A customer rarely churns because of one isolated issue. Most churn is the final outcome of expectations not being met across the journey, whether that breakdown happens during onboarding, engagement, support, or renewal.
Every product creates an implicit promise. Customers expect to reach value quickly, experience consistent service, and feel that the relationship remains worth continuing over time. When those expectations erode, churn becomes increasingly likely. Sometimes it happens immediately. More often, it builds gradually through moments of friction, misalignment, or disengagement.
That is why the most effective churn prevention is not just about reacting to cancellations. It requires understanding the underlying drivers behind them, the behavioral signals that appear early, and the points in the lifecycle where customers silently begin to detach.
In this article, we will break down the most common causes of customer churn and the practical strategies businesses can use to address them before customers leave.
What Is Customer Churn and Why Does It Matter?
Customer churn (also known as customer attrition) is the percentage of customers who discontinue their relationship with a business within a given period. It can take the form of cancellations, non-renewals, inactivity, or reduced engagement depending on the business model. In subscription apps, churn often means subscribers do not renew subscriptions. In e-commerce or fintech, it means customers becoming inactive or closing their accounts.

Churn is not always explicit. Inactivity often signals disengagement long before cancellation. Some users stop using a free app or service. Churn happens when customers actively decide to leave, while involuntary churn occurs due to factors outside the customer’s intent. For example, a credit card failing on renewal, billing interruptions, renewal friction, etc.
Across industries, whether it’s OTT streaming services, online retailers, or mobile apps, churn is the percentage of your user base that drops off over time.
Why Does Customer Churn Matter?
Churn directly reduces revenue and slows growth. When customers leave, you lose not only the recurring revenue they provided but also the customer acquisition cost (CAC) you spent to get them. It also eliminates any chances of future purchases or subscriptions.
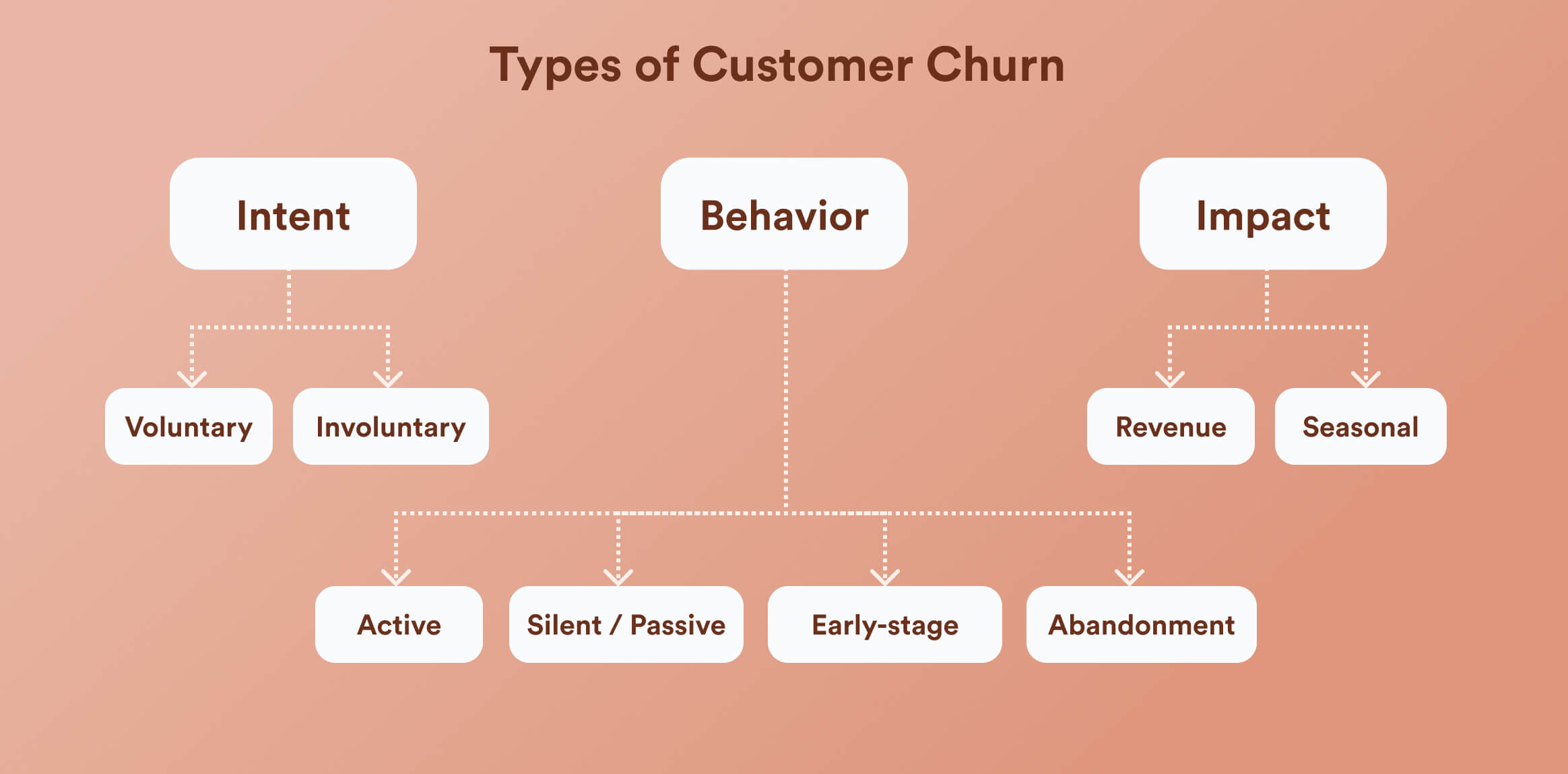
High churn often reflects deeper breakdowns in value delivery, satisfaction, or lifecycle experience. Over time, churn compounds negative sentiment and weakens customer loyalty. However, identifying churn by type makes it easier to understand the why behind it.
- Voluntary churn: When a customer leaves voluntarily.
- Involuntary churn: When the decision to leave isn’t one that a customer takes consciously. For example, a payment failure or a billing issue.
- Active churn: When a customer clearly takes an action to leave, such as canceling a subscription or deleting an account.
- Silent or passive churn: When customers stop engaging with the product but do not officially cancel.
- Product abandonment: When users simply stop using the product
- Early-stage churn: When users leave shortly after signup or onboarding because they do not see value quickly.
- Revenue churn: When a business loses recurring revenue due to downgrades or reduced usage, even if the customer does not fully leave.
- Seasonal churn: When customers leave temporarily due to seasonal needs or limited-time use cases.
In all cases, the goal is to detect churn risk early and intervene.
12 Most Common Causes of Customer Churn
Understanding why customers churn is the first step to preventing it.
1. Poor Onboarding and Early Friction
When there is a difference between the perceived and actual value of a product or service, reaching the aha moment becomes tricky. Sometimes it never comes.
Many users sign up but fail to activate into the product’s primary use case early enough. It leads to high drop-off in the early stages of the customer lifecycle. This is often visible through early activation drop-off signals, such as:
- Users don’t complete key onboarding steps.
- Low login frequency in the first week and consistently short initial sessions.
This is most common during the first-use and early adoption phase.
How to Fix This:
The fix is to set expectations correctly and make strategic improvements to the onboarding process. You provide clear guidance, tooltips, checklists, and even personal support for new users.
Focus on driving them to the core value as fast as possible. Identify any friction points in the first-run experience and remove them. Friction often comes from complex setup steps, unclear next actions, or missing integration guidance. Make the initial processes as simple as possible.
Set realistic expectations during onboarding about what the user should do first. Here are a few additional things you can set up when catering to your early users:
| When Onboarding is Self-Serve | When a CSM assists Onboarding |
| Design a realistic flow that guides customers to reach aha moments quickly. Make sure to add an FAQ section addressing the questions people usually have when they try the product. Leverage Clever AI to automate push notifications and in-app messaging based on unique segments and user journeys. | Adi Aloni, VP of Customer Success at Folloze, argues that onboarding teams work much more effectively when they handle customers with similar profiles and needs. Try to avoid context switches for agents. Train CSMs for different ICPs and ensure they work only on similar profiles. This increases efficiency. |
2. Misaligned Expectations From Acquisition Messaging
Churn increases when acquisition messaging creates expectations the product experience does not reinforce. This gap stems from misaligned expectations, built on sales and marketing promises that don’t match the product.
For example, if your ads or sales team overpromises outcomes (“X will double your revenue overnight!”) or misrepresents features, customers sign up with high hopes, only to be disappointed when those expectations aren’t met. In practice, this often means acquiring customers whose needs or assumptions do not align with the product’s strengths. It becomes apparent quickly after acquisition, when the customer realizes the product isn’t what they thought.
Below are some behavioral variations that customers with misaligned expectations often exhibit.
- Early frustration or confusion
- Support tickets that reveal feature mismatches or unmet assumptions like “I thought this product has ‘feature A,” but it doesn’t.”
- Fast churn after a short trial or first purchase.
This typically affects the acquisition and initial use stage.
How to Fix This:
Take steps to align your marketing and sales promises with reality. Ensure marketing and sales narratives reflect the product’s actual capabilities and time-to-value. Here are a few ideas to try:
- Periodic Sessions on ICP: Educate your sales team on who your ICP is and the real use cases your product excels at. This avoids closing deals with customers who will never find success.
- Set Proper Expectations: Clarify what outcomes are realistic and what steps the customer must take to achieve them. If expectations are aligned from day one, customers are less likely to feel misled and leave.
3. Perceived Value-to-Cost Gap
There is misalignment in pricing. It occurs when customers feel that what they’re getting isn’t worth what they’re paying. It’s essentially a problem of value perception. Either the price is deemed too high for the benefits, or the benefits have faded over time, so the cost feels unjustified. But often in most cases, churn is driven by weakening value perception rather than price alone.

Such causes came to light when:
- Customers downgrade their plan or usage before leaving feedback about the price.
- There’s a low feature engagement, especially with features tied to higher-priced plans. If a customer isn’t using many of the features they’re paying for, they’re likely questioning the value.
In subscription businesses, price increases trigger this if not accompanied by perceived added value. In industries like e-commerce, this might show up as customers not returning for repeat purchases because they found better deals elsewhere.
How to Fix This:
Customer retention depends on consistently reinforcing value throughout the lifecycle. To keep your customers, you must give them value that is worth more than the price they pay.
- Show Them the Proof: Do not just deliver results; communicate them clearly. Use modern data platforms to track buying patterns and predict your customers’ needs. These tools allow you to optimize on customer lifetime value and prove ROI.
- Beat Perceived Indifference: Most people leave because they think you do not care about them. To stop this, you should treat your best customers like raving fans to keep them engaged. Small details, like a warm greeting, matter more than you think.
- Watch the Desire Lines: Pay attention to how customers actually use your service. These are called desire lines. If customers ignore your suggested path and create their own, follow them.
Did you know? CleverTap lets you follow customer journeys closely and automate helpful and strategic messaging to prevent them from churning.
4. Experience Friction That Interrupts Habit Formation
New habits are tricky to build, especially when they undergo change.
Adoption depends on consistency, and repeated disruptions prevent habits from forming. Even when it affects them positively, it’s something that’s outside the ordinary. You need to ensure they don’t experience any friction in the very process that takes them through the change.
This friction can be in the form of bugs, glitches, crashes, slow performance, or downtime. Performance issues interrupt workflows and erode trust with every failed experience. These prevent users from forming a reliable habit with your product. When such experiences repeat, they chip away at trust until the customer gives up. Below are some behavioral signals you’ll see when this happens.
- Sporadic Engagement: Users attempt to use a feature, encounter issues, and log off.
- Numerous Support Tickets: Multiple session drops or error-triggered exits are a telltale sign.
This happens at any stage, but it’s particularly damaging during the onboarding and adoption phase.
How to Fix This:
A significant technical hurdle occurs when a product does not integrate with a customer’s existing tech stack. The solution is to prioritize reliability, integration stability, and continuous monitoring of friction-heavy journeys. The obvious solution is to invest in product quality and reliability.
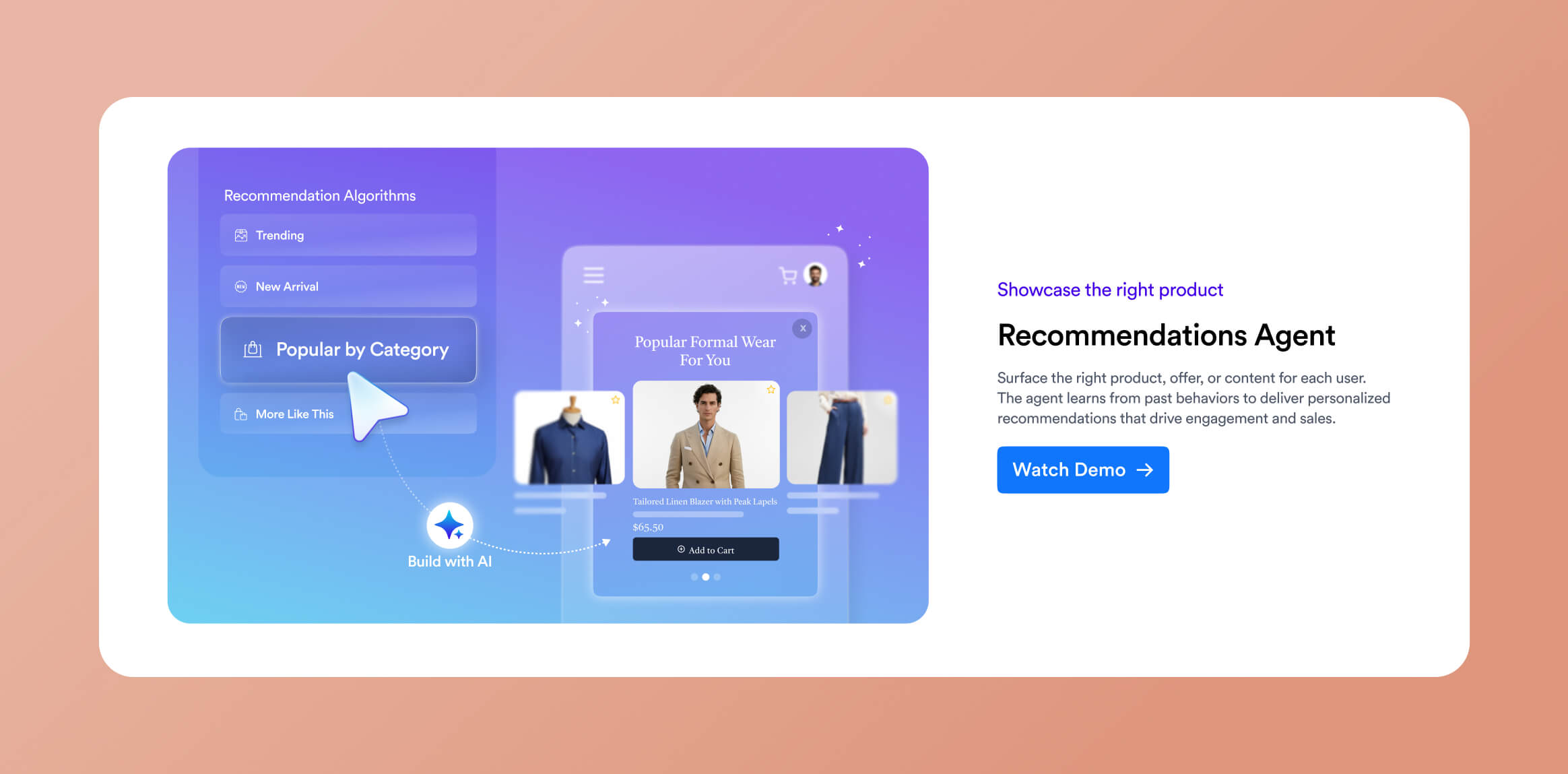
5. Lack of Personalization or Relevance
When engagement feels generic or untargeted, customers disengage because the experience stops reflecting their needs or intent. It’s important to keep the communication relevant to customers’ interests and behavior. Over time, relevance shapes both emotional connection and long-term engagement behavior.
Below are a few signals indicating that customers are experiencing a lack of personalization or relevance.
- Low engagement with marketing touchpoints.
- Low adoption of relevant features because customers are not guided toward what matters to them.
This cause creeps in during the engagement and retention stages.
How to Fix This:
Platforms like CleverTap help you analyze customer journeys in real time and segment them in different funnels based on their interactions (virtual or vocal) with a business’ assets. Clever.AI automatically builds context relevant to each funnel and optimizes communication for relevance, interests, and motivations.

6. Competing Experiences That Feel More Rewarding
Competitive churn occurs when alternatives deliver clearer value or lower effort at key decision points. However, if the value gain or experience loss isn’t significant or truly critical, customers rarely switch unless the perceived improvement is meaningful enough to justify the effort of changing platforms.
In B2C, even a little bit of extra value can work in your favor, especially when you’re selling in e-commerce or industries where customers make repetitive purchases.
Competitive churn is most common around renewal cycles, contract ends, or moments of reassessment.
How to Fix This:
Ensure your product team stays aware of competitor updates so you’re not caught flat-footed. From a customer relationship angle, invest in differentiation and relationship strength so customers have fewer reasons to reconsider alternatives.
This could be through loyalty programs or simply superior customer service that creates an emotional bond.

Keep an eye on your pricing and packaging. If competitors are perceived as better value, consider whether your pricing strategy needs adjustment or if you need to communicate better why you’re worth a premium.
7. Lifecycle Breaks Caused by Billing Friction
Not all churn is due to a customer wanting to leave. In subscription businesses, a meaningful share of churn is involuntary and preventable.
If the process for updating payment info isn’t smooth or if customers aren’t properly alerted, they end up churning without consciously deciding to cancel. This creates an avoidable retention break at the exact moment of renewal.
The immediate signal is a failed payment transaction.
How to Fix this:
Involuntary churn is highly preventable with the right tactics. You can implement a robust dunning process that sends timely reminders before a card expires. Notify customers immediately when payment fails. Use structured retry sequences, immediate failure alerts, and grace periods to reduce unintended cancellations.
8. Unresolved Experience Friction
When customers run into problems or have questions, support experiences often determine whether friction becomes churn or recovery. If your customer support isn’t able to solve a problem, effectively resolve product confusion or unblock critical workflows, it leads to a poor experience for the customer, motivating churn.
If users can’t find answers or help when stuck, they may give up on the product entirely. Churn risk increases when customers struggle repeatedly without timely intervention or guidance. This can happen throughout a customer’s lifecycle.
How to Fix This:
Make customer support a priority and proactively assist on all support channels. High-performing support functions as a retention lever, not just an operational necessity. If you’re a smaller company and can’t do 24/7 phone support, set clear expectations so customers aren’t left in limbo. It’s best to monitor product usage for signs of struggle and proactively reach out.
9. Declining Engagement or Loss of Habit
In many cases, churn is gradual, driven by slow disengagement rather than a single breaking point. Customer engagement fades over time as interest and initial excitement wane. Over time, the product stops becoming part of the customer’s routine, reducing retention momentum.
Without intervention, declining engagement is one of the strongest early indicators of churn risk. In e-commerce, it shows up as fewer pages per session. Many companies use churn prediction models that heavily weigh RFM factors. For instance, a telecom business might flag an account if calls, SMS, or data have been dropping month-over-month.
How to Fix This:
The strategy here is to re-engage and re-invigorate usage before the customer is completely gone. Use those early warning signals: if a user’s activity is dropping, trigger a win-back or re-engagement campaign.
Personalization also helps. Remind them of the value they got before, while personalizing the messaging for unique use cases. CleverTap lets you build user segments for each use case to personalize messaging contextually in reactivation campaigns.
10. Customers Not Feeling Recognized or Appreciated
Recognition is a powerful retention driver, especially in long-term customer relationships. It is sometimes overlooked churn driver is when customers feel the business doesn’t value them. Emotional connection often influences retention as much as functional performance.
Feeling unappreciated is often the real reason behind churn, even when customers attribute churn to more surface-level reasons. Robert Gerrish found that 68% of customers leave a business because of a perception of indifference. They think the company doesn’t care about them.
Loyalty attrition is usually a slow burn. However, it can also strike earlier if your business never makes the customer feel welcome.
How to Fix This:
Consistent customer recognition, proactive outreach, and small moments of appreciation strengthen loyalty. Even small gestures like a personalized thank-you note or a shout-out can make a difference.
11. Emotional or Trust-Based Churn Drivers
Emotional churn is often driven by stress, confusion, or declining trust in the experience. If using your product becomes a source of stress or anxiety, customers often disengage simply to reduce complexity or frustration.
Below are some signs that customers show when experiencing emotional churn drivers.
- Overwhelmed users often retreat into limited usage before eventually dropping off.
- A confused user will have erratic usage patterns, possibly repeatedly attempting specific tasks and failing.
These drivers can strike at various points. Feeling overwhelmed or confused often occurs in the onboarding or expansion phase.
How to Fix This:
Design experiences that feel progressive, guided, and confidence-building rather than overwhelming. To avoid overwhelm, consider simplicity and clarity in design. Don’t dump every feature on the user at once. It’s best to guide them progressively.
12. External Life or Market Factors
Some churn is driven by external factors beyond the product experience itself. Often, external factors in the customer’s life or environment cause them to leave, even if they love your product.
While you can’t prevent the external event, you can adapt your relationship with the customer around it. If the value gap is temporary, consider offering a pause or downgrade option instead of outright cancellation. If a customer says they need to cut costs, offer pause options, downgrade pathways, or short-term relief plans to preserve the relationship.
How to Identify and Act On the Root Causes of Churn
Reducing churn starts with diagnosing root causes at the segment and individual-customer level. Funnels and cohort analysis help teams pinpoint where disengagement begins and why it compounds.
Funnel analysis highlights the exact step where customers fail to progress or drop off. For instance, an e-commerce business might create a funnel:
| Initial Purchase → Second Purchase → Third Purchase |
Suppose there’s a big gap between the first and second purchases. It indicates that onboarding or follow-up after the first purchase is a problem. This gap often signals weak post-purchase onboarding or insufficient follow-up, leading to churn before repeat purchase.
Cohort analysis complements this by tracking retention patterns across users acquired in the same period, examining how their retention curves behave.
Platforms like CleverTap automate cohort tracking and experimentation, helping teams validate retention improvements through A/B testing. The platform includes AI-driven churn prediction models that analyze user behavior patterns and engagement to score how likely each user is to churn.
CleverTap is the complete package when you’re aspiring for maximum retention.
- Feature Usage Analysis: CleverTap tracks granular product events to compare how retained users behave versus churned users. Teams identify missing feature adoption, shallow engagement, or friction-heavy features that correlate with churn.
- Qualitative signals at scale: The platform ingests feedback and in-app sentiment signals, linking them to user behavior. This bridges the gap between what users do and why they do it.
- Predictive churn modeling with CleverAI: CleverTap’s AI models analyze dozens of signals, such as inactivity, declining frequency, missed milestones, and support friction to predict churn risk in advance.
Insight only matters when teams can act on it quickly through timely intervention. CleverTap connects analysis directly with prevention actions. The platform’s AI-driven churn scoring tracks user behavior in real time and flags users who show early signs of disengagement. It allows teams to act before users leave.
CleverTap helps you monitor engagement continuously and trigger immediate responses when activity drops or users face friction. The platform lets teams segment users by activity recency, usage frequency, spending, feature adoption, lifecycle stage, and churn risk. This helps teams address different causes of churn with targeted actions rather than sending the same message to everyone.
Reduce preventable churn with CleverTap’s real-time segmentation, predictive insights & automated engagement workflows.
Churn Is Inevitable, But It’s Not Uncontrollable
Most customer churn is due to fixable issues such as poor onboarding or unmet expectations. When teams identify these signals early and respond with timely, relevant actions, churn becomes preventable. Reducing churn is not just about protecting revenue. It is about creating long-term customer relationships that increase lifetime value.
Effective churn reduction requires cross-functional alignment across marketing, product, and customer success, supported by consistent behavioral data. Platforms like CleverTap make this possible by segmenting users in real time and automating personalized retention journeys at scale. Instead of reacting after users leave, teams engage them at the right moment with the right message. Schedule a demo today!
When you treat churn as a managed, proactive process, retention improves, and long-term loyalty strengthens over time.
Agnishwar Banerjee 
Leads content and digital marketing.Expert in SaaS sales, marketing and GTM strategies.
Free Customer Engagement Guides
Join our newsletter for actionable tips and proven strategies to grow your business and engage your customers.