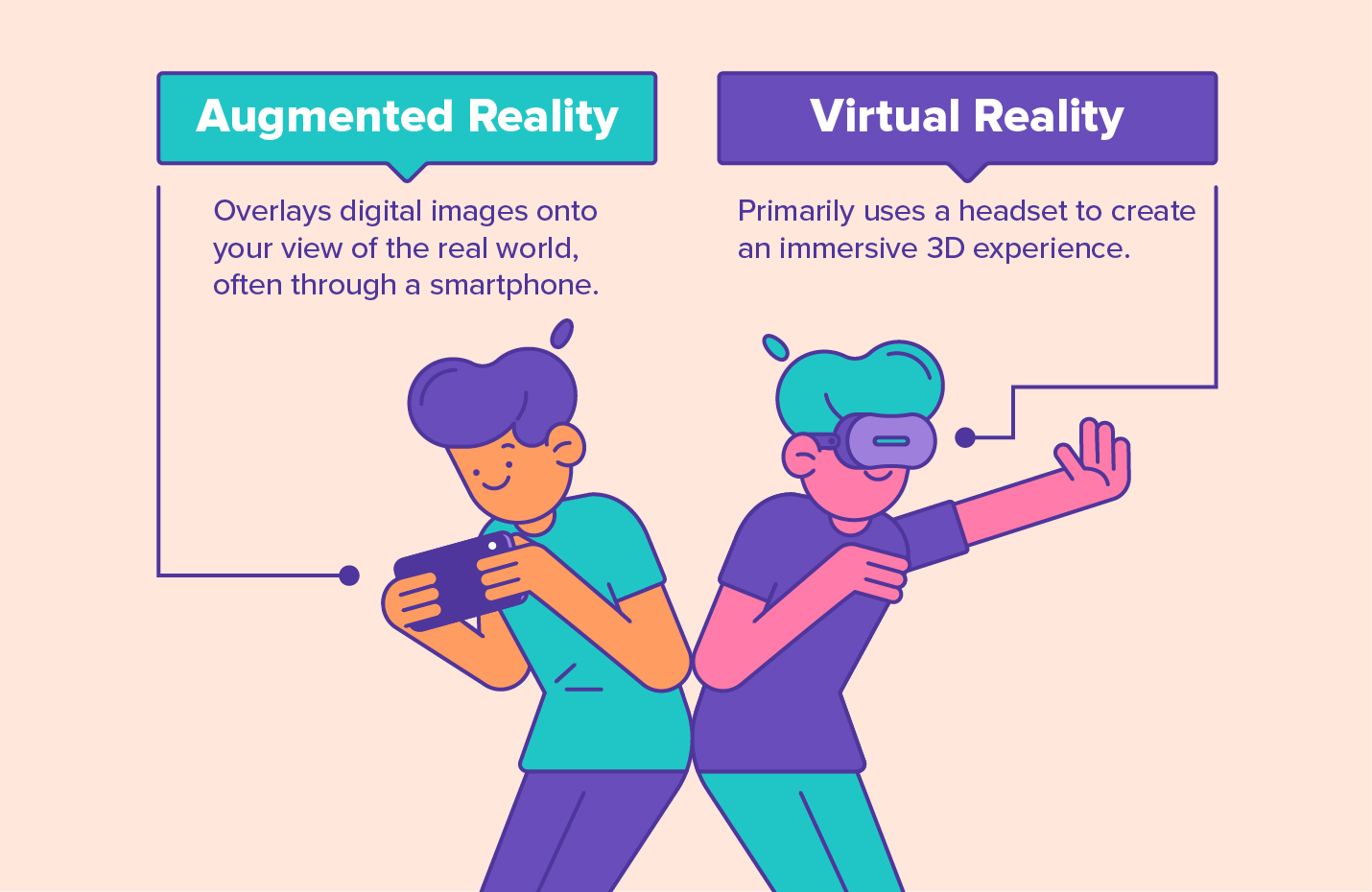
As similar as they sound, augmented and virtual reality are very different technologies.
While augmented reality superimposes digital images onto a real picture or video, leaving the majority of the surrounding environment unaltered, virtual reality (VR) creates an immersive 3D experience.
Customers can easily access AR using only their smartphones, while VR requires additional equipment like goggles or headgear. Because of this, AR can reach a wider audience.
AR and VR can be used by marketers for both fun and informative initiatives. For example, a fashion brand may create a VR campaign that allows customers to “attend” their fashion show, or they could use AR to allow them to try on garments from their latest collection.
How Does Augmented Reality Work?
As futuristic as it may seem, augmented reality is actually quite simple to employ. Large tech companies like Apple are even creating AR toolkits to make development more accessible.
In most forms of AR, the user sees both natural and artificial light through a layering effect. The real world acts as the first layer. The camera recognizes the target, processes the image, and then augments digital assets onto that image. This layering effect is visible through the device, so users can see both the real and synthetic worlds at the same time.
These artificial layers are where mobile marketers can show off their skills by adding in virtual messages, signs, and objects to get consumers interacting with the app, and their brand, on a whole new level. Ray-Ban does this successfully with their “Virtual Try-On” feature where users can test out different lenses from the comfort of their webcam.3
4 Types of Augmented Reality
There are four main types of augmented reality, each with their own unique functionality and application.4
Marker-Based Augmented Reality
Marker-based augmented reality, also known as “image recognition,” uses a smartphone camera and some visual ‘marker’ that produces an augmented reality when it is sensed by the camera. The marker can be a QR code or a specific image, like a movie poster, as long as it has enough distinct visual points.
You could use marker-based AR to bring a still image to life or provide customers with additional information. For example, market your upcoming concert by creating a poster that, when scanned, shows a set list and plays music from the lineup.
Markerless Augmented Reality
Markerless augmented reality uses a GPS, digital compass, or accelerometer to provide data to a device based on location or speed. This is the most popular and versatile type of AR.
It’s especially useful for showing physical objects in relation to other objects, like sizing furniture for a house in IKEA Place, and bringing characters to life in Pokémon Go.
Projection-Based Augmented Reality
Projection-based augmented reality, or spatial augmented reality (SAR), works by projecting artificial light onto a real surface, much like the way a movie projector works. Screens or headsets are not needed.
Projection-based AR is usually done on a larger scale, like at a conference or event. It can be interactive, with the use of sensors, and 3D. This form of AR is helpful to showcase large objects like cars and can even be used in the consumer research phase to get feedback on different models.
Superimposition-Based Augmented Reality
Superimposition-based augmented reality uses object recognition. The augmented image replaces the original image either partially or fully. This type of AR is commonly used in the medical field to superimpose an X-ray onto a patient’s body.
It can also be used to enhance a historical tour. For example, you could use superimposition-based AR to showcase what a statue or structure looked like years ago, visually explaining how it has aged and why that’s significant.
The Benefits of AR for Mobile Marketing
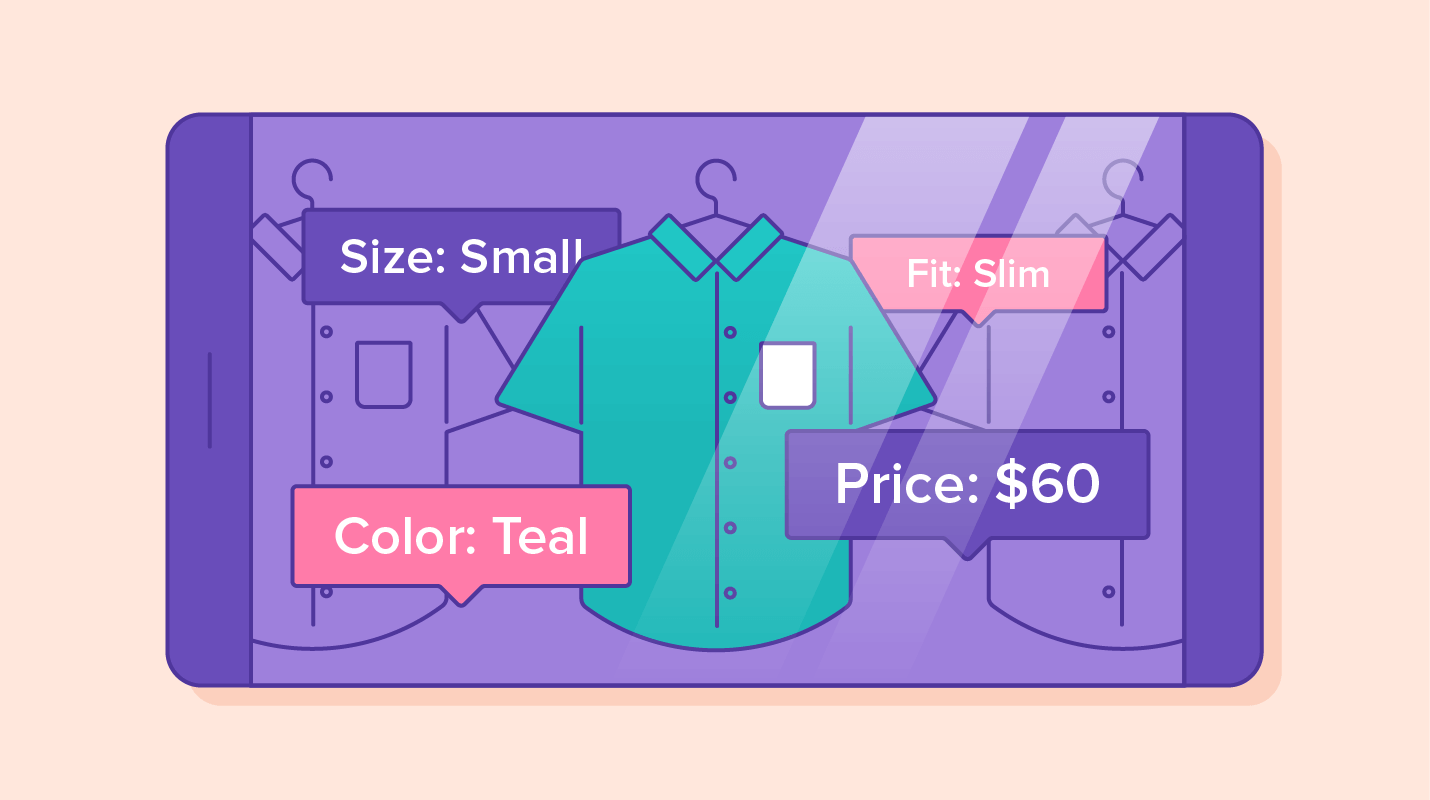
Augmented reality is changing the game of mobile marketing in a big way. Specifically, it’s revolutionizing the way consumers interact with marketing campaigns, products, and brands.5
Product-based brands can show off their merchandise with AR-driven 360º views and interactive experiences where consumers can test products. Service brands can create AR tutorials of their key offerings, showing customers exactly how much bang they’re getting for their buck before they commit.
There’s no limit to how augmented reality can shape mobile marketing, but here are just a few examples of how it’s being used right now:
Customer Experience
Take our IKEA Place app example. What’s so great about the IKEA Place app is that it lets customers try out furniture without leaving their homes.
Customers like simplicity and ease-of-use in their shopping process, so being able to shop in your pajamas is a major win when creating an intimate connection with customers.
What does this mean for you? Create new ways for your customers to engage with your brand in a way that is meaningful to them. For many, that might mean leveraging augmented reality as a means of simplifying the product trial or overall purchase processes.
Consumer Engagement
Sephora, a major cosmetics retailer, created an app that lets users see what different products will look like on their face. Anyone with a smartphone can download the app and by aiming the camera at their face, test shades of lipstick, eyeshadow, and foundation with the flick of a finger.
Not only are customers getting virtual makeovers –– but Sephora marketers are also improving customer engagement by keeping people entertained on their app for longer periods, improving the chances of a purchase for consumers who can now interact with the brand in a new way.
Geo-Targeting
The Lumia City Lens, an augmented reality app developed by Nokia, provides suggestions for nearby restaurants and shops to Lumia phone users. Just open the app and aim your camera at the surrounding buildings to find out what’s inside and get detailed information about each establishment.
Mobile marketers who use AR for this purpose are achieving several key goals. They’re helping customers find their way into a store by providing streamlined information, encouraging a sale by creating interactive experiences, and collecting meaningful data on demographics and behavior by analyzing who interacted with the app.
We’ve covered the bases of AR, including what it is, how it works, and a few of the benefits. Now, it’s time to decide what type of AR would benefit your brand the most. Below, we recap AR and give examples of how it’s used across multiple industries.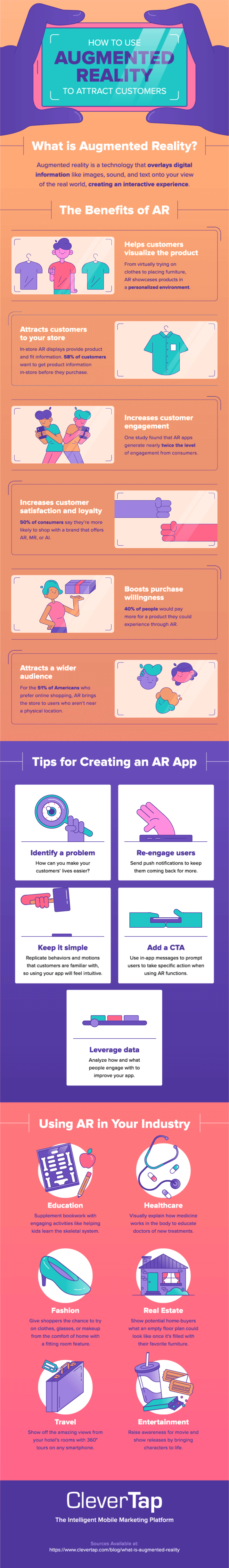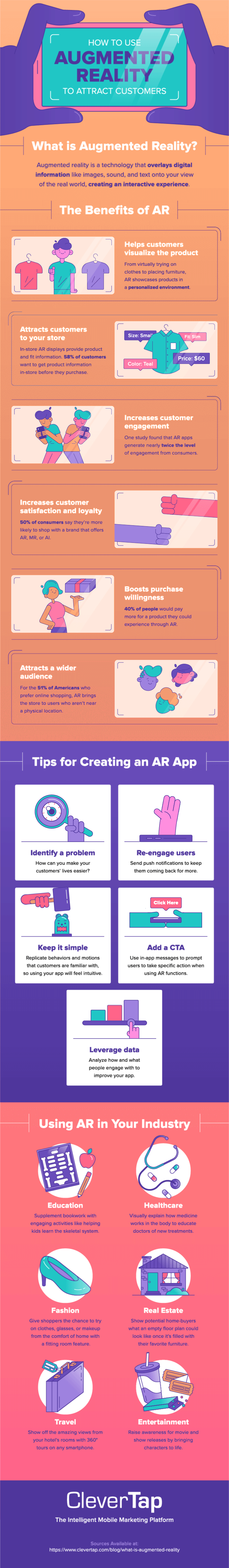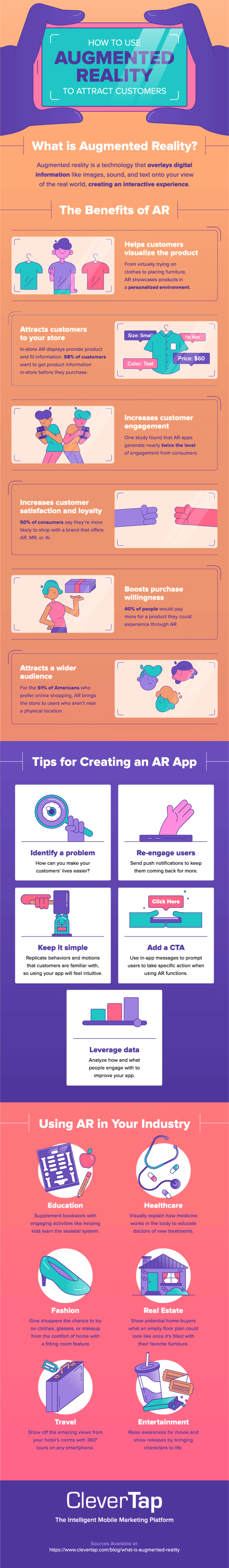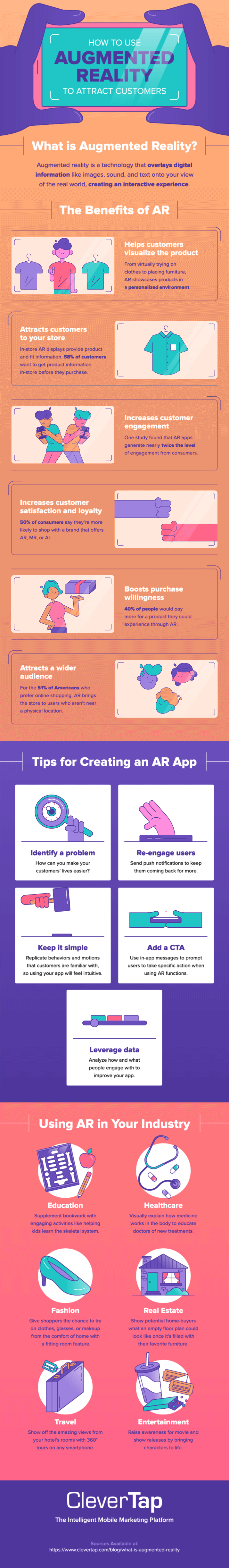

See how today’s top brands use CleverTap to drive long-term growth and retention
Subharun Mukherjee 
Heads Cross-Functional Marketing.Expert in SaaS Product Marketing, CX & GTM strategies.
Free Customer Engagement Guides
Join our newsletter for actionable tips and proven strategies to grow your business and engage your customers.