Price segmentation is a strategic pricing approach that allows businesses to optimize revenue by offering different prices to different customer groups based on their willingness to pay, purchasing behavior, and market dynamics. It plays a crucial role in modern pricing strategies by ensuring that businesses can maximize value capture while meeting customer expectations.
This blog explores the fundamentals of price segmentation, its benefits, types, and best practices to help businesses implement effective segmented pricing strategies.
What is Price Segmentation?
Price segmentation is a pricing strategy that involves setting different prices for the same product or service based on customer characteristics, buying behavior, geography, or other market-driven factors. Businesses can fine-tune their pricing models by leveraging data and customer insights to optimize sales and profitability.
Different customers have different price sensitivities, and price segmentation ensures businesses can capture more value by charging higher prices to those willing to pay more while offering discounts to price-sensitive buyers. For example, airlines adjust fares based on demand and customer profiles, allowing them to optimize revenue. Businesses use segmented pricing to:
- Maximize revenue
- Improve customer satisfaction
- Cater to varying price sensitivities among different groups
Tailoring prices based on customer needs and affordability can make products and services more accessible to different customer segments while ensuring a fair exchange of value. For instance, streaming services like Netflix offer tiered pricing models, catering to both budget-conscious users and premium customers.
Benefits of Price Segmentation
Here’s why a segmented pricing strategy is beneficial for businesses:

- Increased Sales and Revenue: Businesses can optimize pricing to attract a broader customer base while maximizing profits.
- Competitive Advantage: Price segmentation allows businesses to remain competitive by offering customized pricing strategies.
- Better Customer Targeting: Pricing differentiation enables more personalized marketing efforts, leading to improved customer retention.
- Improved Profit Margins: By identifying high-value customers, businesses can charge premium prices where justified, leading to increased margins.
- Enhanced Market Penetration: Companies can expand their reach by offering lower prices to price-sensitive segments while maintaining higher prices for those who value premium offerings.
Types of Segmented Pricing
Pricing segmentation can be done based on several criteria, such as customer segments, volume, channels, and more. Here are some of the common types of price segmentation.
| Type | Description | Example |
| Customer-Based Pricing | Pricing is based on the customer profile, such as first-time buyers, loyal customers, and others. | Loyalty program discounts for frequent buyers. |
| Geographic Pricing | Adjusting prices based on a customer’s location due to cost variations, local demand, or purchasing power. | Different pricing for urban vs. rural markets. |
| Volume-Based Pricing | Offering discounts based on purchase quantity to encourage bulk buying. | Wholesale discounts for retailers buying in large quantities. |
| Time-Based Pricing | Adjusting prices based on demand fluctuations over time. | Peak vs. off-peak pricing for airline tickets and hotel rooms. |
| Channel-Based Pricing | Setting different prices based on the sales channel used. | Lower prices for online purchases compared to in-store prices. |
| Demographic Pricing | Setting different prices based on specific demographic characteristics such as age, gender, or occupation. | Discounted public transport fares for students and elderly citizens. |
| Attribute-Based Pricing | Pricing is based on the features being offered. | Base car models offer fewer features and are less expensive than top models. |
| Value-Based Pricing | Pricing is based on the perceived value of the product or service. | Luxury watches are priced higher due to brand perception. |
How to Build a Segmented Pricing Strategy
A well-structured segmented pricing strategy requires a thorough understanding of customer behavior, market conditions, and business objectives. Here are the key steps to develop and implement an effective segmented pricing strategy.

1. Identify Market Segments and Customer Groups
The first step in building a segmented pricing strategy is identifying different customer groups. You can segment your audience based on demographics, such as age, income, gender, and occupation; geographic location, such as region, country, urban vs. rural; behavioral patterns, such as purchase frequency, brand loyalty, and price sensitivity; and psychographics such as lifestyle, values, interests.
2. Analyze Purchase Behavior and Willingness to Pay
Understanding how different segments interact with your product and their price sensitivity is crucial. This requires analyzing historical sales data to identify purchasing trends, conducting customer surveys and interviews to assess perceived value, and competitor analysis to benchmark pricing strategies.
3. Choose the Right Segmentation Model
Decide which pricing segmentation method best aligns with your business objectives, i.e., determine whether to segment based on geography, customer demographics, purchase volume, or other criteria.
4. Develop Pricing Tiers and Set Price Points
Once segments are defined, the next step is to establish pricing tiers based on value perception and willingness to pay. This can be done by:
- Creating multiple pricing levels to cater to different segments.
- Using anchor pricing (showing premium and economy options to make mid-range products more appealing).
- Offering add-on services to justify higher prices for premium users.
5. Test and Optimize Pricing Strategies
Before full implementation, it is recommended to run A/B tests to evaluate the impact of pricing variations. You can perform dynamic pricing tests by adjusting prices in real-time to gauge elasticity, market segmentation analysis to measure how different groups react to price changes, and promotional pricing experiments to test limited-time offers for specific segments.
6. Maintain Transparency and Avoid Price Discrimination
To ensure customer trust, the price segmentation strategy should be transparent and justified. Businesses should avoid hidden fees or misleading discount structures.
7. Monitor Performance and Adjust Strategies
Ongoing analysis is necessary to refine price segmentation. Businesses should track conversion rates and revenue trends across segments, watch over customer feedback and complaints related to pricing, and adjust price points based on market shifts and competitive actions.
Examples of Segmented Pricing
Let’s look at how some of the leading businesses across industries are using price segmentation:
E-Commerce
- Amazon: Uses dynamic pricing algorithms to adjust prices based on demand, user behavior, and competition.
- eBay: Offers volume discounts to buyers purchasing multiple quantities.
Financial Services
- American Express: Provides different credit card pricing structures based on customer spending habits and rewards eligibility.
- Robinhood: Provides commission-free trading for general users while offering a premium Gold membership with added benefits at a higher price.
Online Streaming
- Netflix: Provides different pricing tiers, including a basic ad-supported plan and a premium 4K plan.
- Spotify: Offers discounts to students and family plans for shared access.
Education
- Coursera: Offers lower pricing for students and financial aid options for users from low-income countries.
- Adobe Creative Cloud for Education: Provides significant discounts to students and teachers compared to business pricing.
Challenges in Price Segmentation
Implementing an effective segmented pricing strategy is not without challenges. These include:
- Balancing Customer Perception and Profitability: Finding the right balance between customer satisfaction and maximizing revenue.
- Risks of Customer Alienation: Customers may perceive price segmentation as unfair if not properly communicated.
- Market Sensitivity: Segmented pricing may face resistance in highly competitive markets where customers compare prices across segments.
- Regulatory Considerations: Some industries, such as financial services, healthcare, and telecommunications, have legal restrictions on how pricing can be segmented.
- Managing Complexity: Multiple pricing tiers can increase administrative and operational challenges.
Best Practices for Price Segmentation
Here are the best practices for implementing a price segmentation strategy effectively.
- Leverage Data-Driven Insights
Successful price segmentation starts with data. Businesses should analyze purchase history, customer demographics, behavior patterns, and market trends. AI-driven pricing models and analytics tools can help in identifying pricing trends and opportunities for segmentation.
- Implement Transparent and Justifiable Pricing Policies
To maintain trust and avoid customer backlash, businesses should communicate why different prices exist. Customers should feel that pricing differences are fair and based on value rather than arbitrary discrimination.
- Regularly Monitor and Adjust Pricing Strategies
Market dynamics change, and so should segmented pricing strategies. Regularly review performance metrics and adjust pricing to match customer expectations and competitive movements.
- Avoid Over-Segmentation
Too many pricing tiers can confuse customers and complicate operations. Keep pricing structures simple, targeted, and easy to understand.
- Test and Optimize Pricing with A/B Experiments
A/B testing allows businesses to compare different pricing models and determine which drives the best conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
- Align Pricing with Customer Perceived Value
Pricing should reflect what customers believe the product is worth. Brands should emphasize quality, exclusivity, and benefits to justify higher price points for premium segments.
- Balance Profitability and Customer Accessibility
Price segmentation should ensure that while premium segments maximize revenue, cost-sensitive customers still have access to the product.
- Consider Legal and Ethical Implications
Segmented pricing should comply with consumer protection laws and industry regulations. Companies should ensure that price segmentation does not lead to illegal price discrimination.
How CleverTap Can Help With Price Segmentation
CleverTap’s segmentation capabilities can be effectively used for price segmentation by leveraging its advanced segmentation models and real-time data processing. Here’s how:
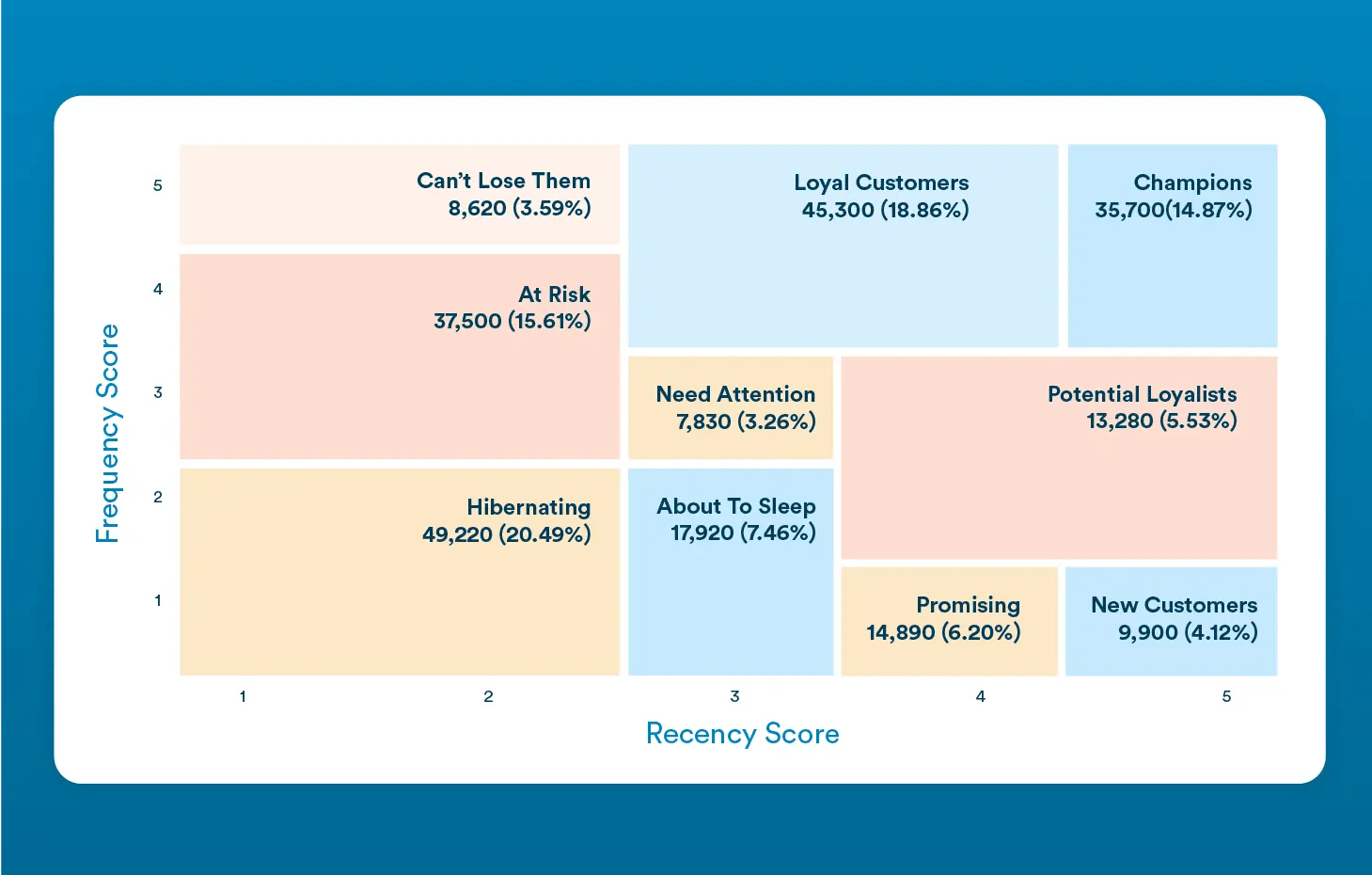
- RFM-Based Price Segmentation
CleverTap’s Recency, Frequency, and Monetary (RFM) Segmentation helps identify high-value customers based on their purchasing behavior. This allows businesses to offer premium pricing to high-value customers, discounted pricing to at-risk customers, and special promotions or exclusive deals to price-sensitive customers.
- Behavioral and Intent-Based Segmentation
CleverTap can track user behavior in real time by analyzing:
- Past purchase history to segment users into different pricing tiers.
- Browsing behavior to determine interest in high vs. low-priced products.
- Cart abandonment to offer personalized price incentives to buyers.
- Real-Time Segmentation for Flash Sales
With CleverTap’s real-time segmentation, brands can instantly identify users who respond to discount-based campaigns, send personalized price offers based on a user’s purchase urgency, and dynamically adjust pricing for different user cohorts during flash sales.
Maximizing Revenue and Customer Value with Price Segmentation
Price segmentation is a powerful strategy for businesses looking to optimize revenue, improve customer satisfaction, and enhance market penetration. By understanding different types of segmented pricing and leveraging data-driven strategies, businesses can implement effective pricing models tailored to different customer segments.
Implementing a well-structured segmented pricing strategy requires ongoing analysis, transparency, and a keen understanding of customer behavior. Companies that master price segmentation can create a win-win scenario—offering fair value to customers while driving business growth.

Explore how price segmentation can transform your pricing strategy and boost profitability.
Shivkumar M 
Head Product Launches, Adoption, & Evangelism.Expert in cross channel marketing strategies & platforms.
Free Customer Engagement Guides
Join our newsletter for actionable tips and proven strategies to grow your business and engage your customers.