Geographic segmentation segments customer groups to deliver hyper-targeted, location-based strategies for maximum engagement and ROI. This comprehensive guide will explore what geographic segmentation is, why it’s important, its key components, real-world examples across industries, practical strategies for leveraging location data, and the limitations to keep in mind.
In an era where retaining customers is just as crucial as acquiring new ones, understanding where your customers are can be the key to keeping them. Imagine trying to sell snow shovels in Miami or promoting beach vacations to Alaskans in January – those campaigns would likely fall flat. 84% of businesses report revenue growth from localization.
Geographic segmentation is a type of customer segmentation that ensures you send the right message to the right people at the right place, boosting relevance and resonance.
What is Geographic Segmentation?
Geographic segmentation involves dividing a broad market into smaller groups based on location. It simply means categorizing customers by where they live or work – country, region, state, city, ZIP code, or even neighborhood. Geographic market segmentation helps recognize that customer needs and preferences often vary significantly from one location to another.
Why Geographic Segmentation Matters in Marketing
For keeping customers happy and engaged, leveraging location information can dramatically improve campaign performance and customer loyalty.
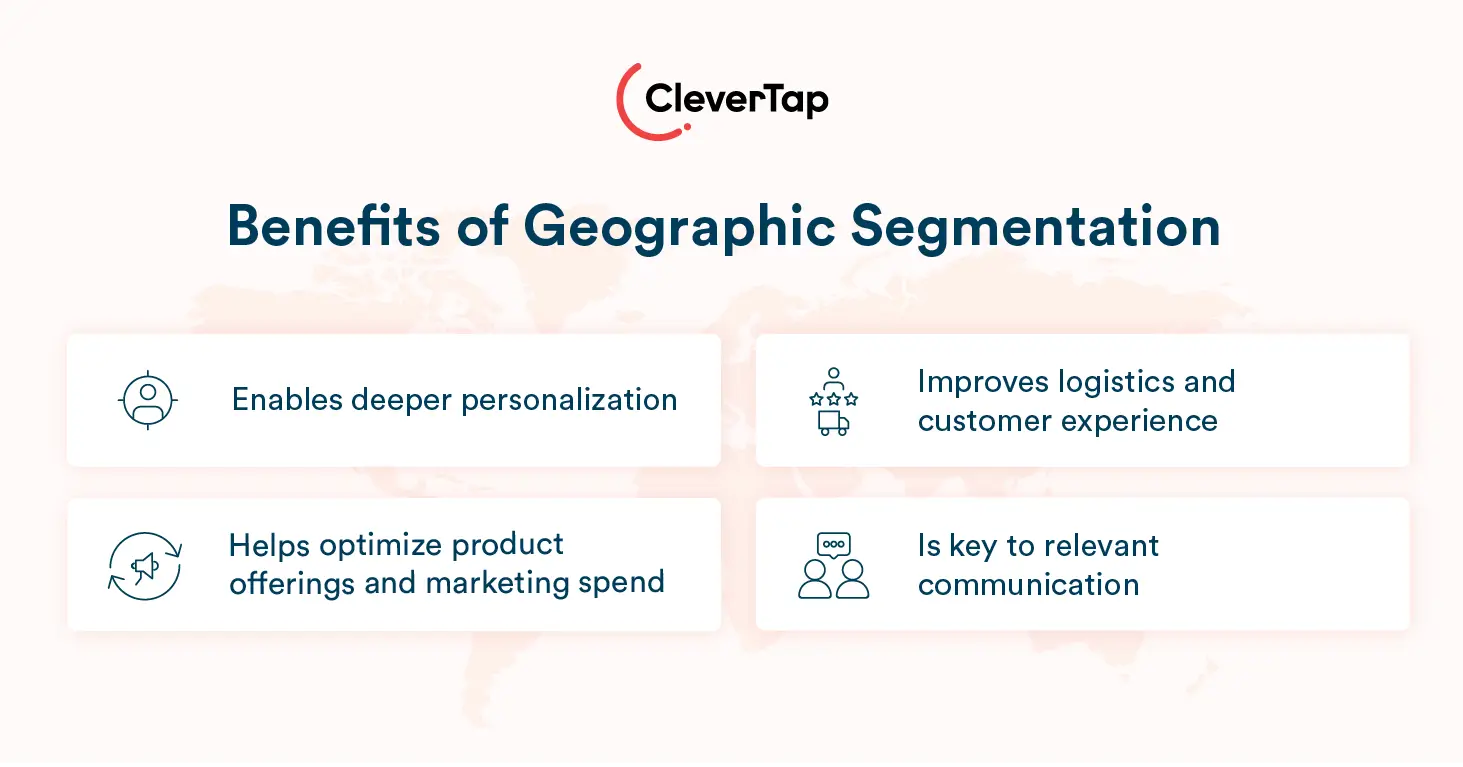
- Geographic segmentation enables deeper personalization and relevance. By segmenting by region, marketers can understand regional preferences and adjust messaging. Different areas have unique cultural nuances, buying habits, and even humor. Recognizing and reflecting these differences in your campaigns shows customers that your brand “gets” them. Customers who feel a brand is in tune with their local culture are more likely to stay engaged and stick around.
- Geographic segmentation helps optimize product offerings and marketing spend. It doesn’t make sense to market products where they won’t sell. Many companies use geographic data to focus their resources where demand is highest. A retailer can allocate more inventory and advertising budget to cold-weather markets and avoid wasting money in warm locales. Geographic analysis aligns supply and demand geographically, ensuring that marketing efforts (and dollars) are spent in the right place.
- Geographic insights can improve logistics and customer experience. Understanding where your customers are helps in practical ways like distribution and customer service. Businesses can position warehouses or service centers strategically or adjust shipping options based on region. Smoother service builds satisfaction, which feeds directly into retention – a customer who consistently gets timely deliveries or region-specific support will trust the brand more over time.
- Geography is key to relevant communication. If you know a customer’s location, you can engage them with timely, place-aware messages: send a push notification about a sale at their local store or email them about an event happening in their city. These gestures show that your brand is not treating them as just IDs in a database but as people with a real-world context. The result is often higher customer engagement. Content localized to a specific region can dramatically outperform generic content – geotargeted social posts can get 6 times more likes, comments, and shares than national posts.
Geographic Segmentation Variables to Consider
Geographic segmentation involves several criteria marketers consider when dividing audiences:

Location (Country, Region, City): Where people live affects consumer behavior. Marketers tailor campaigns by geographic units ranging from continents down to specific cities. Global brands might run different campaigns in Europe versus Asia, reflecting regional preferences. Even within one country, urban areas and rural towns often form separate segments with distinct characteristics.
Climate and Weather: Climate fundamentally affects customer needs. Companies consider whether an area is tropical, arid, temperate, or polar. For example, clothing retailers promote raincoats in rainy regions while pushing swimwear in sunny coastal areas. An outdoor gear company might market snow equipment in winter-prone regions but focus on camping gear in mild-weather locations.
Urban vs. Rural (Population Density): City dwellers typically have different lifestyles and preferences compared to those in small towns. Urban consumers often value convenience and trendy experiences, while rural consumers might prioritize practicality. A home improvement retailer wouldn’t advertise ride-on lawn tractors to Manhattan residents but would target such products to rural communities with appropriate space.
Language and Culture: Multinational companies segment markets by language or cultural regions since these influence message reception. A telecom company might develop separate campaigns for North America (English) and Latin American countries (Spanish). Cultural variations exist even within countries, requiring adaptation to local traditions, values, and customs in marketing materials.
Local Environment and Infrastructure: Whether an area is coastal or inland, mountainous or flat, and the available infrastructure (public transport, internet connectivity) affects product relevance. Ride-sharing apps might target cities with scarce public transit more aggressively. Streaming services could offer high-quality video in regions with good broadband but data-saving features where internet is slower or expensive.
Time Zone: Businesses operating across time zones schedule communications to reach customers at appropriate local times. Companies stagger emails or social media posts so users in different locations receive them at optimal times (e.g., morning hours) rather than middle of the night.
Marketers often combine these components, perhaps segmenting by country and then by urban/rural divisions within each or focusing on climate patterns across regions. Geographic segmentation provides practical frameworks to group customers and create targeted marketing strategies for each segment.
Real-World Examples of Geographic Segmentation in Marketing
Nothing illustrates the value of geographic segmentation better than real examples. Across industries, many companies have used geographic segmentation to improve customer engagement and retention.
Here are six real-world examples of geographic segmentation in action:
1. McDonald’s – Localizing Menus Worldwide
McDonald’s divides its global market by country and even by region or city, and customizes its menu to local tastes. Each market’s preferences can vary wildly, so the company doesn’t push a one-size-fits-all menu. For instance, in Japan, McDonald’s offers seasonal items like a spring-themed Teritama Burger and an autumn Tsukimi burger to align with local tastes and traditions.
By geographically segmenting and then adapting products, McDonald’s stays relevant in each market, which fosters customer loyalty. A person in Tokyo doesn’t get a generic American menu – they get one that feels made for Japanese customers, and that’s a direct outcome of savvy geographic segmentation.
2. Nike – City-Specific Ad Campaign
Nike took geographic targeting to a city-specific level with its acclaimed “Nothing Beats a Londoner” advertising campaign. This video ad was hyper-local, filled with London references, landmarks, local sports heroes, and humor of London’s youth.
The campaign went viral in the UK, shooting to the top of YouTube’s trending chart in hours and even drawing praise from London’s mayor on X.
This example shows that even within a single country, treating a major city as its own segment (with its own culture and attitude) can pay off hugely. It’s a lesson that delivering city-level relevance – referencing a New Yorker’s daily commute in your copy – can make your message far more compelling to that segment than a generic national message.
3. Oddbox – Expanding a Delivery Zone
Oddbox, a UK-based e-commerce subscription service that delivers surplus or “odd-looking” fruits and vegetables to customers, took a smart, localized approach when expanding beyond London, tailoring its marketing to each new region.
Instead of running a broad, one-size-fits-all campaign, the company analyzed consumer behavior in different areas and adjusted its strategy accordingly. Oddbox focused on influencer partnerships and leafleting to build trust in the Midlands, where brand awareness was already high. Meanwhile, in the South West, where consumers were more skeptical of ads, they leaned into grassroots efforts and community-driven messaging.
By segmenting its audience geographically and adapting outreach to match local attitudes, Oddbox kept marketing costs low while ensuring each new market felt personally engaged.
4. Netflix – Region-Based Pricing and Content
Netflix operates globally, but it doesn’t use a single uniform strategy everywhere. One way it segments by geography is through pricing. The price of a Premium plan in wealthier markets differ from those in emerging markets, where the later also has access to cheaper mobile-only plans.
Beyond pricing, Netflix also heavily localizes content. It invests in region-specific content (think Money Heist in Spain or Sacred Games in India) and curates recommendations based on what’s popular locally.
By segmenting its user base country by country, Netflix can boost customer retention: subscribers feel they’re getting content that fits their culture and a price that fits their budget, reducing reasons to churn.
5. Uber – Focusing on Urban Markets
Uber, the ride-hailing app, demonstrates geographic segmentation in its market entry and targeting strategy. Uber operates in thousands of cities worldwide, but notably, it primarily targets urban areas and dense cities rather than rural markets. In fact, using geographic segmentation, Uber realized that its service appeals most to people in cities (who have frequent transportation needs, parking hassles, etc.), so it “only targets the urban demography” when expanding services..
By zeroing in on geographic segments with high demand, Uber efficiently allocates resources and marketing. This focus means Uber can concentrate on improving service in key cities – like offering loyalty programs or special promos in New York, London, or Mumbai – to retain riders there, instead of stretching itself thin trying to cater to everyone everywhere.
6. Wise – Targeting Key Corridors in Fintech
Wise provides a clear example of geographic segmentation in the fintech arena by starting with specific markets. Wise is a digital service for low-cost international money transfers. Rather than launching globally at once, Wise strategically targeted one huge geographic corridor first: the U.S.–Mexico remittance market.
Wise officially launched its service for U.S.-to-Mexico transfers to tap into that concentrated demand, effectively segmenting its initial customer base by that geographic pair. By focusing on a specific region (North America) and a specific use case (sending money to Mexico), the company gained traction among a well-defined audience.
This strategy shows how even in financial services, understanding geographic concentrations of customers allows a company to roll out targeted marketing and product optimizations.
Each of these examples underscores the central point: marketing that accounts for geography can dramatically improve relevance and results. The possibilities range from creative (unique local content) to operational (different service levels by region), all with the aim of delighting customers where they are.
How Marketers Can Use Geographic Segmentation
Knowing the theory of geographic segmentation is one thing – implementing it effectively is another. For retention marketers looking to put location-based marketing insights into practice, here are some actionable strategies and best practices:
1. Tap into Local Culture and Preferences
Think local in your content and messaging. Research the cultural nuances, values, and habits of customers in your key regions. Then, reflect those in your marketing. This could mean referencing local events or holidays in your emails and using imagery that locals identify with. Engaging local influencers can also amplify your message in a way that feels authentic to that community.
2. Adjust to Regional Conditions and Regulations
Every area has its practical realities – laws, regulations, economic conditions, even weather – that should inform your marketing. Ensure you stay informed about local rules (like data privacy laws or advertising regulations) and adapt your strategies accordingly. For instance, if you operate in Europe, you must account for GDPR restrictions.
Adapting to local conditions also means timing around seasons: promote winter sales in the winter of that region, and be aware of local holidays or shopping seasons.
Pro tip: Create a marketing calendar for each major region you serve, mapping out key local dates (from public holidays to big sporting events) and planning campaigns around them. This way, your offers and messages always feel timely and relevant to each geographic segment.
3. Leverage Geographic Data Analytics
Modern analytics tools can break down your customer behavior by geography, showing you where engagement or sales are highest, which regions underperform, and more. Visualization aids like heat maps are especially useful.
For example, if you see that a certain city has a low adoption of a feature, you can run a targeted re-engagement campaign just in that city to boost usage. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and location-intelligence platforms can enrich your data with external factors: population demographics, proximity to stores, etc. The key is to move beyond overall averages and segment your KPIs by region.
4. Use Geo-Targeting in Communications
Many CRM and email marketing platforms allow you to segment lists by city, state, or country. You can create dynamic content in emails that changes based on recipient location.
For push notifications and mobile marketing, consider using geofencing – sending messages to users when they enter a certain area. A classic use case: a retail app might ping a customer with a special offer when they come within a few blocks of one of your physical stores. Location-based push campaigns have seen success in driving in-store visits and can be highly engaging (“Welcome back to [City]! Here’s 20% off at our local branch just for you.”).
Social media ads should also be geographically segmented. If you’re running Facebook or Instagram campaigns, take advantage of location filters so that, say, your West Coast audience sees one version of the ad (perhaps mentioning a local store or using an image of their city skyline) and your East Coast audience sees a different, locally tailored version.
5. Customize Offers and Services by Region
Analyze what features or products resonate in different areas and tailor your retention offers accordingly. Consider this retail market segmentation example: an e-commerce marketplace might find that customers in coastal cities buy more outdoor gear, so they could create a loyalty program tier or special discounts around outdoor products for those regions.
Even loyalty incentives can be localized: a ride-hailing app could offer discounted rides during a city’s big annual festival to reward local users, knowing that’s when they need the service most.
6. Integrate Geographic Segmentation with Other Segmentation Methods
Geography provides a powerful lens, but it shouldn’t exist in a vacuum. The best retention strategies often layer multiple segmentation criteria. Once you have your geographic segments, consider overlaying demographic info (age, gender, income) or behavioral info (loyalty status, purchase history) to craft even more precise campaigns.
For instance, instead of a one-size-fits-all email to all California customers, you might send one version to your Gen Z California customers and a slightly different one to your Gen X California customers, blending demographic and geographic insights (also known as geodemographic segmentation). This integrated approach brings nuance: you acknowledge that within a geographic segment, there are sub-segments.
Modern marketing platforms make it feasible to manage these complex segment combinations. The result is highly personalized retention tactics that consider the full context of the customer – where they are, who they are, and how they behave.
Searching for smarter targeting? See which of the 10 best customer segmentation tools is best for your business.
Driving Engagement with Geographic Segmentation: How BharatPe Boosted CTRs with CleverTap
BharatPe, a leading Indian fintech company, sought to enhance user engagement and reduce drop-offs in their app. By using CleverTap’s advanced geographic segmentation capabilities, BharatPe tailored their communication strategies to align with regional preferences and behaviors.
For instance, when targeting Marathi-speaking merchants, they segmented users based on geographic location and past behavior to deliver messages in Marathi, fostering a more personalized user experience.
Incorporating CleverTap’s analytics, segmentation, and funnels helped BharatPe create automated, personalized journeys, finally helping them double their push notification CTRs.
Limitations and Challenges of Geographic Segmentation
While geographic segmentation is powerful, it has important limitations:
- Over-Segmentation Risks: Dividing markets too granularly can create segments too small to be economically viable. This can dilute marketing efforts and waste resources on campaigns that don’t yield meaningful results. The challenge is finding balance—segments should be distinct enough to customize for but large enough to matter.
- Data Collection and Accuracy: Effective geographic segmentation depends on good data. Customer location information may be incomplete or outdated as people move and neighborhoods change. Collecting accurate data might require third-party sources, GIS databases, or customer updates, which can be resource-intensive. Marketing teams also need appropriate tools and expertise to analyze geographic data properly. Maintaining current and precise geographic information is an ongoing challenge.
- Integrating with Other Factors: Geography alone might overlook vital customer attributes. Two neighbors could have entirely different behaviors or needs. Geographic segmentation doesn’t account for age, gender, income, lifestyle, or purchase behavior without incorporating other segmentation types. Relying solely on location risks broad-brushing audiences and missing nuances. The challenge is combining segmentation approaches effectively.
- Generalization and Stereotyping: This approach risks assuming everyone in a particular area is alike, leading to stereotyping. Geography is a blunt instrument; without qualitative understanding, marketers may rely on generalizations that don’t apply to every individual. Geographic segmentation should be a starting point, with assumptions validated through research.
- Globalization and Digital Communities: In the internet age, geography isn’t always the defining factor it once was. People worldwide might share interests unrelated to physical location. Geographic segmentation can miss cross-border commonalities, while trends spread quickly online, reducing regional differences in certain segments.
Despite these limitations, geographic segmentation remains foundational when used thoughtfully—leveraging its strengths while addressing its blind spots with additional data and sound judgment.
The Enduring Role of Geographic Segmentation in Modern Marketing
Geographic segmentation has evolved through sophisticated tools like real-time geolocation and big data analytics. It can transform generic campaigns into finely tuned initiatives that resonate with customers on a personal level, driving satisfaction, loyalty, and lifetime value.
Knowing where customers are often provides the foundation for truly knowing them, anchoring retention marketing in real-world contexts that make geographic segmentation indispensable.
Shivkumar M 
Head Product Launches, Adoption, & Evangelism.Expert in cross channel marketing strategies & platforms.
Free Customer Engagement Guides
Join our newsletter for actionable tips and proven strategies to grow your business and engage your customers.