01000011 01101100 01100101 01110110 01100101 01110010 01010100 01100001 01110000.
Did you get that? For those of you who can’t read binary, the direct translation is “CleverTap.”01
Don’t be ashamed to admit you can’t read binary. After all, computers have difficulty understanding human speech too. When you think about the variability of the spoken word, you must consider the number of different languages, dialects, speech impediments, mispronunciations, and more.
In the English language alone, the possibilities for unique combinations of words are just shy of infinity. And with roughly 6,500 spoken languages in the world today… you do the math.
What Is Natural Language Processing?
Natural language processing (NLP) is the interdisciplinary field of computer science and linguistics, using machine learning to achieve the end goal of artificial intelligence. Simply put, it allows computers to understand human language — speech or text.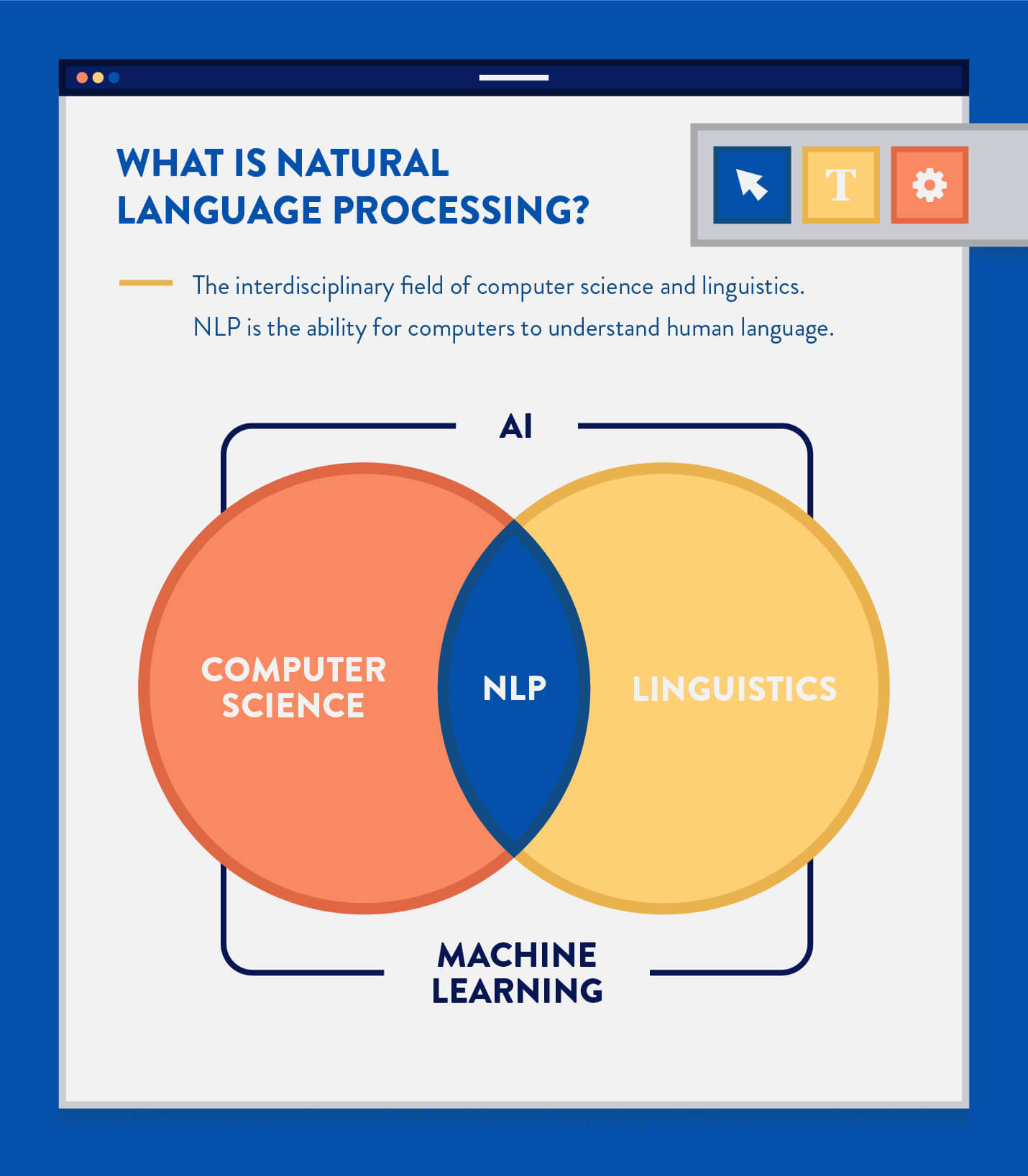
NLP is the ability to automatically receive, understand, and operate on human language in the raw written or spoken form.
Think about the communication loop between humans: a sender encodes a message through a medium (spoken or written word), and the receiver decodes the message and responds with feedback, whether it be an answer or simply an acknowledgment.
Computers must use this very same communication loop with a lot of gray area in the receiving and decoding of messages.
In this article, we explore innovations within natural language processing, the products currently built with it, and how marketers can leverage this technology. Continue reading or jump directly to our infographic for a concise summary.
Why Natural Language Processing Is So Difficult
We should start with the problem.
Computers are very good at processing structured data. Language, however, is about as far from “structured” as data gets.
There is a whole field of scientific study dedicated to linguistics and the attempt to make language structured. Unfortunately, in the case of real-world language, the laboratory is staffed by average people, which makes uniformity a near impossibility.
Meaning-full Words
A single spelling of a word can have multiple meanings (homographs) and two words can sound alike but have very different meanings (homonyms).02 Full sentences have grammatical syntax, semantic meaning, and desired message intent.
Here are some examples:
- Homograph: Think about the phrase “try our new app.” This could be a mobile marketer trying to promote their application or a restaurant advertising a new appetizer.
- Homonym: The words “be” and “bee,” although they sound the same, have very different meanings.
These subtleties make natural language processing extremely difficult. Humans have a firm grasp on the context of each word being used, and therefore understand when we are talking about a “bee sting” and not “be Sting” (The Police, anyone?).
Parts of Speech and Phrase Structure
This complexity doesn’t stop with individual words. Phrase and sentence structure further complicate the computer’s task of understanding human language. A full sentence often includes various parts of speech, each with a different role — such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions, and more.
When you put everything together, new obstacles arise, including grammatical conventions and how the words contextually depend on each other to convey the intended message. Let’s see how computer scientists have worked to solve these problems.
How Natural Language Processing Works
Computers must first be trained on the grammatical rules of the language in order to build a parse tree, which identifies the parts of speech within a sentence. Once computers are able to understand the very basics of the language’s conventions, simple questions and commands can be parsed with a high rate of success.
If the language input is spoken, instead of written, a new set of problems arise. We have come to understand this problem as speech recognition.
Speech Recognition
The ability for computers to “hear” speech and analyze the content being spoken is extremely difficult. If you ask Siri, Alexa, or Google a question, it compares the audio to millions of other audio files that have been tagged as accurate to match what the speaker meant.
But first, the computer must understand the difference between vowels and consonants. The computer microphone hears the audio and plots the magnitude of the frequencies each sound emits. Just as lightwaves have a “signature” of color, soundwaves that resonate in a microphone from a vocal tract have a signature known as “formants.”
Formants are how NLP enables conversational interfaces to recognize each sound and compose individual words and sentences.
Speech Models
Early NLP efforts were constructed on verbose rule-based algorithms that were very strict and the rules actually became hindrances for progression. As machine learning grew in ability and popularity, new algorithms were developed based on statistical modeling.
These statistical models make probabilistic decisions based on the plethora of data available to pull from. One such model is Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), developed by Google.
Using the enormous amounts of data available on the web, Google has pre-trained the model to increase accuracy for question answering and sentiment analysis. The results have been outstanding and have even surpassed human-level performance.03
How Natural Language Processing Is Used Today
NLP is used in many different ways today, from the analysis of social media harassment to answering questions about weather forecasts and more. If you’ve ever asked Siri or Alexa a question, you have interfaced with NLP.
Some of the most basic ways in which NLP is used is for spam detection and identifying parts of speech. The spam filter on Gmail, for example, analyzes incoming emails for header information, IP addresses, and content for any signals of spam.
A more difficult use case for NLP is sentiment analysis. Analyzing the entire text for context, semantics, and pragmatics is extremely difficult. Sarcasm, for example, no matter how subtle, is understood by few readers, and even fewer computers.
As the field of study around NLP progresses, the problems being tackled have naturally increased in difficulty. OpenAI, for example, has successfully created an unsupervised model for text generation.04 The NLP model is given a corpus of text about a given topic and is tasked with composing original prose about the subject.
Here is a summary of ways NLP can be used:
- Spam detection
- Parts of speech identification
- Sentiment analysis
- Text composition
- Question answering
- Automatic summarization
- Conversational interfaces
Now that we understand how it can be used, who exactly is putting NLP to use in the real world?
Who Uses Natural Language Processing?
Developer tools built to extend natural language processing are becoming widely available. IBM’s Watson, for example, has solutions for translation, natural language understanding, sentiment analysis, and much more.05
Here are some of the most common examples of natural language processing being used by businesses today.
Alexa and Siri Integrations
Many companies have seen the transition to voice interfaces as an important area to address for their business. Amazon’s Alexa Skills Kit (ASK) and Apple’s SiriKit provide developers with the documentation and tools to build conversational interfaces for Alexa and Siri.
Ride-hailing companies, for example, have enabled users to hail a ride by simply asking Siri or Alexa for an Uber, Lyft, or their ride-sharing app of choice.
News briefings, connected car and home capabilities, and games are all being built using the NLP tools of the day. In fact, 50% of Alexa users reported asking for news updates and weather forecasts the most.06
Chatbots
You may be more familiar with the early forms of chatbots when calling a large company’s customer service hotline and the subsequent maze of options leading to a string of digits longer than the original phone number. Since these tools first became an option (and nuisance) AI chatbots have become the customer service option du jour for many businesses.
Although it can be equally frustrating to receive the reply “Sorry, I didn’t understand that” from modern chatbots, many businesses have built intelligent chatbots. Expedia, for example, uses a Facebook Messenger chatbot to help manage trips, including booking hotels and flights, by directly interfacing with the chatbot.07
Natural Language Processing For Your App
Whether you decide to build an Alexa skill for your users to interface with the Echo, or a chatbot for your customer service, language interfaces are on track to become a large component of the user experience.
Understanding how natural language processing works can give you a competitive advantage for managing customer data throughout the user journey. You can use sentiment analysis, for example, to gauge the user’s experience through their tone of voice or text.
Intelligent marketing platforms are becoming essential tools for modern mobile marketers to grasp. CleverTap has built a suite of intelligent marketing tools to provide valuable insights that allow marketers to focus on their respective business goals. Sign up for a free demo to see how CleverTap can optimize your mobile marketing efforts.

See how today’s top brands use CleverTap to drive long-term growth and retention
Subharun Mukherjee 
Heads Cross-Functional Marketing.Expert in SaaS Product Marketing, CX & GTM strategies.
Free Customer Engagement Guides
Join our newsletter for actionable tips and proven strategies to grow your business and engage your customers.