Gender segmentation is the practice of dividing your audience based on their gender identities. This blog explores what it is, why it matters, effective strategies, real-world examples, key challenges, and how tools like CleverTap can help.
Segmenting the target audience based on gender has been used by marketers for decades to tailor products and advertising strategies. A study found that female leads had a 20% higher lifetime value than male leads, while another study found that female order values were 5–9% lower than male order values.
Today, shifting cultural landscapes and increasing consumer consciousness around equality and representation make it more important than ever to apply gender market segmentation in a thoughtful, inclusive manner. Businesses that get it right can unlock loyal, long-term customer relationships—provided they avoid stereotypes and remain sensitive to the evolving nuances.
What is Gender Segmentation?
Gender segmentation, a subset of demographic segmentation, is a marketing strategy that divides a target audience based on gender. This helps brands categorize their target markets based on gender to create more personalized marketing campaigns, develop relevant products, and optimize user experiences.
Businesses leverage data points such as gender and consumer behavior to create marketing messages that resonate with each segment. For example, fashion and beauty brands often create gender-specific product lines, such as men’s grooming kits and women’s skincare collections.
Why is Gender Segmentation Important
Gender-based segmentation allows brands to refine their marketing strategies for higher engagement, better conversion rates, and increased customer satisfaction. Here’s why it matters:
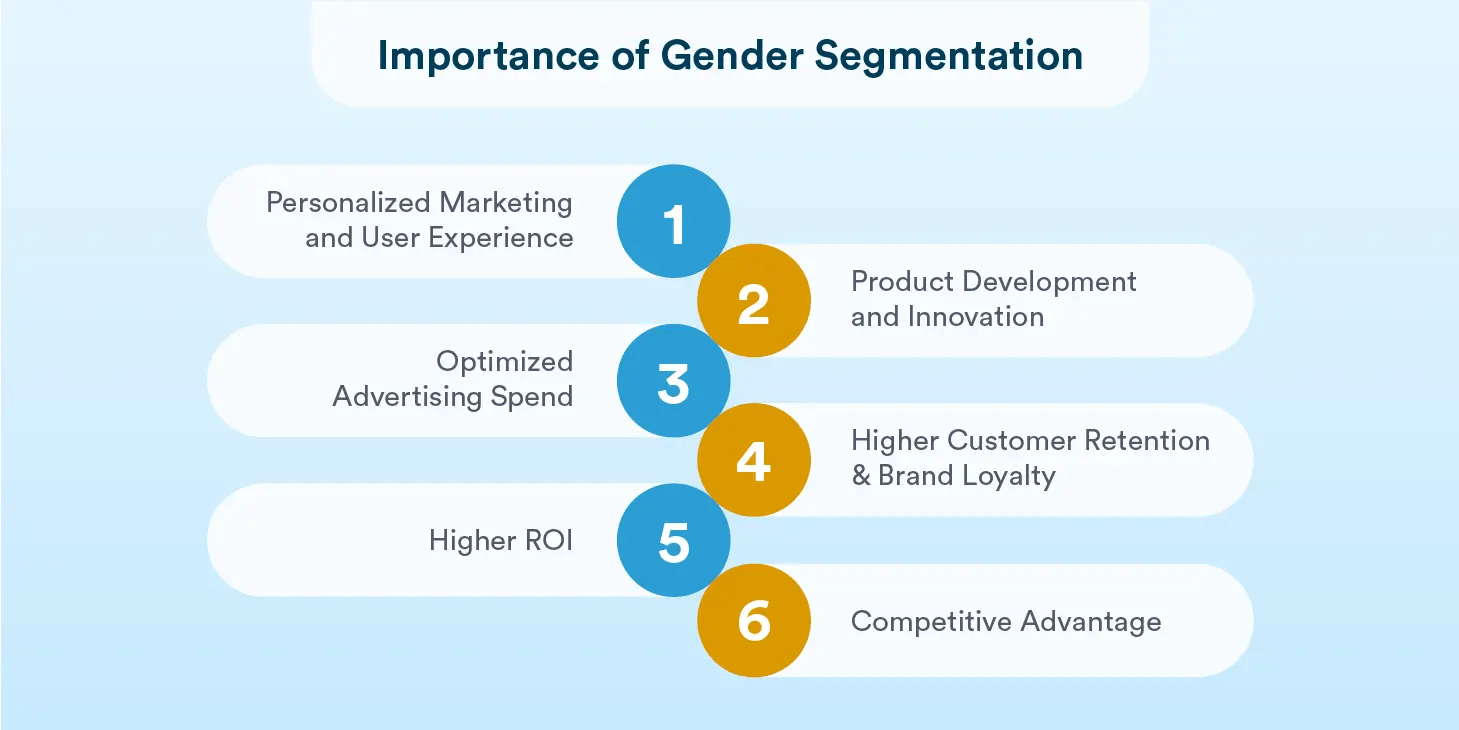
- Personalized Marketing and User Experience: Businesses can craft targeted messages, visuals, and campaigns that appeal to different genders, leading to stronger customer engagement.
- Product Development and Innovation: Understanding gender-specific preferences helps brands design products that cater to different market needs (e.g., fitness gear, skincare, fashion apparel).
- Optimized Advertising Spend: Rather than taking a one-size-fits-all approach, segmenting the audience based on gender enables brands to allocate budgets efficiently for gender-targeted ads.
- Higher Customer Retention & Brand Loyalty: When customers feel that a brand understands their preferences and needs, they are more likely to stay engaged and return for future purchases.
- Higher ROI: When marketing messages resonate on a deeper level—particularly through design, tone, or product features—brands often see higher engagement and improved ROI.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies that leverage gender insights effectively can differentiate themselves in the market by offering products and experiences that resonate with their audience.
Effective Strategies for Gender Segmentation
To successfully implement gender segmentation in marketing, businesses must take a modern, data-driven, and inclusive approach while avoiding outdated stereotypes. Here are some key strategies:
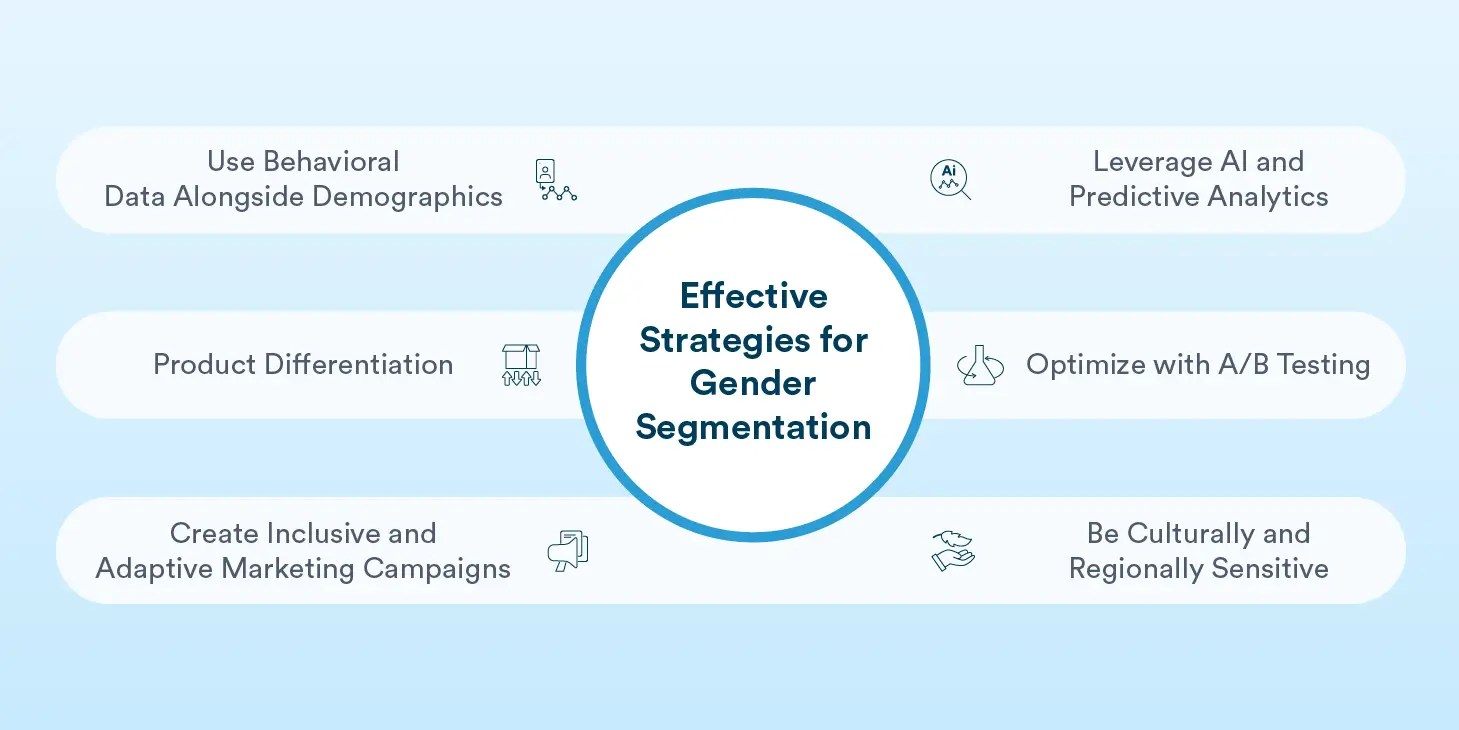
1. Use Behavioral Data Alongside Demographics
Businesses can gather voluntary gender information through surveys or user account sign-ups. However, instead of relying solely on gender as a determining factor, it should be combined with purchase history, browsing behavior, and preferences to create a more nuanced understanding of different gender segments.
2. Product Differentiation
Many industries now recognize that gender-based segmentation alone isn’t enough—segmenting by lifestyle and interests can provide more effective targeting. For example, creating visually distinct packaging and product design elements or adjusting product features or benefits to better align with different gender needs, such as specialized ergonomic differences in clothing or accessories.
3. Create Inclusive and Adaptive Marketing Campaigns
With evolving perspectives, businesses must navigate gender segmentation carefully to avoid outdated stereotypes and ensure ethical marketing practices. Even if you have gender-specific product lines, ensure your broader brand messaging celebrates diversity and avoids stereotypes.
4. Leverage AI and Predictive Analytics
AI-powered tools can analyze customer data to identify trends in gender-based shopping behaviors, enabling businesses to craft hyper-personalized marketing campaigns.
5. Optimize with A/B Testing
Running multiple variations of campaigns for different gender segments helps businesses determine which messaging resonates best with each audience.
6. Be Culturally and Regionally Sensitive
Gender-based segmentation strategies should be aligned with local cultural norms and evolving discussions on gender preferences and sensitivities, ensuring campaigns are relevant and respectful.
Gender Segmentation Examples
Here are a few examples of leading brands benefitting from segmentation based on gender:
1. Nike’s Women’s Campaigns
Nike develops specialized athletic wear for women, showcasing female athletes and promoting empowerment through targeted campaigns like “Dream Crazier.” These campaigns resonate strongly with women, driving engagement and reinforcing Nike as a leading brand that champions inclusivity and athletic excellence for all genders.
2. Birchbox & Birchbox Man
Initially focused on beauty product samples for women, Birchbox later launched Birchbox Man, featuring grooming products tailored specifically for men. The brand widened its subscriber base and addressed the distinct preferences of male and female consumers by curating gender-specific product offerings, and boosting subscription and retention rates.
3. Coca-Cola’s Diet Coke vs. Coke Zero
Diet Coke has long been marketed more heavily toward women, focusing on themes like fashion partnerships and sleek packaging. Coke Zero was introduced with branding, colors, and ad campaigns (often featuring sports or action themes) to appeal more to men. By positioning two low-calorie products for different gender segments, Coca-Cola expanded its overall market share in the diet soda category and satisfied varied consumer preferences.
Challenges and Considerations in Gender Segmentation
While gender segmentation offers numerous benefits, businesses must be cautious of potential ethical and strategic pitfalls, including:
1. Risk of Reinforcing Stereotypes
Overly simplistic segmentation based on traditional gender norms can alienate consumers who feel misrepresented. This can manifest in product packaging, messaging, and advertising that leans too heavily on outdated gender roles—such as assuming that all women prefer pink or that men are only interested in rugged, hyper-masculine branding.
Marketing that relies on such stereotypes can not only reduce brand credibility but also drive away modern consumers who seek more inclusive and nuanced messaging.
2. Gender-based Price Discrimination
In some markets, there’s a notable disparity in pricing known as the “pink tax,” where products for women are priced higher than the same or similar products for men. This pricing practice has faced increasing scrutiny, with regulatory bodies pushing for more transparency.
For example, the European Union has addressed this issue with a 2012 ban on gender-based pricing in insurance. In the United States, while no federal law explicitly prohibits it, some states, such as California, have taken legislative steps to ban gender-based price discrimination. Companies engaging in such practices risk reputational damage and potential regulatory intervention.
3. Cultural Sensitivity
Gender perceptions and expectations vary widely across regions and cultures. A marketing campaign that is well-received in one country may be seen as insensitive or offensive in another.
Furthermore, some regions have stronger consumer protection movements and stricter guidelines on stereotypical advertising, making it crucial for marketers to tailor their strategies accordingly. Understanding cultural nuances is key to ensuring that marketing efforts remain relevant and respectful.
4. Privacy & Data Collection
The collection and use of gender data must comply with strict privacy regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe, CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in the U.S., and similar policies in other regions. Companies must be transparent about why they collect gender data, how it is stored, and whether it is shared with third parties.
Failure to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines, legal repercussions, and loss of consumer trust. Read our detailed blog on GDPR and CCPA Compliance to understand how you can ensure compliance with these critical privacy laws to protect consumer data.
5. Over-Segmentation Leading to Market Fragmentation
While gender-based segmentation can help tailor marketing efforts, excessive segmentation may result in unnecessary complexity and inefficiencies. When businesses create hyper-targeted products for different gender groups, they may inadvertently increase production, distribution, and marketing costs while limiting their potential audience.
Leveraging CleverTap for Effective Gender Segmentation
With CleverTap’s robust gender segmentation capabilities, businesses can group and target users based on their gender-specific behaviors and preferences. Here’s how it works:
- User Profile Attributes: CleverTap captures gender as a user property, allowing marketers to create segments based on gender-specific attributes.
- Advanced Segmentation: CleverTap’s segmentation engine allows businesses to create real-time, nested, and actionable segments based on user behaviors, demographics (including gender), and engagement history.
- Hyper-Personalized Engagement: Once gender segments are created, brands can tailor content, offers, and messaging styles that resonate with different gender groups, optimizing engagement and conversion rates.
- Omnichannel Targeting: CleverTap supports multi-channel marketing, ensuring that gender-specific campaigns can be executed through push notifications, emails, WhatsApp, SMS, and more.
- AI-Powered Insights: Using AI and machine learning, CleverTap can analyze gender-based engagement trends, helping marketers refine their strategies to maximize impact.
See CleverTap’s robust segmentation capabilities in action! Request a personalized demo today!
The Future of Gender Segmentation
As gender perceptions and consumer expectations continue to evolve, businesses must rethink their approach to gender segmentation in marketing. Rather than relying on traditional distinctions, forward-thinking brands are shifting toward interest-based and lifestyle-driven segmentation, ensuring their marketing strategies resonate with a broader and more diverse audience.
Additionally, advancements in AI and machine learning are enabling hyper-personalized experiences, allowing businesses to refine their targeting without reinforcing outdated gender norms. Ultimately, ethical and transparent marketing practices are no longer optional—they are essential for maintaining consumer trust. As audiences demand greater social responsibility from brands, companies must embrace inclusive segmentation strategies that prioritize authenticity and representation.
Explore how CleverTap can help implement smarter segmentation strategies. Request a demo today!
Kiran Pius 
Leads Product Launches, Adoption, & Evangelism.Expert in cross-channel marketing strategies & platforms.
Free Customer Engagement Guides
Join our newsletter for actionable tips and proven strategies to grow your business and engage your customers.