Retail has become omnichannel, with customers able to shop seamlessly across physical stores, websites, and mobile apps. Even brick-and-mortar stores now have some online presence. With this shift, businesses now have access to vast amounts of customer data, enabling them to deliver more personalized shopping experiences.
But how can retailers effectively use this data to engage customers and boost sales? The answer lies in retail market segmentation—a strategy that categorizes customers into distinct groups based on shared characteristics, helping businesses optimize marketing, product offerings, and overall customer experience. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of retail market segmentation, the steps to implement it, real-world examples of customer segmentation in action, and the challenges retailers must overcome to make it work effectively.
What is Retail Market Segmentation?
Retail market segmentation is the strategic process of dividing a diverse customer base into distinct groups based on shared characteristics, such as customer demographics, behaviors, preferences, or needs. These groups allow retailers to tailor their marketing strategies, product offerings, and shopping experiences to better meet customer needs.
Imagine a national grocery chain analyzing customer data. In urban areas, they notice high demand for plant-based and organic products, while suburban locations see more purchases of bulk and family-size groceries. Instead of taking a one-size-fits-all approach, the retailer adjusts its inventory and marketing strategies for each region:
- In city stores, they stock more organic snacks and vegan-friendly meals and send app-based promotions for plant-based alternatives.
- In suburban stores, they expand family-friendly bulk discounts and promote value packs through loyalty rewards.
This type of geographic segmentation helps the retailer optimize its inventory and target customers with relevant offers, increasing both sales and customer satisfaction.
There are four main types of customer segmentation in retail: demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral. By segmenting the customer base according to these categories, retailers can create hyper-personalized campaigns, predict customer behavior, and refine their segmentation strategy for maximum effectiveness.
Benefits of Retail Market Segmentation
Retail market segmentation gives businesses a clearer understanding of their customers, allowing them to personalize experiences, improve marketing efficiency, and increase revenue. By analyzing customer behavior, retailers can optimize everything from product assortment to promotions and customer loyalty programs.
Here’s how segmentation makes a measurable impact:
- Enhanced customer targeting and personalization. Instead of using generic marketing, retailers can craft highly personalized shopping experiences. For example, a beauty retailer can send skincare recommendations based on a customer’s past purchases and preferences.
- Improved marketing efficiency and ROI. Segmentation helps businesses focus their advertising spend on the customers most likely to convert. A fashion brand, for instance, can target frequent buyers with VIP promotions while running separate campaigns for first-time shoppers.
- Better inventory management and product assortment. By analyzing shopping trends across different customer segments, retailers can stock the right products in the right locations. A grocery store may increase organic product inventory in health-conscious neighborhoods while focusing on bulk discounts in suburban areas.
- Pinpoint seasonal buyers and optimize promotions. Identifying purchase patterns helps businesses time their sales efforts effectively. If a segment of customers primarily shops during Black Friday, retailers can send early access deals to maximize conversions.
- Create more effective marketing campaigns. Knowing which customer groups respond best to specific marketing channels allows retailers to tailor their messaging. Younger shoppers may engage more with TikTok ads, while older customers prefer targeted email promotions.
- Identify full-price buyers vs. discount shoppers. Some customers wait for seasonal sales, while others buy new arrivals at full price. In this case, price segmentation helps businesses balance their pricing strategy by offering targeted promotions to price-sensitive shoppers while maintaining premium pricing for loyal, high-spending customers.
- Increased customer loyalty, retention, and satisfaction. No two customers are the same, and segmentation enables brands to deliver tailored experiences that keep shoppers coming back. Personalized loyalty programs, product recommendations, and birthday discounts make customers feel valued, strengthening long-term relationships.
Understanding customer differences and addressing them effectively is the key to long-term success in retail.
Steps to Conduct Retail Market Segmentation
Here’s how to implement an effective segmentation strategy in your retail business.
1. Collect and Analyze Customer Data
Segmentation starts with data. The more information you have about your customers, the more precise and effective your strategy will be.
Where does this data come from?
- Point-of-sale (POS) systems to track purchase history.
- Loyalty programs that highlight repeat buyers.
- Website and mobile analytics showing browsing behavior.
- Social media interactions and engagement metrics.
- Customer surveys and feedback forms for direct insights.
Understanding who your customers are and how they shop lays the foundation for meaningful segmentation.
2. Identify Key Customer Segments
Once you have data, the next step is to define the groups that matter most to your business. These might include:
- Demographic Segments: Age, gender, income level, family size.
- Geographic Segments: Urban vs. rural shoppers, regional product preferences.
- Psychographic Segments: Lifestyle, values, interests, and personality traits.
- Behavioral Segments: Purchase frequency, brand loyalty, spending habits.
3. Create Detailed Customer Personas
Customer personas help retailers visualize their audience by turning data into real-life customer profiles. Persona segmentation provides actionable insights for tailoring promotions, messaging, and product offerings to each unique customer group.
4. Apply Segmentation to Marketing and Sales Strategies
Segmentation is only valuable if it translates into better marketing and sales execution. Retailers can use segmentation to:
- Personalize email and ad campaigns. Target loyal customers with VIP offers and first-time buyers with welcome discounts.
- Optimize in-store experiences. Use location-based segmentation to adjust store layouts and promotions based on regional buying preferences.
Enhance social media marketing. Run targeted ads tailored to specific demographics or interests.
5. Continuously Monitor, Optimize, and Adjust
Segmentation requires ongoing refinement.
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs) like conversion rates, average order value, and customer retention.
- Use A/B testing to determine which segmented campaigns are most effective.
Stay flexible—customer behaviors change, and your segmentation strategy should evolve with them.
Retail Market Segmentation Examples
We’ll go through 10 retail market customer segmentation examples to see how segmentation can provide personalized value to your customers.
Targeting Grocery Shoppers Based on Household Size
Segmentation Type: Demographic
Household size impacts shopping behavior, influencing product choices and package sizes. Supermarkets can segment customers using loyalty program data, purchase history, and online cart behavior to optimize promotions and product offerings.
Example: A grocery store identifies large families based on frequent bulk purchases and offers them discounts on family-sized products. Meanwhile, single-person households receive personalized promotions for ready-to-eat meals and smaller portion sizes.

Offering Tech Products Based on Income Level
Segmentation Type: Demographic
Income level influences purchasing power, allowing retailers to tailor promotions and product recommendations. Consumer electronics brands can use customer spending patterns, financing preferences, and past purchase data to segment buyers.
Example: A smartphone retailer promotes flagship models with financing options to high-income customers, while offering discounts and trade-in deals to budget-conscious shoppers. Customers who previously purchased mid-range models receive targeted emails about affordable upgrade options.

Customizing Menus Based on Local Tastes
Segmentation Type: Geographic
Consumer preferences vary across regions, and tailoring menu offerings to local tastes helps restaurants improve relevance and customer satisfaction. A restaurant chain can analyze regional purchase trends from POS systems and online orders to identify high-demand items in different locations.
Example: A coffee chain notices that spicy and flavored lattes sell well in the Southwest, while health-conscious smoothies perform better in West Coast cities. To capitalize on these insights, they introduce a chili mocha latte in Arizona locations while promoting matcha and protein smoothies in Los Angeles and San Francisco.

Adjusting Product Assortment Based on Climate
Segmentation Type: Geographic
Stocking region-appropriate products reduces inventory waste and ensures customers find what they need. Retailers can use climate data, store-specific sales reports, and e-commerce shipping trends to determine demand.
Example: A furniture retailer observes that memory foam mattresses sell more in colder states, while breathable, cooling mattresses perform better in warm regions. To optimize sales, they increase inventory of cooling mattresses in Florida and Texas while stocking heated mattress pads and plush bedding in the Midwest and Northeast.

Targeting Health-Conscious Consumers with Fitness Products
Segmentation Type: Psychographic
Health-conscious consumers prioritize products that align with their fitness goals and lifestyle choices. Retailers can analyze psychographics such as, purchase history, engagement with health-related content, and loyalty program preferences to identify customers who are serious about their fitness.
Example: A sportswear retailer segments its audience into performance athletes, casual gym-goers, and eco-conscious shoppers. Performance-focused customers receive personalized recommendations for high-performance running shoes, while eco-conscious shoppers are targeted with ads for sustainable, recycled-material sneakers.

Promoting High-End Travel Gear to Luxury Lifestyle Consumers
Segmentation Type: Psychographic
Luxury lifestyle consumers seek premium experiences and are willing to invest in high-end, travel-friendly products. Retailers can identify them through spending patterns, engagement with luxury-focused content, and loyalty program tiers.
Example: A luggage brand segments its audience based on high-value travelers who purchase premium suitcases, leather travel accessories, and first-class travel experiences. These customers receive exclusive invitations to shop limited-edition collections and tailored promotions for ultra-lightweight, durable luggage.

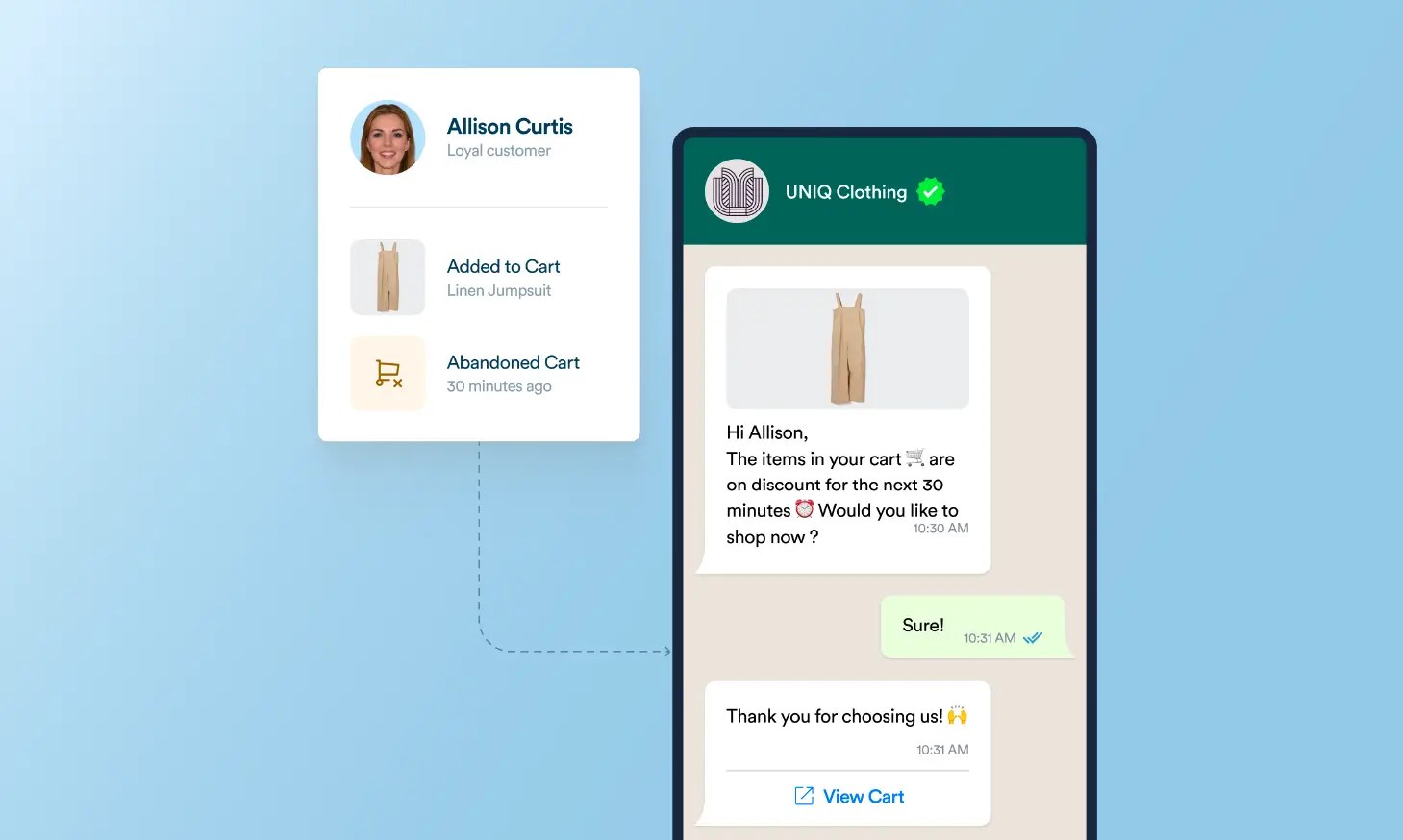
Retargeting Cart Abandoners with Personalized Discounts
Segmentation Type: Behavioral
Many shoppers browse products online but leave without completing a purchase. Retailers can track cart abandonment data, browsing history, and session duration to re-engage these potential customers with personalized incentives.
Example: An apparel brand notices that a customer added jumpsuit to their cart but didn’t check out. A day later, the customer receives an email reminder featuring the abandoned product, along with a limited-time 10% discount to encourage purchase completion.
Sending Automated Pet Food Reorder Reminders
Segmentation Type: Behavioral
Pet owners purchase food on a recurring basis, making automated reminders crucial for customer retention. Retailers can track purchase frequency, past order dates, and auto-replenishment settings to anticipate customer needs.
Example: A pet supply retailer detects that a customer typically orders dog food every six weeks. Just before they are likely to run out, the brand sends a personalized email with a one-click reorder button, along with an incentive for subscribing to automatic refills.

Catering to Gourmet & Specialty Diet Shoppers
Segmentation Type: Needs-Based
Customers with dietary restrictions or gourmet preferences seek products that fit their specific lifestyle. Grocery stores can segment them by analyzing purchase history, online searches for specialty products, and dietary preference settings in customer accounts.
Example: A grocery store recognizes shoppers who regularly buy gluten-free, keto-friendly, or organic products. These customers receive targeted promotions on new specialty items, exclusive early access to gourmet imports, and personalized recipe suggestions based on their preferred diet.

Personalizing Pharmacy Offers Based on Health and Wellness Needs
Segmentation Type: Needs-Based
Customers with specific health concerns benefit from tailored product recommendations and targeted promotions. Pharmacies can segment them using prescription refill data, past purchases of over-the-counter medications, and responses to health-related quizzes or consultations.
Example: A pharmacy chain identifies customers who regularly purchase allergy medication in spring and summer. To enhance their experience, the retailer sends pre-season reminders with personalized discounts on allergy relief products, alongside helpful tips on managing seasonal allergies.

Challenges to Solve for in Retail Market Segmentation
While segmentation improves personalization and marketing efficiency, retailers must navigate key challenges to ensure effectiveness, compliance, and scalability.
1. Common Pitfalls in Retail Segmentation and How to Overcome Them
- Over-segmentation: Too many small segments make marketing inefficient. Focusing on high-impact segments ensures scalable targeting without overwhelming resources.
- Static segmentation: Consumer behavior changes, yet many retailers use outdated models. Leveraging real-time data and AI-driven analytics keeps segmentation relevant.
- Misaligned messaging: Poorly targeted promotions lead to disengagement. A/B testing and customer feedback help optimize messaging and campaign effectiveness.
2. Addressing Data Privacy and Ethical Considerations
- Regulatory Compliance: Laws like GDPR and CCPA require transparency in data collection. Retailers must obtain explicit consent, offer opt-out options, and audit data practices regularly.
- First-Party & Zero-Party Data Usage: As third-party cookies phase out, businesses should collect first-party data (website visits, purchase history) and zero-party data (customer preferences from surveys and settings) to personalize marketing while maintaining transparency.
- Customer Trust & Transparency: Consumers expect control over their data. Providing customizable privacy settings and secure data storage enhances trust and long-term engagement.
3. Tips for Effective Implementation of Retail Segmentation
- Ensure Cross-Channel Consistency: Segmentation must align across in-store, online, and mobile experiences to provide seamless personalization.
- Use Automation & AI: AI-powered CRM tools help manage segmentation at scale, optimize real-time targeting, and enhance personalization.
- Continuously Measure & Optimize: Tracking conversion rates, engagement, and retention ensures segmentation remains effective. A/B testing refines targeting for better results. You can also conduct a segmentation analysis to iterate on your segmentation strategy.
By addressing these challenges, retailers can implement scalable, compliant, and data-driven segmentation strategies that improve personalization, efficiency, and customer loyalty.
How AJIO Used CleverTap for Retail Market Segmentation
AJIO, a leading Indian online fashion retailer, leveraged CleverTap’s advanced segmentation and automation tools to drive customer engagement and retention. By implementing behavioral and lifecycle-based segmentation, AJIO was able to identify high-intent shoppers, re-engage inactive users, and personalize marketing campaigns across multiple channels.
Using CleverTap’s Journeys feature, AJIO segmented customers based on purchase behavior, browsing activity, and engagement levels to trigger hyper-personalized campaigns. Customers who had abandoned their carts received timely nudges with personalized discounts, while first-time buyers were onboarded with targeted recommendations and exclusive offers to encourage repeat purchases.
Results:
- 4X increase in conversions through lifecycle-based customer segmentation.
- 41% improvement in month-over-month customer retention by delivering personalized messaging to different audience segments.
- 28% more reactivated customers through precise targeting of inactive users with behavior-driven outreach.
By segmenting its audience with real-time insights and predictive analytics, AJIO optimized engagement strategies and strengthened long-term customer relationships. This case demonstrates how data-driven segmentation, when combined with automation, can significantly improve marketing efficiency and business outcomes.
Read the full case study.
Conclusion
Retail market segmentation is the key to delivering personalized shopping experiences, optimizing marketing spend, and driving customer loyalty. When retailers understand their audience’s needs, behaviors, and preferences, they can create targeted, high-impact campaigns that boost engagement and sales.
Success in segmentation depends on real-time data, automation, and ethical data practices. Brands that embrace AI-powered insights and continuously refine their strategies will stay ahead in an increasingly competitive retail landscape.
CleverTap enables retailers like AJIO to execute precision-driven segmentation, resulting in higher conversions, better retention, and reactivation of lost customers. By leveraging behavioral insights and automated engagement, retailers can drive lasting relationships and revenue growth.
Shivkumar M 
Head Product Launches, Adoption, & Evangelism.Expert in cross channel marketing strategies & platforms.
Free Customer Engagement Guides
Join our newsletter for actionable tips and proven strategies to grow your business and engage your customers.